You’ve made an excellent decision aiming for the Amazon Web Services (AWS) Certified Cloud Practitioner certification. Given the overwhelming amount of study materials and limited time to prepare for the examination, it can be challenging to decide what aspects of AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner are the most important items to review.
Our AWS Cloud Practitioner cheat sheet is handy as an overview or a refresher in such a predicament. It introduces high-level cloud computing concepts and explains AWS security and compliance, core services, billing, pricing, and support.
Keep this AWS Cloud Practitioner cheat sheet handy by downloading it here. When you’re ready, let’s dive in.
AWS Cloud Practitioner Cheat Sheet Search
Search our AWS Cloud Practitioner cheat sheet to find the right cheat for the term you're looking for. Simply enter the term in the search bar and you'll receive the matching cheats available.
About AWS Cloud Practitioner
The AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner exam (CLF-C02) is a single test that consists of 65 questions. It lasts for 90 minutes and has four domains:

The exam has no prerequisites. The passing score is 700 out of 1000. Each exam attempt costs $100 USD.
Although AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner doesn’t appear to be a vendor-neutral certification, the cloud computing concepts it covers apply to other cloud computing platforms such as Azure and Google Cloud Platform. That’s what makes it such an in-demand certification across the IT industry.
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Cheat Sheet Search
- About AWS Cloud Practitioner
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Cheat Sheet Domains
- Introduction to Cloud Computing
- Identity and Access Management (IAM)
- Virtual Private Clouds
- Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
- Amazon Storage
- Fault Tolerance and Elasticity
- DNS and Content Delivery Networks
- Monitoring, Auditing, and Alerts
- Databases
- Serverless Computing
- Security and Compliance
- AWS Pricing, Billing, and Support Services
- Conclusion
- Frequently Asked Questions
AWS Cloud Practitioner Cheat Sheet Domains
This AWS practitioner cheat sheet arranges concepts according to our course subtopics. Diagrams put concepts into a visual form, and tables compartmentalize information. Here’s a key to finding items by domain:
| Hashtag (remember to type the # symbol) | Domain |
|---|---|
| #cloud | AWS Cloud concepts |
| #sec | Security and compliance in the AWS Cloud |
| #core | Core AWS Services |
| #econ | Economics of the AWS Cloud |
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing allows you to access servers, storage, databases, and other IT resources on demand through a cloud services platform online with pay-as-you-go pricing.
| Domain | Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| #cloud | Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) | Provides access to networking features, computers (virtual or on dedicated hardware), and data storage space |
| #cloud | Platform as a Service (PaaS) | Provides supporting infrastructure, usually hardware and operating systems, to allow users to focus on deploying and managing applications. |
| #cloud | Software as a Service (SaaS) | The service provider runs and manages a completed product for end users. |
| #cloud | Public Cloud | Fully deploys all parts of an application in the cloud, e.g., AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud Platform (GCP). |
| #cloud | Hybrid | Connects infrastructure and applications using cloud-based and local resources. |
| #cloud | Private Cloud/On-Premises | Dedicates resources for specific deployment aims through virtualization and resource management tools. |
| #cloud | AWS Availability Zone (AZ) | Consists of one or more discrete data centers, each with redundant power, networking, and connectivity, housed in separate facilities. |
| #cloud | AWS Region | A physical location in the world where AWS hosts multiple AZs. |
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
AWS IAM is a web service that helps you securely control access to AWS resources. It appears on every AWS exam, involving services taking on different IAM roles. A deep understanding of IAM will lay a solid foundation for the rest of your educational journey in AWS.
| Domain | Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| #sec | Root User | A single sign-in identity with complete access to every AWS service and resource in an AWS account. |
| #sec | IAM User | Individuals granted access to an AWS account. Each IAM user has three components:
|
| #sec | Group | A collection of users with policies attached to it. |
| #sec | Role | A created identity assumed by trusted entities defines a set of permissions for making AWS service requests. |
| #sec | Policy | A JSON document defining permissions that apply to users, groups, and roles. Default: implicit deny. |
| #sec | AWS Security Token Service (AWS STS) | A web service that enables you to request temporary, limited-privilege credentials for IAM users or for external users that you authenticate. |
Virtual Private Clouds
AWS Virtual Private Clouds are logically isolated virtual networks hosted on AWS cloud servers. You define a VPC’s IP address space from your selected IP ranges.
| Domain | Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| #cloud #core | Subnet | A segment of a VPC’s IP address range where you can place groups of isolated resources (maps to an AZ, 1:1). |
| #cloud #core | Internet Gateway | The Amazon VPC side of a connection to the public Internet. |
| #cloud #core | NAT Gateway | A highly available, managed Network Address Translation (NAT) service for your resources in a private subnet to access the Internet. |
| #cloud #core | Virtual Private Gateway | The Amazon VPC side of a VPN connection. |
| #cloud #core | Customer Gateway | Your side of a VPN connection. |
| #cloud #core | Router | Routers interconnect subnets and direct traffic between Internet gateways, virtual private gateways, NAT gateways, and subnets. |
| #cloud #core | Peering Connection | A peering connection enables you to route traffic between two peered VPCs via private IP addresses. |
| #cloud #core | VPC Endpoint | Enables private connectivity to services hosted in AWS from within your VPC without using an Internet Gateway, VPN, Network Address Translation (NAT) devices, or firewall proxies. |
| #cloud #core | Egress-Only Internet Gateway | A stateful gateway to provide egress-only access for IPv6 traffic from the VPC to the Internet. |
Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2)
AWS EC2 is a web service that resizes with computational load in the cloud. With EC2, you can launch virtual servers on the AWS cloud called “instances.” You or AWS can assign IP addresses to EC2 instances.
| Domain | Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| #core | Amazon Machine Images (AMIs) | Preconfigured templates for instances. Each AMI includes the information needed to launch your EC2 instance, such as the operating system and included software packages. |
| #core | EC2 Compute Units (ECUs) | Provide the relative measure of the integer processing power of an Amazon EC2 instance. |
| #core | Public IP Address |
|
| #core | Private IP Address |
|
| #core | Elastic IP Address |
|
| #core | Elastic Network Interface | A logical networking component in a VPC that represents a virtual network card. |
| #core | Elastic Network Adapter (ENA) | It enhances networking capabilities such as bandwidth, packet-per-second (PPS) performance, and inter-instance latencies. |
Information Security Courses Bundles
Want lifetime access to expert-led cyber security training? Explore our Information Security Course Bundles — one-time purchase packages covering top topics like Ethical Hacking, Cloud, Linux, DevSecOps, and CompTIA certifications.
Amazon Storage
AWS contains many cloud storage services, including S3, EBS, EFS, FSx, and Storage Gateway.
| Domain | Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| #core | Persistent Data Store | Data is durable and sticks around after restarts or power cyclesExamples: S3, Glacier, EBS, EFS |
| #core | Transient Data Store | Temporarily stored data gets passed along to another process or persistent storeExamples: SQS, SNS |
| #core | Ephemeral Data Store | System stopping causes data lossExamples: EC2 Instance Store, Memcached (Elasticache) |
| #core | Bucket |
|
| #core | Object | A unique key (ID or name) helps one store and retrieve objects in a bucket. |
| #core #security | Sub-Resources | These are data subordinate to objects and buckets. They include:
|
| #core #security | Cross-Origin Resource Sharing (CORS) | (Applies to S3 buckets) Used to allow requests to a different origin when connected to the main origin. |
Fault Tolerance and Elasticity
This section refers to AWS services Elastic Load Balancing and EC2 Auto Scaling. These services help ensure your AWS application can handle the load of requests for it.
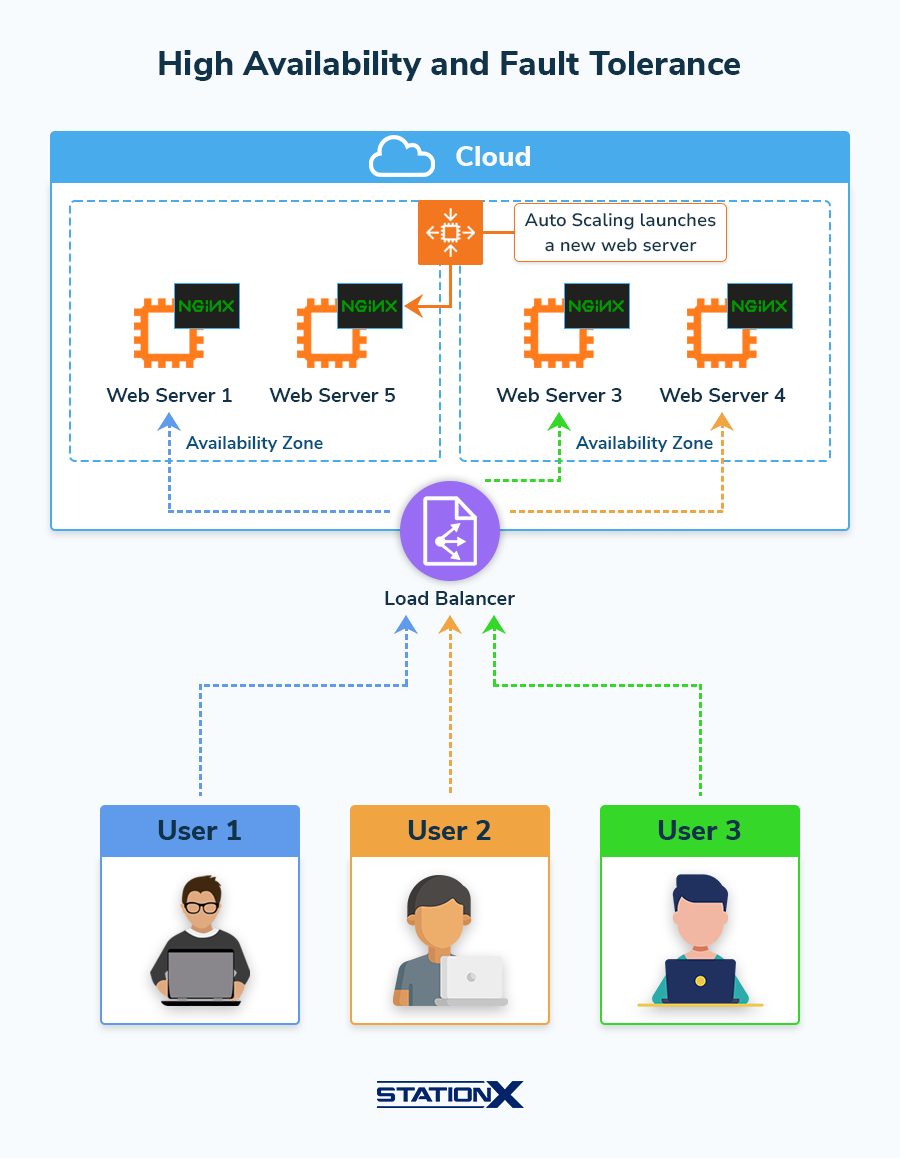
| Domain | Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| #core | Auto Scaling | Automates launching (scaling out) and terminating (scaling in) EC2 instances based on the traffic demand for your application. |
| #core | Auto Scaling Group (ASG) | Collections of EC2 instances defining their Auto Scaling capacity. |
| #core | Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) | Automatically distributes incoming application traffic across multiple targets, such as EC2 instances, containers, and IP addresses. |
| #core | Application Load Balancer (ALB) | Operates at OSI Layer 7, for load balancing of HTTP and HTTPS traffic. Provides advanced request routing targeted at delivering modern application architectures, including microservices and containers. |
| #core | Network Load Balancer (NLB) | Operates at OSI Layer 4, for load balancing of extreme TCP traffic. |
DNS and Content Delivery Networks
Have you ever been to a website hosted on AWS? This section is about the backbone supporting those websites: Route 53 and CloudFront.

| Domain | Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| #core | Route 53 | AWS Domain Name Service. It performs three main functions:
|
| #core #security | CloudFront | A content delivery network (CDN) that allows you to store (cache) your content at edge locations located around the world. It has built-in Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attack protection. |
| #core | Edge Location | The location where AWS caches content but is separate from AWS Regions or Availability Zones. |
| #core | Regional Edge Cache | A large cache server between origin web servers and global edge locations that bring content closer to users. |
Monitoring, Auditing, and Alerts
AWS provides several tools to monitor running services and alert you when they fail: Amazon CloudWatch, AWS CloudTrail, Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS), and Amazon Config.
| Domain | Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| #security #core | Amazon CloudWatch | For performance monitoring, it collects and tracks metrics, creates log files, and sets alarms. |
| #security #core | AWS CloudTrail | For auditing, it records activity made on your account and delivers log files to an Amazon S3 bucket. |
| #security #core | Amazon Simple Notification Service (SNS) | For sending messages to different devices and platforms. |
| #security #core | Amazon Config | A tool for assessing, auditing, and evaluating the configurations and relationships of your resources. |
Databases
AWS provides a variety of database services. Here are their names and when to use them:
| Domain | Name | Use cases |
|---|---|---|
| #core | Database on EC2 |
|
| #core | RDS |
|
| #core | DynamoDB |
|
| #core | RedShift |
|
| #core | Neptune |
|
| #core | ElastiCache |
|
| #core | S3 |
|
Serverless Computing
This section focuses on the AWS Lambda service.
| Domain | Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| #core | Lambda | You run code on this platform as functions without provisioning or managing servers. |
| #core | Synchronous Invocation | You wait for the Lambda function to process the event and return a response. |
| #core | Asynchronous Invocation | Lambda places the event in a queue and returns a “success” response without additional information. |
| #core | Event Source | An AWS service or developer-created application that produces events that trigger an AWS Lambda function to run. |
| #core | Versioning | Having multiple versions of your function. |
| #core | Aliases | Pointers to a specific Lambda version. |
Security and Compliance
The section is about how Amazon and you manage the cyber security posture of your virtual environment on AWS.
| Domain | Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| #security | Shared Responsibility Model | Name of the shared responsibility between AWS and the customer in security and compliance. |
| #security | Security of the Cloud | AWS is responsible for protecting the infrastructure that runs all the services offered in the AWS Cloud. |
| #security | Security in the Cloud | The AWS Cloud services you choose determines the amount of configuration work you must perform as part of your security responsibilities. |
| #security | Key Management Service (KMS) | For easy data encryption, to centrally manage and securely store your keys. |
| #security | KMS Key |
|
| #security | AWS-Managed KMS keys | Used by AWS services that interact with KMS to encrypt data. |
| #security | Customer-Managed KMS Keys | You have full control over these KMS keys. |
AWS Pricing, Billing, and Support Services
This final section briefly touches upon the economics of AWS usage.
| Domain | Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| #econ | Organizations | Consolidation of multiple AWS accounts into an organization for central management. |
| #econ | Pricing Model |
|
| #econ | Pricing Calculator | Gets cost estimates: https://calculator.aws/#/ |
Conclusion
As you can see, AWS encompasses many topics broadly. Therefore, the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner certification helps prove to employers your competence in navigating the intricacies of cloud computing and AWS. This AWS Cloud Practitioner cheat sheet is an essential checklist covering the examination syllabus, giving you a bird’s-eye view of key AWS topics to remember.
We offer a complete course (listed below) to help you prepare for the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner exam. Don’t forget to check out our StationX Master's Program to access a wide range of cloud computing, security, and related courses. No matter how you prepare for the AWS Certified Cloud Practitioner exam, we wish you great success and a bright future.
This Cloud Computing Courses Bundle: Digital Cloud Training includes:
- CompTIA Cloud+ Certification Course: CV0-003
- AWS Cloud Practitioner Study Guide - Essential Course
- Best AWS Solutions Architect Course (SAA-C03)
- Microsoft Azure Fundamentals AZ-900 Course
- AZ-104 Training: Azure Administrator Associate
- Microsoft Cybersecurity Architect - SC-100 Exam Preparation
- CCSP Certification Training Course




