Whether you’re a security professional, IT administrator, or tech enthusiast, understanding how to use AI for cyber security can strengthen your defenses and help you stay one step ahead of emerging threats.
This article will help you understand the numerous benefits of utilizing AI to assist with various cyber security tasks. We'll discuss the role of AI in cyber security and practical applications, help you get started using it, and finally, explore how you can leverage it in your day-to-day job as a cyber security training tool and create projects that enhance your skills or resume.
If you're ready to dive into using AI for cyber security, let's begin.
The Role of AI for Cyber Security
Over the last few years, AI tools have advanced significantly, and they’re now in use for everything from customer service chatbots to self-driving cars.
This technology has revolutionized many industries by increasing efficiency and streamlining processes, ultimately improving user experience and cost savings.
This is also the case for cyber security, where there has been a major shift in how those in the field have embraced it as a tool rather than something to be scared of.
For example, AI has enabled organizations to detect and respond to cyber attacks in real time, allowing for quicker and more effective risk mitigation.
AI systems can process vast amounts of data at incredible speeds and much faster than humans. See 10 Examples of AI in Cyber Security (Latest Research) for more information.
So why should you consider using an AI model like ChatGPT?
ChatGPT, which can generate human-like responses, will play an increasingly vital role in all areas of cyber security, such as threat actor detection, vulnerability assessment, security awareness training, automation of routine tasks, customer support, security incidents management, and more.
Having said all of this, you may wonder if AI will replace cyber security jobs.
While AI will undoubtedly change the landscape of cyber security jobs, it’s more likely to augment rather than replace human roles. The human element in cyber security, including critical thinking, creativity, and adaptability, will continue to be essential in addressing evolving threats.
Practical Applications of AI for Cyber Security
Let’s quickly discuss some practical applications of AI for cyber security.
AI is not just a new buzzword—it's a tool that can enhance the lives of students and professionals alike.
For example, ChatGPT can be used for cyber security jobs to help automate report generation, assist with incident management, and create compliance checklists.
As a tool for cyber security training, it can help develop courses and awareness training to prevent social engineering attacks, complete a CTF, and prepare for cyber security exams.
You can also use AI tools to help with personal projects, such as creating practice labs, tools, and plugins, and even a YouTube video series.
While AI helps defenders, threat actors are also leveraging AI for automated phishing campaigns, polymorphic malware, and reconnaissance. Understanding both sides of this arms race is crucial - the same tools that help you analyze code can help attackers generate it.
Getting Started With AI for Cyber Security
We'll start by looking at ChatGPT, which remains the most popular AI provider, and then move on to Claude and Gemini.
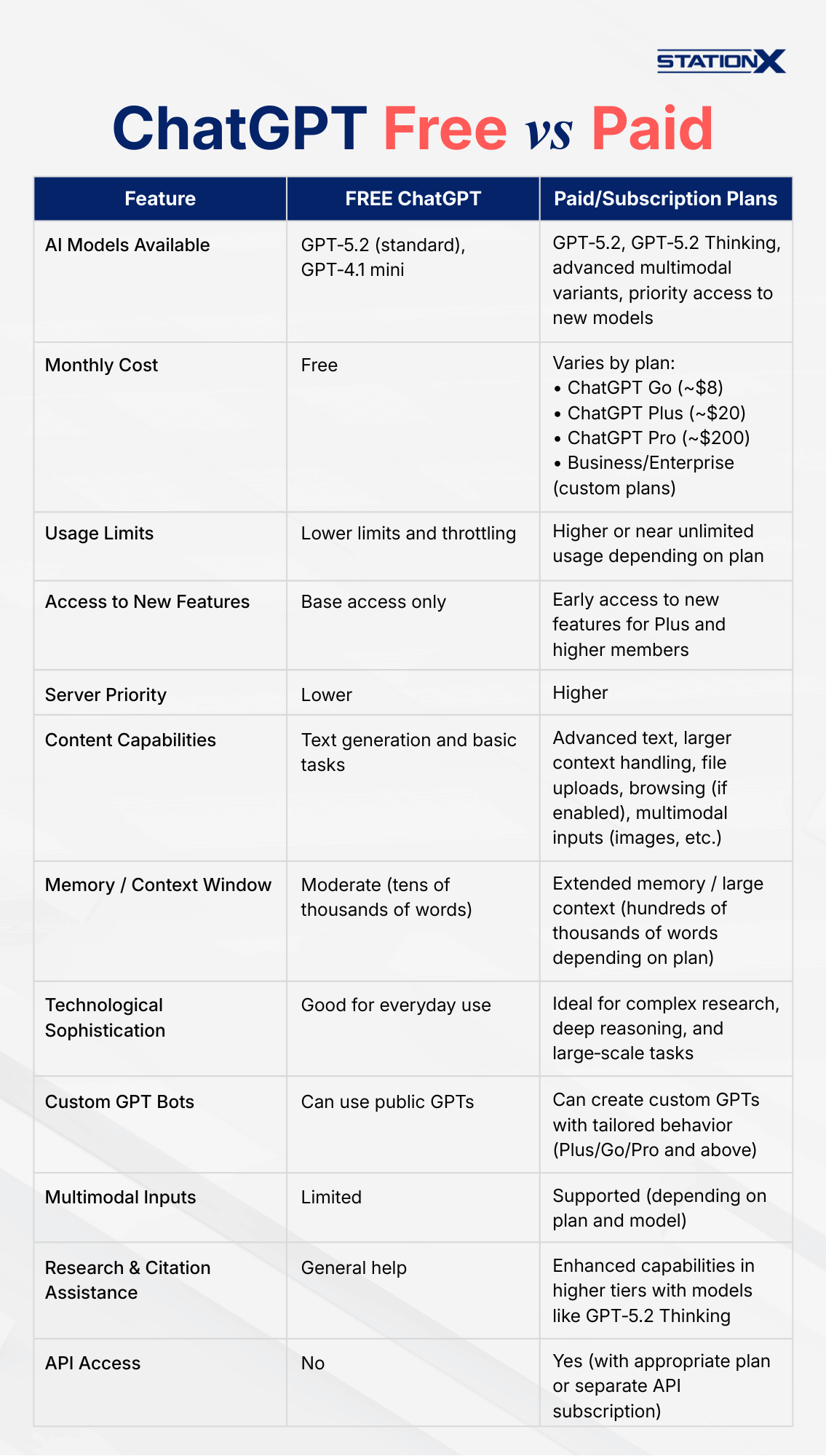
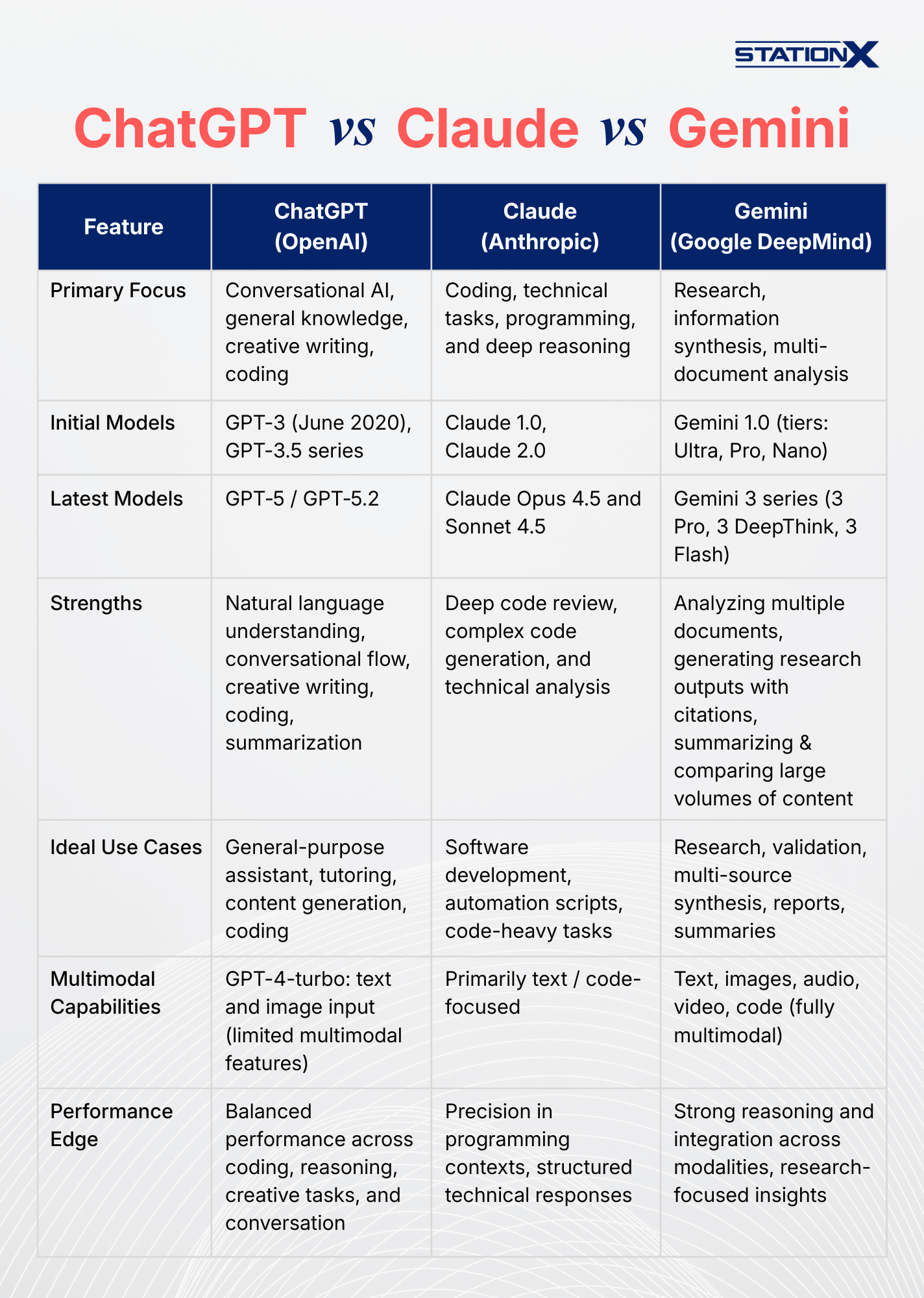
ChatGPT
ChatGPT is provided by OpenAI, an artificial intelligence research lab based in San Francisco. Their mission is to ensure that artificial general intelligence benefits all of humanity. ChatGPT is excellent for quick scripting explanations, general coding help, and content generation.
Before you begin using ChatGPT, you’ll want to decide which plan suits your needs. Each tier gives you access to different models and features.
Free Tier
The Free plan lets you use ChatGPT at no cost. You still get access to powerful models like GPT‑5.2 and GPT‑5.2 Thinking, though with usage limits, slower speeds during peak times, and fewer advanced features compared to paid users.
ChatGPT Go (~$8/month)
A newer, lower‑cost subscription between Free and Plus, ChatGPT Go offers expanded access compared to the Free tier, including more messages, longer memory, and greater upload capacity, though it may include ads for some users.
ChatGPT Plus (~$20/month)
ChatGPT Plus enhances your experience with:
- More usage and faster response times.
- Access to advanced AI models and expanded context.
- Options for voice mode, file uploads, and custom tasks. This makes it a better choice for power users, students, and professionals who need more than what the Free plan offers.
Pro (~$200/month)
ChatGPT Pro is aimed at users who need the highest‑level performance, including:
- Greater limits and priority access
- Access to advanced reasoning variants and expanded tools
- Better support for demanding, research‑level tasks. It’s ideal for developers, researchers, and heavy professional use.
Custom GPT Bots
With a paid ChatGPT subscription above Go (Plus, Pro, Business, or Enterprise), you can create custom GPTs - AI assistants tailored to specific tasks by providing instructions, context files, and optional capabilities like browsing or data analysis. These custom GPTs are highly versatile and can be used in cyber security for tasks such as structured analysis, incident reporting templates, blue team operations, red team simulations, and other domain-specific tasks, automated guidance, and repeatable workflows.
Even if you don’t have a paid plan, Free plan users can still access and use GPTs from the GPT Store, but creating your own bots requires a paid subscription. Custom GPTs are most useful when you need specialized knowledge or workflows tailored to your domain rather than general-purpose assistance.
For more information, see our article Top 18 Cyber Security GPTs and How to Use Them.
Two other AI models worth mentioning are Claude and Gemini.
Information Security Courses Bundles
Want lifetime access to expert-led cyber security training? Explore our Information Security Course Bundles — one-time purchase packages covering top topics like Ethical Hacking, Cloud, Linux, DevSecOps, and CompTIA certifications.
Claude
Claude is a family of AI assistants developed by Anthropic. The earliest widely known models included Claude 1.0 and Claude 2.0, and more recently, Anthropic has released the Claude Opus series (including Opus 4.5, which offers significantly improved capabilities for deep reasoning and code understanding.
Claude excels at coding and technical tasks, particularly with the Opus models, making it especially strong for deep code review, complex code generation, and thorough technical analysis. Use Claude when you need robust, structured responses for programming and engineering‑oriented challenges.
If your primary focus is software development, automation scripts, or code-heavy tasks, Claude is often the best choice due to its precision and understanding of programming contexts.
Gemini
Gemini, developed by Google DeepMind, shines in research and information synthesis. The platform started with Gemini 1.0, which introduced the foundational architecture and came in different tiers - Ultra for the largest tasks, Pro for general use, and Nano for on-device efficiency. This first generation replaced the older Bard system and laid the groundwork for subsequent, more capable models.
The latest generation, Gemini 3, was released in late 2025 and represents the most advanced version to date. It includes variants like Gemini 3 Pro for high-end reasoning, Gemini 3 DeepThink for deep analytical tasks, and Gemini 3 Flash, which balances speed and cost-efficiency for everyday use.
Gemini 3 now serves as Google’s flagship AI, powering conversational assistants, coding tools, and multimodal applications with unprecedented reasoning and integration.
Its strengths include:
- Analyzing multiple documents at once
- Generating research outputs with citations
- Summarizing and comparing large volumes of technical or academic content
Gemini is ideal when you need to conduct research, validate information, or process multiple sources to generate insights, reports, or summaries.
It is worth trying different AI models to see what best suits your particular needs.
Beware that AI tools aren’t perfect and can make mistakes. You need to verify the information before taking action based on their suggestions. It's always important to use critical thinking and not rely solely on AI-generated content when making important decisions.
What Not to Use AI For
When using AI tools, it’s extremely important to prioritize data privacy. Any information you provide - including text, code, or documents - may be stored on the provider’s servers and retained indefinitely. This means that sensitive data, proprietary code, or confidential business information could be inadvertently used to train future AI models, creating privacy and security risks for both individuals and organizations.
Avoid including:
- Credentials and passwords
- API keys or authentication tokens
- Proprietary or confidential code
- Internal exploits or security vulnerabilities
- Sensitive project details or trade secrets
- Real company or client names
- Personal identifiable information (PII) of employees or customers
- Financial data or confidential business reports
- Any data that could compromise security or privacy
Safe to use with AI:
- Sanitized logs or anonymized code snippets
- General coding patterns and public algorithms
- Publicly available CVs or résumés
- Open-source code examples
- Generic names or placeholder data for testing
- Non-confidential learning materials
Understanding AI Limitations
While AI can significantly enhance cyber security workflows, it’s important to understand its limitations and avoid relying on it blindly in security‑critical situations.
- AI hallucinates - Can confidently give wrong security advice, outdated CVE info, or non-existent commands
- Always verify outputs against official documentation, especially for security configurations
- Test all code in isolated environments before production use
- AI doesn't understand context - It can't assess your specific threat model or environment
Following these guidelines helps you leverage AI effectively while minimizing the risk of exposing sensitive or confidential information.
Tips for Effective Security Prompts
- Be specific about context (your role, environment, security standards)
- Ask for explanations WITH outputs ("explain why this approach is secure")
- Request alternatives ("give me 3 approaches and compare them")
- Iterate and refine based on results
AI for Cyber Security Jobs
AI is becoming an essential tool in modern cyber security roles, helping professionals work faster, smarter, and more efficiently. In daily operations, AI can assist with threat detection, log analysis, and incident triage by quickly identifying patterns and anomalies that might indicate malicious activity.
Instead of manually reviewing massive volumes of data, security teams can use AI to surface high-risk events, prioritize alerts, and reduce false positives, allowing analysts to focus on the most critical threats. Let’s see how:
Automated Report Generation
AI tools can streamline the creation of various security reports, such as incident reports, audit summaries, and regular security status updates. Automating these processes ensures that reports are produced quickly and consistently, allowing security personnel to focus on analysis and decision-making rather than routine documentation.
Threat Intelligence
AI can sift through massive amounts of data, such as logs and threat intelligence feeds, to identify patterns or anomalies that might indicate the presence of threat actors. This can significantly speed up the threat detection process and free up human analysts and security teams to focus on more complex tasks.
Network Traffic and Log Analysis
AI can analyze network packet captures and logs to identify security incidents, explain attack patterns, and correlate suspicious activity. By processing .pcap files and log data, AI can quickly surface anomalies that might take analysts hours to find manually, while providing clear explanations of technical details and attack methodologies.
To demonstrate this capability, we'll analyze a real-world packet capture from the 4SICS ICS Security Conference (October 2015, GeekLounge capture), provided by Netresec. This capture contains actual network traffic that includes security-relevant events. Let's see how Claude Opus 4.5 performs a comprehensive security analysis of this network data.
Here's the prompt we used:
I'm uploading a pcap file for security analysis. Please analyze it and provide:
1. Summary: What's happening in this capture? What's the story?
2. Key Indicators: Identify suspicious patterns, anomalies, or attack signatures
3. Technical Details: Break down the relevant packets/conversations
4. Attack Analysis: If malicious activity is present, what technique is being used? (Include MITRE ATT&CK references if applicable)
5. Investigation Steps: What should I look at next?
6. Mitigation Recommendations: How to defend against this activity
Context: [Add any relevant context - timeframe, network segment, what triggered the capture, etc.]
The output was very detailed. Here are some highlights:
Claude first provides an executive summary of the events recorded within the .pcap file.

It provided a list of the indicators of compromise.
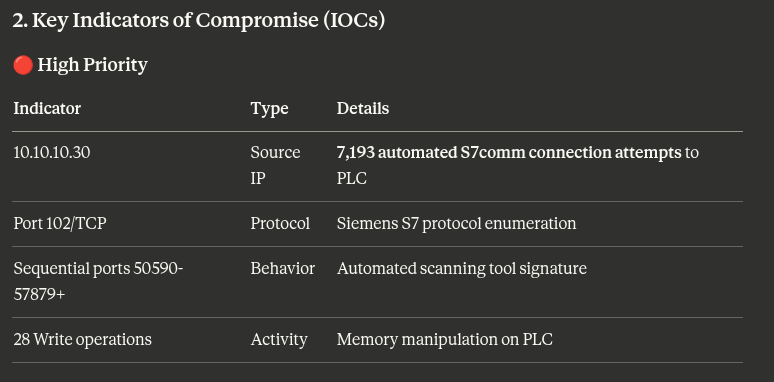
We were given a mapping of the events to the MITRE ATT&CK Framework, showing the techniques and evidence, along with an attack timeline.
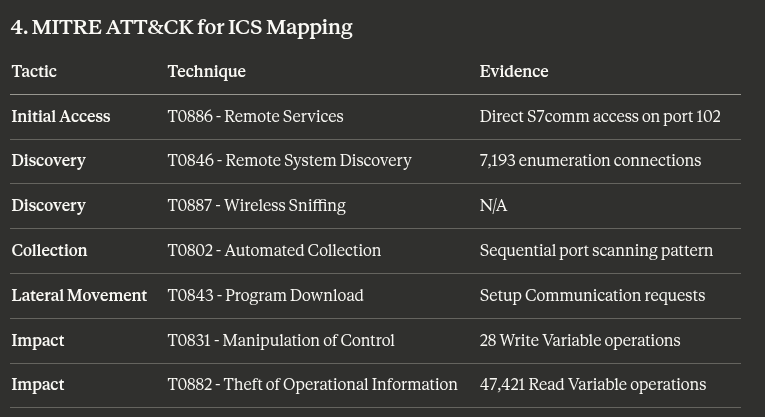
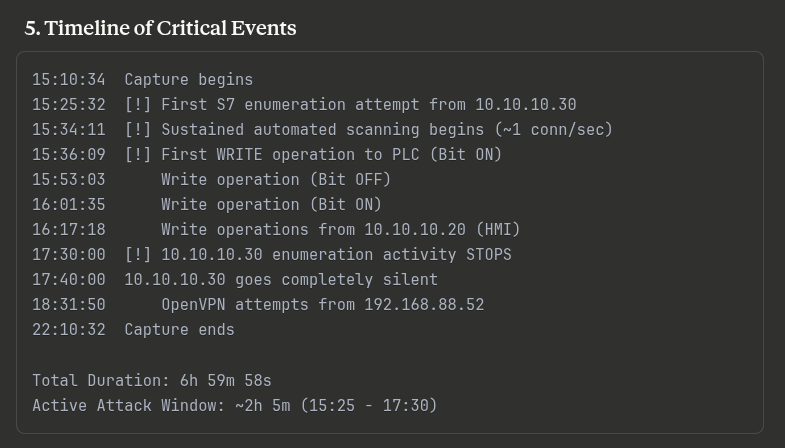
Claude was able to map our network using the .pcap file.
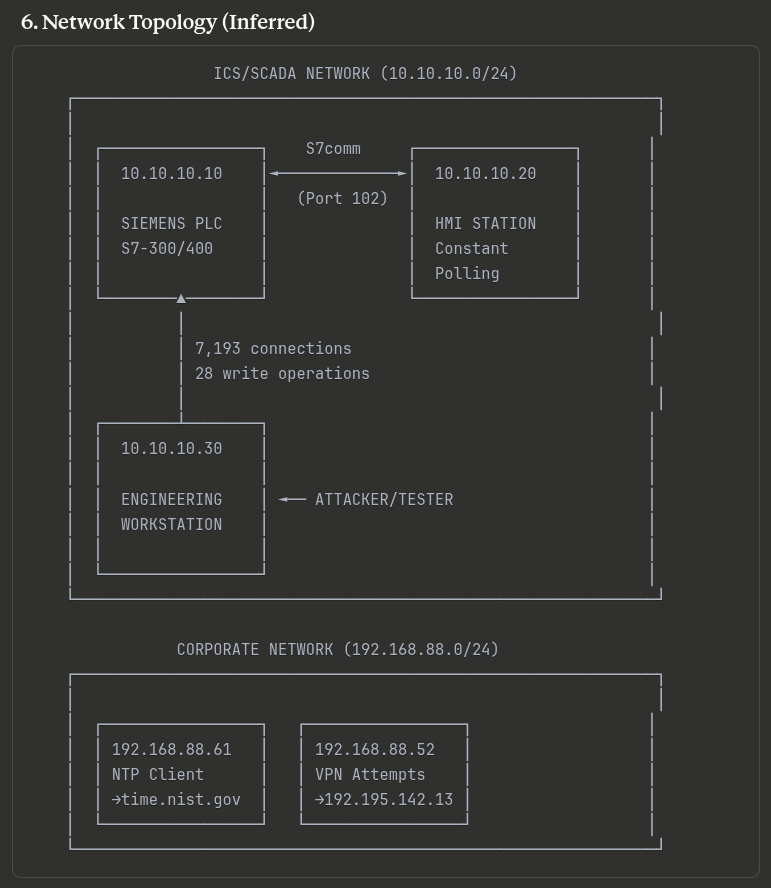
We were also given steps for further investigation, specific commands to use in Wireshark to assist forensic analysis, detailed mitigation strategies, and even Snort and Suricata rules we could implement.
Incident Response
Quick and effective communication is crucial during a cyber security incident. AI can help draft notifications to stakeholders and even guide less experienced staff through the steps of the incident response protocol, ensuring a coherent, coordinated approach.
Vulnerability Research and Assessment
When new vulnerabilities emerge or are discovered in your environment, security professionals need to quickly understand the threat landscape, affected systems, and remediation steps. AI can rapidly synthesize information from multiple sources including CVE databases, vendor advisories, and security research to provide comprehensive vulnerability intelligence with authoritative citations.
For this example, we'll use Gemini to research the MOVEit Transfer vulnerability, a significant supply chain attack that affected numerous organizations. Let's see how Gemini can compile detailed threat intelligence from multiple authoritative sources.
Here's the prompt we used:
Summarize the MOVEit Transfer vulnerability including CVEs, attack vectors, affected versions, and remediation strategies with citations
Gemini provided a clear summary with all the details we asked for, and offered to draft a checklist for auditing our environment for these specific IoCs.


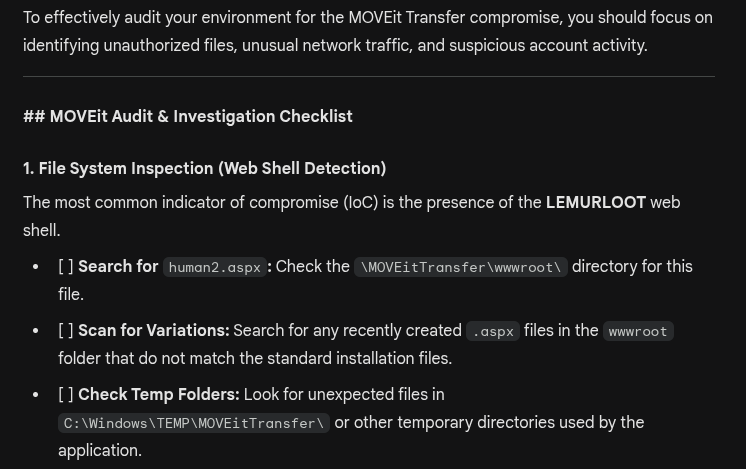
The checklist continued with another four sections.
FREE Cyber Security Career Guide
Thinking of a career in cyber security? Our Cyber Security Career Guide walks you through the industry landscape, skill-paths, certifications, and realistic timelines to become job-ready.
Compliance Checklists
Compliance with industry standards and regulations is a major component of cyber security. AI tools can automate the creation of compliance checklists aligned with regulations such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS. It can also update these checklists as regulations change, ensuring ongoing compliance without requiring extensive manual oversight.
Always validate AI-generated checklists against the official standard documentation, as AI may reference outdated requirements. Using unverified AI outputs in security configurations or audits could lead to misconfigurations or compliance gaps. Treat AI as a support tool, not a final authority, and ensure every recommendation is cross-checked with current, authoritative sources before applying it in production or critical environments.
As an example, let’s see how easy it is to have ChatGPT create a PCI-DSS compliance checklist for you. This checklist will ensure your organization follows all necessary security protocols and protects sensitive customer data.
Here’s the prompt we’re using.
I need you to generate a comprehensive compliance checklist for the payment card industry data security standard (PCI-DSS). This checklist should cover all the requirements and controls outlined in the latest version of the PCI-DSS standard. The checklist should be organized clearly and structured, with each requirement and its associated sub-requirements listed separately.
Also, please provide a brief explanation or description for each requirement to ensure a clear understanding of what needs to be addressed for compliance. The goal is to create a practical and actionable checklist that our organization can use to evaluate our current security posture, identify gaps, and implement the necessary measures to achieve and maintain PCI-DSS compliance effectively.

Here’s the checklist that GPT creates for us.

AI for Cyber Security Training
AI tools can be a great resource if you want to learn about cyber security or need to create training material for your workplace or organization. Let’s look at four examples where we’ll demo one of them for you.
Course Creation
AI can assist with building course outlines and training frameworks by suggesting relevant topics, subtopics, and learning objectives. It helps organize material in a logical sequence, identify skill gaps, and ensure that training content aligns with real-world cyber security roles and responsibilities.
Awareness Training
AI is especially useful for security awareness and phishing simulations. It can generate realistic social engineering scenarios, phishing emails, and interactive exercises to test employee awareness. By simulating real-life situations, employees can better understand the importance of staying vigilant and protecting sensitive information.
CTF Help
AI can act as a learning aid during Capture The Flag (CTF) exercises and lab-based training. You can provide it with information about your end goal, and it can walk you through each step, one by one. From initial scanning to enumeration and eventually exploiting security vulnerabilities, AI can offer guidance, tips, and explanations to help you complete the challenge.
Use AI as a learning aid and hint system, but always verify commands and techniques in safe environments before execution. While CTFs are designed to be safe testing grounds, real-world environments are not. AI-generated techniques can be inaccurate or incomplete, so never run unfamiliar commands on client or production systems without first verifying their impact in a secure testing environment.
AI Cyber Security Projects
ChatGPT is an excellent tool for on-the-job tasks or creating training materials, and it can also help you develop projects for fun, practice, or build your resume and portfolio. Here are four examples of how you can use AI with one demo.
Designing and Creating Practice Labs
AI can help you design and create practice labs, including setting up specific challenges or simulations. It can also assist you in scripting the automation of lab setups. This might include writing scripts to configure virtual machines, deploy applications, or generate network traffic.
Developing Tools and Plugins
AI can help you brainstorm ideas for new tools or plugins based on your needs or gaps in existing tools. It can also provide development steps, including advice on which programming languages, libraries, and frameworks might be most effective.
Exam Preparation
One of AI’s most significant benefits is its ability to assist with exam preparation, such as CompTIA exams, where you must thoroughly understand the syllabus and numerous concepts. It can help you grasp challenging topics by providing explanations and examples, and generating practice questions to reinforce your understanding and preparedness for exam day.
We’ll show you how to use it to help you prepare for the Security+ exam. We’ll use a custom GPT specifically set up for this task.
We are using the Security+ 701 Exam Coach GPT. To use custom GPTs, you’ll need a paid subscription.
With this GPT, we get four conversation starters. Alternatively, we can give it other prompts. Let’s start by asking it to test us on RAID.
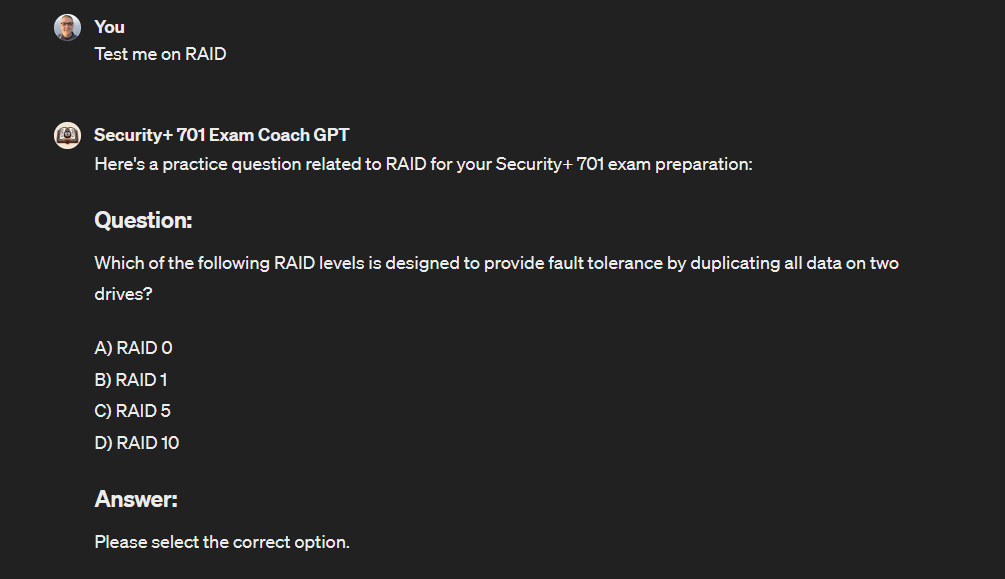
Let’s select our answer.

It even provides us with the reason our answer is correct, which is beneficial for learning and understanding the material more deeply.
You can also ask questions if you’re unsure about a topic or want to understand it better. Let’s ask it to explain the difference between symmetric and asymmetric encryption.
Explain the difference between asymmetric and symmetric encryption and how I can remember the difference for the exam.

These are just a few examples of what AI can do to help you with training, whether you’re a student or an instructor.
Creating a Custom GPT
You can also create your own cyber security GPT that can be used for various functions. Creating one is as easy as starting a conversation, where you provide it with instructions and knowledge and decide what it can do, such as searching the web, creating images, or analyzing data. The best part is that no coding expertise is required on your end.
Creating a Blog or Video Series
AI can help you create and manage a blog or video series by assisting with ideas, SEO optimization, and audience engagement. It can help generate topic ideas, draft and refine posts, suggest SEO strategies, and develop social media content to promote your series.
Let’s see how easily this can be accomplished using the power of ChatGPT.
Help me plan a comprehensive video series on web application penetration testing for YouTube.
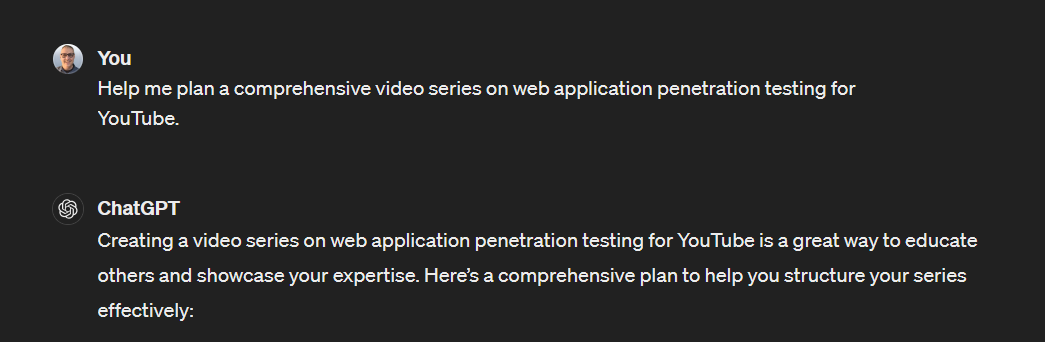
Here is the breakdown we’re given.


ChatGPT breaks down the production, planning, promotion, and engagement strategies and provides feedback. You can always ask for more detailed help at every step of the process.

Overall, ChatGPT can be a great help when completing skills development projects or enhancing your portfolio.
Conclusion
As you can see, using AI for cyber security has many benefits and applications.
You've seen how it can be used on the job, as a training aid, and to help you create projects to practice and enhance your skills.
If you're looking for an all-in-one resource to help you stand out, consider joining the StationX Master's Program today. Take advantage of all our tools and resources, from mentorships, roadmaps, courses, and a supportive community.
Master cyber security from beginner to advanced with our Complete Cyber Security Course Bundle covering network security, ethical hacking, endpoint protection, and online anonymity. Click the banner below.
The Complete Cyber Security Course Bundle includes:
- The Complete Cyber Security Course! Volume 1: Hackers Exposed
- The Complete Cyber Security Course! Volume 2: Network Security
- The Complete Cyber Security Course! Volume 3: Anonymous Browsing
- The Complete Cyber Security Course! Volume 4: End Point Protection
- The Complete Cyber Security Course Practice Test - Volume 1




