Cyber security has moved from a behind-the-scenes IT function to a top-line business priority, and salaries are rising fast as a result. So, how much does cyber security make? As organizations work to protect themselves from more frequent and sophisticated digital threats, professionals with modern security expertise are among the most sought-after in tech.
Recent surveys point to healthy year-over-year pay growth across many roles, and while the biggest jumps aren’t universal, 10%+ increases appear regularly in areas facing the tightest talent shortages, particularly when skills are rare or responsibilities expand.
This surge reflects a wider expansion across the technology workforce. Tech jobs are projected to grow significantly faster than the overall labor market, powered by demand across cloud computing, data analytics, DevOps, and machine learning. For cyber security professionals, the combination of talent shortages and rising risk has created a strong advantage at the negotiating table.
In this salary guide, we explore what cyber security professionals are earning today and where compensation is headed next. Let’s begin.
Cyber Security Salary by Role, Country, and Experience
Here’s a quick look at how salaries in cyber security vary depending on role, location, and experience level. Compensation can vary widely across countries and job functions, with factors such as demand, cost of living, and organizational priorities shaping pay scales.
Below, you’ll find tables that break down average salary ranges for key cyber security positions in several major markets, from entry-level analysts to seasoned security leaders, helping you understand where you stand and what you might expect at each stage of your career.
Cyber Security Analyst Salary
Cyber Security Analysts monitor networks and systems for threats, investigate incidents, and help prevent breaches through continuous risk analysis and real-time response. They collaborate with IT and software development teams to strengthen defenses and use strong analytical skills to identify suspicious activity, often supported by tools powered by artificial intelligence.
This role is one of the most common entry level positions in cyber security and a strong foundation for career advancement into engineering, threat intelligence, or management paths. Demand is rising rapidly, with employment projected to grow by 29% between 2024 and 2034, creating expanding job openings.
| USA Salary | UK Salary | India Salary | Canada Salary | Germany Salary | Japan Salary | |
| Overall | $127k | £41k | ₹642k | CA$82k | €61k | ¥9m |
| Beginner | $82k | £35k | ₹500k | CA$71k | €51k | ¥5.1m |
| Intermediate | $99k | £47k | ₹900k | CA$100k | €67k | ¥8.4m |
| Advanced | $121k | £65k | ₹1.1m | CA$109k | €84k | ¥10m |
Cyber Security Consultant Salary
Cyber Security Consultants advise organizations on strengthening their security posture by assessing risks, evaluating vulnerabilities in an organization’s computer networks, and designing strategies to protect systems and data from cyber threats. Their work often involves reviewing and improving security protocols, aligning technical controls with business goals, and helping leadership make informed risk decisions.
Because the role requires strong communication skills alongside deep technical knowledge, professionals with specialized expertise in areas such as cloud security, compliance, and incident response are especially valued.
In 2026, compensation for this role remains strong due to the global cyber security talent gap. The average annual salary for Cyber Security Consultants frequently exceeds $120,000 in the USA, and experienced consultants working in high-demand sectors or niche specialties can earn significantly more, particularly when performance bonuses or consulting premiums are included.
| USA Salary | UK Salary | India Salary | Canada Salary | Germany Salary | Japan Salary | |
| Overall | $154k | £52k | ₹995k | CA$93k | €66k | ¥12.7m |
| Beginner | $113k | £41k | ₹790k | CA$65k | €48k | ¥7.3m |
| Intermediate | $144k | £57k | ₹1.1m | CA$98k | €77k | ¥11m |
| Advanced | $189k | £78k | ₹2.5m | CA$118k | €134k | ¥14.3m |
FREE Cyber Security Career Guide
Thinking of a career in cyber security? Our Cyber Security Career Guide walks you through the industry landscape, skill-paths, certifications, and realistic timelines to become job-ready.
Incident and Intrusion Analyst Salary
Incident and Intrusion Analysts detect, investigate, and respond to security alerts, breaches, and suspicious activity, helping contain attacks and reduce business impact. Their work involves analyzing logs and telemetry, validating threats, coordinating response actions, and strengthening security measures across systems and networks.
These specialists also contribute to security management processes by documenting incidents, improving detection workflows, and supporting long-term risk reduction.
In addition, they often help promote security awareness by sharing insights from incidents, advising teams on safe practices, and highlighting emerging threat patterns. Demand for these professionals remains high as organizations continue to face talent shortages and increasingly complex threats across cloud, hybrid, and modern enterprise environments.
| USA Salary | UK Salary | India Salary | Canada Salary | Germany Salary | Japan Salary | |
| Overall | $87k | £41k | ₹850k | CA$76k | €44k | ¥7.2m |
| Beginner | $81k | £35k | ₹200k | CA$67k | €38k | ¥4.6m |
| Intermediate | $98k | £47k | ₹600k | CA$84k | €50k | ¥8.4m |
| Advanced | $135k | £61k | ₹1m | CA$90k | €62k | ¥11.2m |
Penetration Tester Salary
Penetration Testers simulate real-world cyberattacks to uncover vulnerabilities before malicious actors can exploit them. These professionals use advanced technical skills to test applications, networks, and operating systems, often incorporating threat intelligence to simulate current attacker tactics. Their work helps organizations identify weaknesses early and strengthen defenses through targeted remediation and improved security controls.
Penetration Tester jobs remain in high demand as businesses prioritize proactive security testing to stay ahead of increasingly sophisticated and frequent attacks.
Employers often value hands-on experience alongside recognized cyber security certifications, and compensation reflects this need. In many markets, the median annual wage for penetration testers sits well into the six-figure range, with higher earnings common for those specializing in complex environments or advanced offensive techniques.
| USA Salary | UK Salary | India Salary | Canada Salary | Germany Salary | Japan Salary | |
| Overall | $154k | £52k | ₹710k | CA$94k | €63k | ¥6.3m |
| Beginner | $115k | £50k | ₹400k | CA$75k | €55k | ¥5.5m |
| Intermediate | $153k | £60k | ₹1.2m | CA$88k | €64k | ¥7.1m |
| Advanced | $184k | £81k | ₹2.7m | CA$120k | €72k | ¥11.4m |
Chief Information Security Officer Salary
CISOs hold a senior position, responsible for leading an organization’s overall security strategy and aligning risk management, technology, and business objectives to protect critical assets. In today’s job market, the role extends beyond technical oversight into governance, regulatory alignment, and executive decision-making.
As organizations mature, CISOs are also shaping internal career paths by building security teams, mentoring leaders, and strengthening long-term resilience.
In 2026, the CISO role continues to evolve, not only in scope but in hiring philosophy, with more CISOs easing formal degree requirements and prioritizing real-world results, leadership effectiveness, and ongoing professional development. This shift supports broader career growth opportunities for experienced practitioners who advance through engineering, architecture, or security management tracks into executive leadership.
Compensation remains strong, with the national median salary for CISOs positioned at the top tier of cyber security pay scales.
| USA Salary | UK Salary | India Salary | Canada Salary | Germany Salary | Japan Salary | |
| Overall | $286k | £138k | ₹3.8m | CA$136k | €126k | ¥16.8m |
| Beginner | $194k | £100k | ₹730k | CA$109k | €101k | ¥11.4m |
| Intermediate | $239k | £166k | ₹3.3m | CA$136k | €132k | ¥19.6m |
| Advanced | $355k | £251k | ₹6m | CA$169k | €181k | ¥21.2m |
How Much Do Cyber Security Jobs Pay in the USA?
Cyber security remains one of the most lucrative and in-demand fields in the U.S. tech industry, with salaries rising as organizations shift more resources to defend against growing cyber threats.
According to EC-Council's analysis, base salaries vary widely by role and experience level, from roughly $80,000 for entry-level positions to more than $300,000 for senior and leadership roles. This broad range reflects the growing importance of cyber security expertise across sectors such as finance, healthcare, government, and technology.
Typical pay ranges across roles include:
- Entry & mid-level roles: Cyber Security Analyst (~$80–$120K), SOC Analyst (~$80–$100K), Penetration Tester (~$110K–$180K)
- Skilled technical roles: Security Engineer (~$100–$140K), Cloud Security Engineer (~$120–$160K)
- Senior & leadership positions: Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) (~$190–$300K), Security Architect (~$130–$190K)
Salaries are influenced by multiple factors that reward both experience and specialized knowledge:
- Certifications (Certified Ethical Hacker, Certified CISO) can boost earnings by 10-15% or more compared to non-certified peers.
- Industry demand & location matter, with high-cost tech hubs typically offering higher compensation.
- Company size and benefits (bonuses, stock options, retirement plans) affect total pay beyond base salary. Overall, investing in relevant skills and credentials can open doors to more competitive compensation packages and long-term growth in the cyber security workforce.
How Much Do Cyber Security Jobs Pay in the UK?
Overall, cyber security salaries in the UK are competitive with those in many other tech fields. The average annual salary for cyber security professionals is around £53,600-£55,000 per year as of early 2026, with variation depending on location, role, and experience. Top earners in high-demand or senior technical positions can make significantly more, while entry-level roles tend to start lower.
Typical salary ranges by role include:
- Cyber Security Analyst: around £41,000 per year on average, with most salaries falling between ~£31,700 and £64,900.
- Cyber Security Engineer: around £49,000 per year, with typical ranges from ~£36,300 to £66,800.
- Cyber Security Specialist: roughly £57,900 per year, with most in the ~£43,300–£78,900 bracket.
In London specifically, tech hubs often pay a premium, with analysts earning closer to £48,000 and senior analysts averaging about £61,700.
Several factors influence pay levels:
- Experience & seniority: More experienced or senior titles typically command higher averages.
- Location: Salaries in London and South East England tend to be higher than in other regions.
- Specialisation: Roles like cloud or network security engineering often pay more than generalist positions, especially when specialised skills are in demand.
- Industry & company size: Larger firms or those in finance/technology may offer above-average compensation.
What Impacts Your Cyber Security Salary?
We’ve already touched on experience and role level in the salary breakdowns above, but a few big levers consistently influence how high your pay can go in cyber security. These don’t guarantee a massive salary on their own, but stacked together, they can seriously boost your market value.
Certifications
Certifications are among the clearest salary signals in cyber security. Employers often use them as proof that you meet industry standards, especially for senior or specialized roles. Credentials from organizations like ISC2, ISACA, and Amazon Web Services are widely recognized.
Certs often linked with higher pay include:
- CISSP / CCSP - Common in senior engineering, architecture, and leadership tracks
- CISM / CRISC / CISA - Strong for governance, risk, and management roles
- OSCP / OSCE3 - Highly respected in penetration testing and offensive security
- AWS Certified Security - Specialty - Valuable for cloud-focused security roles
Certifications aren’t always mandatory, but for competitive roles, especially six-figure technical or leadership positions, they can help you pass HR filters, justify higher offers, and stand out against similarly experienced candidates.
If you're working toward these, training platforms like StationX can help build the technical foundation required for many of these certifications. Structured course bundles can be useful for mapping learning paths to cert goals rather than studying topics in isolation.
Education Level
A degree isn’t the golden ticket it once was; hands-on skills and proven ability now carry more weight, but education can still influence salary ceilings in some paths.
- Entry to mid-level roles: Employers often prioritize practical skills over formal education.
- Bachelor’s degree: Still helpful for HR screening, enterprise environments, and some government roles.
- Master’s degree: Can make more of a difference when pursuing upper management or executive tracks (like director or CISO paths).
Overall, the industry is moving toward skills-first hiring, so lacking a degree doesn’t block high earnings - you may just lean more heavily on certifications and experience to demonstrate expertise.
Security Clearance
For US candidates, security clearance can be a huge salary multiplier in defense, government, and contractor roles.
Important nuance:
- Employers frequently sponsor clearance during employment, meaning candidates do not always need to possess it beforehand.
- Active clearance can reduce onboarding timelines and enhance candidacy.
- Roles requiring clearance often include compensation premiums due to the limited eligible workforce.
So while it’s not mandatory for most private-sector cyber jobs, in certain sectors, it can directly translate to higher compensation.
Experience
Professional experience remains the most influential determinant of cyber security compensation. Beyond years in the field, employers evaluate the scope, complexity, and impact of prior work.
Key experience-related factors include:
- Exposure to large-scale, cloud-based, or highly regulated environments
- Level of responsibility (implementation vs. architecture vs. strategic oversight)
- Demonstrated outcomes, such as incident response leadership, risk reduction initiatives, or security program development
Certifications and degrees can open doors, but experience is what usually determines how high the offer goes once you’re in the room.
Location
Geographic market conditions remain an important structural factor in determining compensation ranges within the cyber security profession.
- Major tech and financial hubs tend to offer higher salaries.
- Government and defense regions often pay more for cleared roles.
- Remote work is narrowing some gaps, but location still influences salary bands.
Bottom line: your cyber security salary isn’t just about job title - it’s driven by your skills, certifications, experience, sector, and location, especially in how you help organizations handle evolving potential threats.
While the national average and broader labor statistics offer benchmarks, your actual earning potential depends on the value and specialization you bring to the role.
Remote Cyber Security Jobs Database
Looking to work from anywhere? Tap into our Remote Cyber Security Jobs Database — over 360 remote-friendly companies, 70+ cyber employers hiring remotely, and 50+ niche job boards all organised into one curated resource.
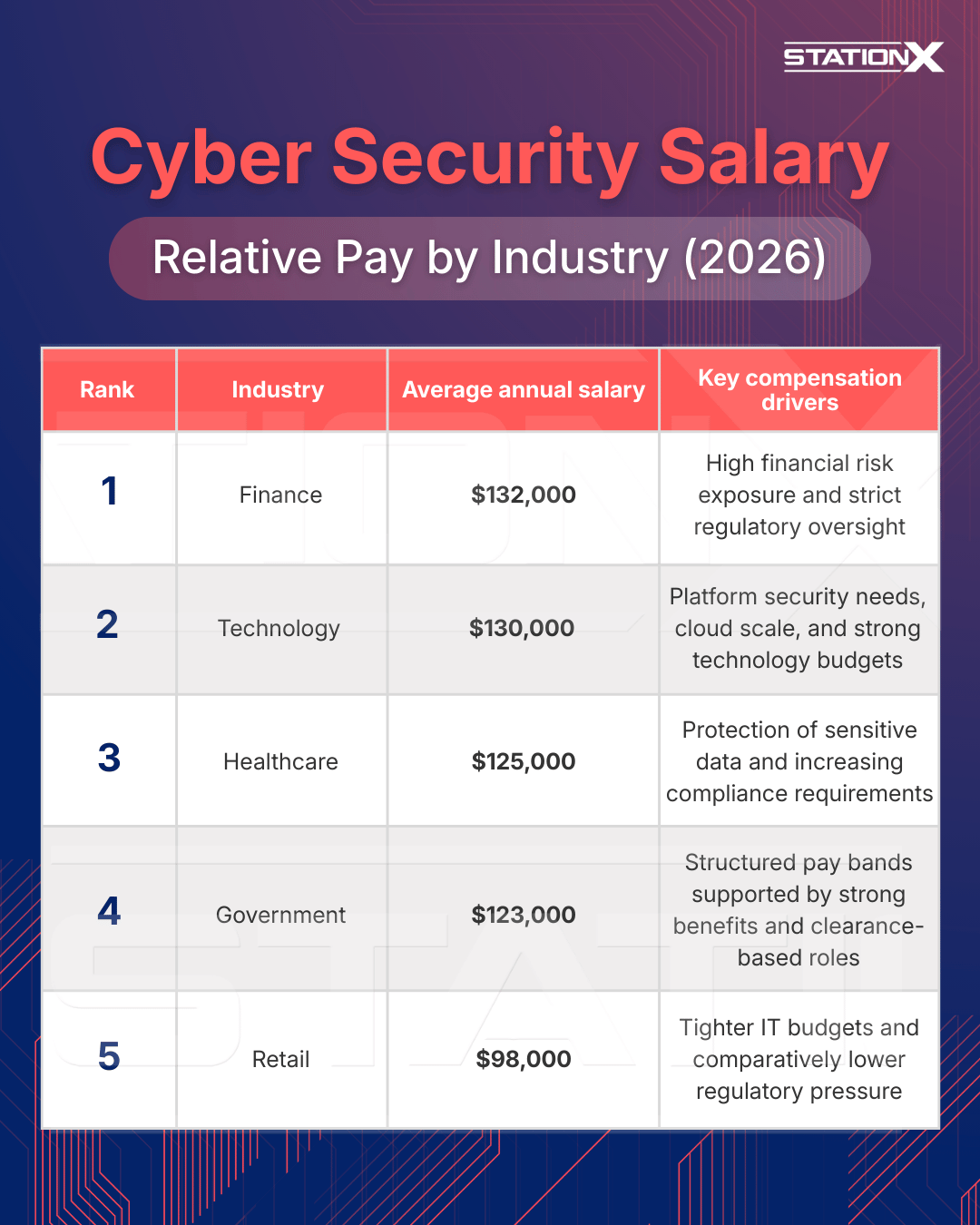
Industry Sector Salary Rankings
Below is a ranked list of potential cyber security salaries by industry sector, based on typical employer pay scales, median wage trends, and market demand drivers. This hierarchy is a simple, shareable way to show where compensation tends to be strongest, and how responsibilities such as enforcing security policies, defending against evolving threats, and supporting security event management influence pay across different career paths.
Industries that rely heavily on secure infrastructure (finance, technology) often pay more because they depend on resilient computer systems design, secure architectures, and protected network protocols to keep operations running. These sectors face higher financial and operational risk, so organizations invest more in experienced security professionals to reduce exposure and maintain trust.
Other sectors may offer slightly lower salary ranges than top-paying industries, but compensation remains competitive as cyber risk continues to grow. As threat landscapes evolve, the need for specialists who can manage incidents, strengthen defenses, and align technical controls with business priorities ensures cyber security remains a high-value profession across all major industry sectors.
1. Finance - $132K/yr (Median total pay)
Financial institutions face some of the most severe consequences from cyber attacks, including direct financial loss, regulatory penalties, and reputational damage. Because of this, banks, investment firms, and insurance companies generally offer top compensation packages to attract and retain top cyber talent. Competitive pay is common, along with performance bonuses and benefits.
2. Technology - $130K/yr (Median total pay)
Technology companies also pay very well for cyber security professionals. Large tech firms and cloud providers often lead edge innovation, requiring deep security expertise - and they can afford premium salaries to fill those needs. While pay may be slightly below top-tier finance in some roles, tech remains one of the most lucrative markets for cyber security specialists.
3. Healthcare - $125K/yr (Median total pay)
Healthcare organizations may not pay as consistently as finance or tech, but they still offer solid compensation due to the sensitive nature of patient data and regulatory requirements like HIPAA. Budgets can vary widely by institution, but demand for security expertise is strong, and average salaries tend to sit in the upper-middle of the market.
4. Government - $123K/yr (Median total pay)
Government agencies often sit in the middle of the salary spectrum. On base pay alone, bureaucracy and standardized pay bands can limit how high salaries can go compared to private-sector peers. However, government roles frequently include valuable benefits (retirement plans, job stability, generous leave) that enhance total compensation. In certain defense and national security areas, security clearances can also boost pay.
5. Retail - $98K/yr (Median total pay)
Retail and other smaller sectors typically offer lower cyber security salaries compared to finance, tech, healthcare, and government. This reflects tighter IT budgets and lower risk tolerance for highly paid specialists. That said, strong performers or leaders in these spaces can still earn good pay, especially when part of broader IT leadership.
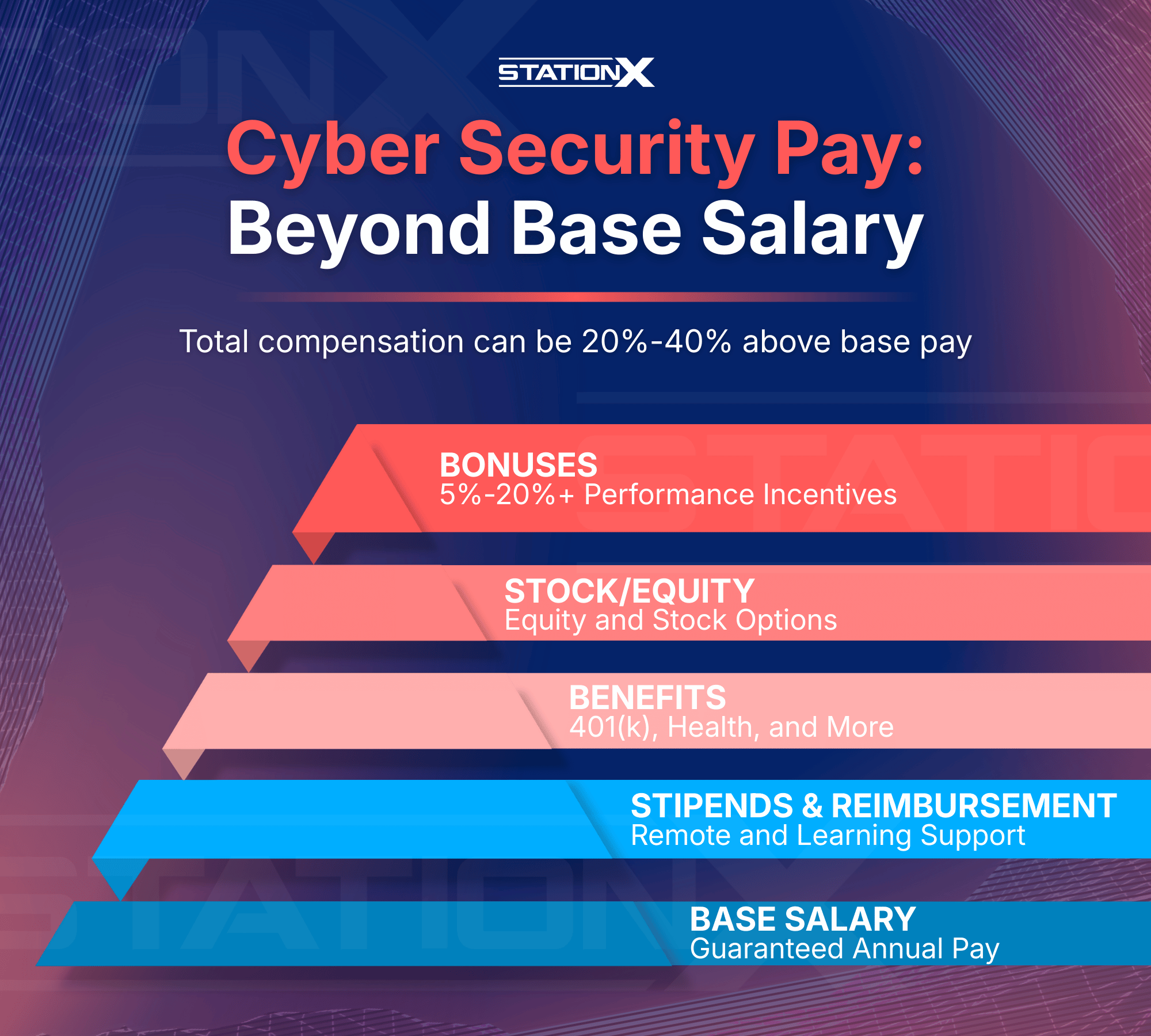
Total Compensation: Beyond Base Salary
Base salary is only part of what cyber security professionals actually earn. In many roles, especially mid-to-senior level, total compensation can be 20–40% higher than base pay once additional components are included. Understanding these elements gives a more accurate picture of real earning potential.
Performance Bonuses
Many employers offer annual or quarterly bonuses tied to individual, team, or company performance. In cyber security roles, bonuses commonly range from 5–20% of base salary, with higher percentages possible in leadership or high-impact technical roles.
Stock / Equity (Common in Tech)
Equity compensation is especially prevalent at technology companies, startups, and cloud-focused organizations. Stock grants or options can significantly increase long-term earnings, particularly if the company grows or performs well.
Benefits Value
Benefits represent a substantial financial contribution from employers, often underestimated.
These may include:
- Retirement contributions (e.g., 401(k) matching in the USA)
- Employer-sponsored health insurance
- Life and disability coverage
- Paid time off and parental leave
- Education or tuition reimbursement programs
Collectively, benefits can add thousands, sometimes tens of thousands, of dollars in annual value.
Remote Work Stipends
With hybrid and remote models more common, many employers now provide stipends for home office equipment, internet costs, or coworking access. While smaller than other components, they still contribute to overall compensation.
Conference & Certification Reimbursement
Cyber security is a certification-driven field, and many employers cover:
- Certification exam fees
- Training courses
- Industry conference attendance
This support not only reduces personal expenses but also helps professionals advance more quickly, indirectly supporting higher future earnings.
Conclusion: How Much Does Cyber Security Make?
Cyber security careers consistently rank among the best-paid paths in technology. The annual salary in this field is competitive with other high-earning tech roles and often surpasses general web development salaries, while matching or exceeding many programming and cloud positions, depending on specialization, geographic location, and hands-on experience.
Roles such as Cyber Security Analyst, Incident & Intrusion Analyst, Cyber Security Consultant, Penetration Tester, and Chief Information Security Officer offer strong annual salary potential across global markets. Entry opportunities are solid, and there is clear progression into senior roles in engineering, architecture, consulting, and leadership.
Long-term growth is supported by continuous learning, practical expertise, and, in some leadership paths, a graduate degree can provide an additional advantage.
For those looking to enter this high-growth, well-compensated field, structured training can make the path more direct. StationX Master’s Program provides access to an extensive library of over 30,000 cyber security courses and labs, mentorship, career guidance, and a community of peers - resources designed to help learners build practical skills and move confidently into professional cyber security roles.
Master cyber security from beginner to advanced with our Complete Cyber Security Course Bundle, covering network security, ethical hacking, endpoint protection, and online anonymity. Click the banner below.
The Complete Cyber Security Course Bundle includes:
- The Complete Cyber Security Course! Volume 1: Hackers Exposed
- The Complete Cyber Security Course! Volume 2: Network Security
- The Complete Cyber Security Course! Volume 3: Anonymous Browsing
- The Complete Cyber Security Course! Volume 4: End Point Protection
- The Complete Cyber Security Course Practice Test - Volume 1
![How Much Does Cyber Security Make? [2026 Salary Guide]](https://www.stationx.net/wp-content/uploads/2024/02/How-Much-Does-Cyber-Security-Make-2026-Salary-Guide.png)



