You’ve made an excellent choice aiming for the CompTIA A+ certification. It goes without saying that you want to excel in these exams. A+ gives you a solid footing as you embark on a new career in IT, and it contains essential IT knowledge for a journey into cyber security.
As A+ covers many technical topics broadly, it can be challenging to recall fine details, especially when troubleshooting problems described in the exam questions.
Therefore, we’ve prepared this CompTIA A+ cheat sheet for you as an ongoing revision checklist and to provide direction in your exam preparation. Get a copy of this CompTIA A+ cheat sheet for your desk here. When you’re ready, let’s review our must-know concepts below.
About CompTIA A+ Certifications
CompTIA A+ is a popular entry point into the IT and cyber security industry. If you’re seeking to become a technical support specialist, field service technician, help desk technician, service desk analyst, data support technician, or desktop support administrator, A+ will get your foot in the door.
You must pass two examinations to obtain A+:
- Core 1 (220-1201), which focuses on mobile devices, hardware, networking, virtualization, and cloud computing; and
- Core 2 (220-1202), which is about software, cyber security, and operational procedures.
Troubleshooting is a main component in both exams.
Each of the Core examinations has at most 90 questions, either multiple-choice or performance-based. You must complete each exam in 90 minutes. On a scale of 100–900, the passing scores for Core 1 and Core 2 are 675 and 700, respectively.
The latest CompTIA A+ exam codes are 220-1201 for Core 1 and 220-1202 for Core 2. They have been available since March 2025 and will retire in 2027–2028. Both exams cost a combined total of $265 USD (see all pricing).
As an authorized CompTIA partner, we are able to offer significant discounts on exam vouchers. Click the banner below to see our prices.
A+ has no formal prerequisites, but CompTIA recommends that you have 12 months of hands-on experience in an IT support specialist job role.
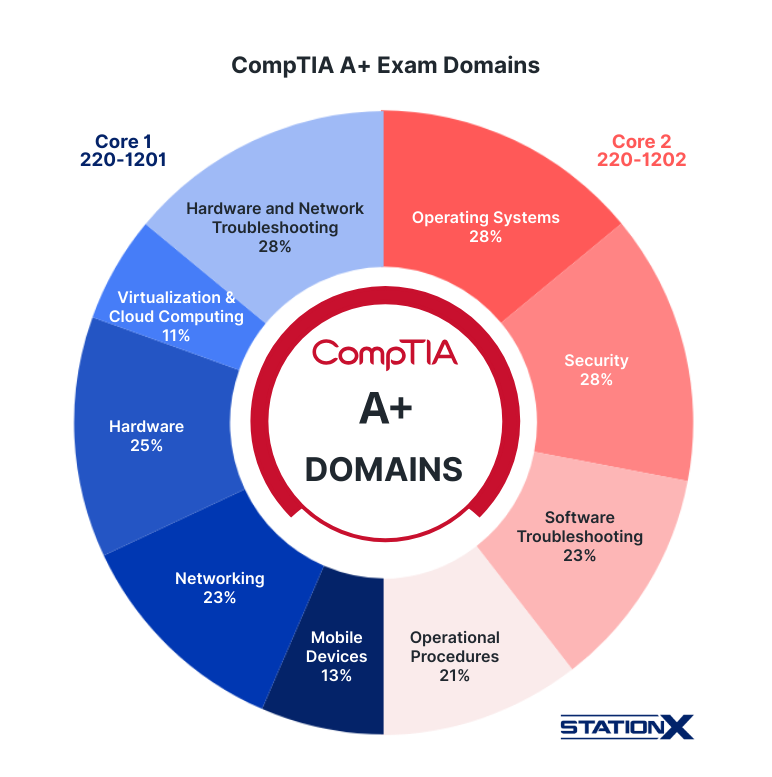
Here is a chart on CompTIA A+ exam objectives (domains):
CompTIA A+ Exam Domains
A+ Core 1 (220-1201) Domains:
| Domain | % of exam |
|---|---|
| Mobile Devices | 13% |
| Networking | 23% |
| Hardware | 25% |
| Virtualization and Cloud Computing | 11% |
| Hardware and Network Troubleshooting | 28% |
A+ Core 2 (220-1202) Domains:
| Domain | % of exam |
|---|---|
| Operating Systems | 28% |
| Security | 28% |
| Software Troubleshooting | 23% |
| Operational Procedures | 21% |
Despite its practicality and necessity for A+ competence, the Troubleshooting Methodology illustrated below is no longer a formal A+ examination objective with explicit test items. Still, you’ll have to apply it in answering A+ exam questions.
Technical Troubleshooting—Best Practice Methodology
Without further ado, let’s plunge into the cheat sheets for each of 220-1201 and 220-1202.
Core 1 220-1201 Cheat Sheet
This section covers important concepts for Core 1. We skip the domain on troubleshooting as it builds upon the other domains.
Mobile Devices
With the ubiquity of mobile devices, mastering the configuration of mobile devices is an essential skill for aspiring IT support technicians.
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Random Access Memory (RAM) | • RAM DIMMs include DDR (184 pins), DDR2 (240 pins), DDR3 (240 pins) and DDR4 (288 pins). • RAM SODIMMs include DDR (200 pin), DDR2 (200 pin), DDR3 (204 pin), and DDR4 (260 pin). • Dual-channel: 2× width of 128-bit bus. • Triple-channel: 3× width of 192-bit bus. • Quad-channel: 4× width of 256-bit bus. • Latency measured as CL or CAS. |
| Hard disk drive (HDD) | Speeds: 5,400 RPM, 7,200 RPM, 10,000 RPM, 15,000 RPM Form factors: 3.5”, 2.5” |
| Solid-state drive (SSD) | Communication interfaces: • Non-Volatile Memory Express (NVMe) SATA • Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe): x1, x2, x8, x16 Form factors: M.2, mSATA |
| Bluetooth | Short-range technology for simplifying communication and connectivity among network devices |
| Bluetooth transmission range lengths | • Class I: 100m • Class II: 10m (most popular) • Class III: 1m (unpopular) |
| Bluetooth maximum data transfer rate | • Version 1: 721 Kb/s • Version 2: 2.1 Mb/s • Version 3: 24 Mb/s |
| Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)/eSIM | Used for identifying a user to a mobile network, allowing access to voice and data services. |
| Tethering | Using smartphone cellular data connection to provide internet access to another device |
| Docking station | Hardware containing multiple ports to connect your laptop or mobile device to other devices, such as larger monitors, and lets you charge devices |
| Port replicator | Hardware for quickly connecting multiple peripherals to a laptop via USB technologies. Be prepared for exam questions comparing docking station vs port replicator. |
Recognizing data caps | • Monitor data usage • Set data limits and warnings • Limit background data • Adjust sync frequency • Disable automatic downloads • Use Wi-Fi when possible |
Networking
A+ covers network topologies, the devices connecting them, ports, protocols, and the software aspects of networking.
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| AAA | Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting |
| WISP | Wireless internet service provider |
| Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) | Connection-oriented, SYN-ACK handshake (SSD) |
| User Datagram Protocol (UDP) | Connectionless, best-effort |
| LAN | Local area network |
| WAN | Wide area network |
| MAN | Metropolitan area network |
| PAN | Personal area network |
| SAN | Storage area network |
| WLAN | Wireless local area network |
| VLAN | Virtual LAN |
| VPN | Virtual private network |
| Switch | Connect computers in LAN |
| Router | Connects ≥2 LANs to the Internet |
| Firewall | Safeguards computers and networks against unauthorized access |
| UTM | Unified threat management |
| MAC | Media access control |
| DSL | Digital subscriber line |
| ONT | Optical network terminal |
| APIPA | Automatic Private IP Addressing |
| PoE | Power over Ethernet |
| DKIM | DomainKeys Identified Mail |
| SPF | Sender Policy Framework |
Wireless Ethernet:
| Version | Data transmission rate | Frequency modulation (GHz) |
|---|---|---|
| 802.11a | 54 Mb/s | 5 |
| 802.11b | 11 Mb/s | 2.4 |
| 802.11g | 54 Mb/s | 2.4 |
| 802.11n | 300/600 Mb/s | 2.4, 5 |
| 802.11ac | ≥1.7 Gb/s | 5 |
| 802.11ax | ≤9.6 Gb/s | 2.4, 5, 6 |
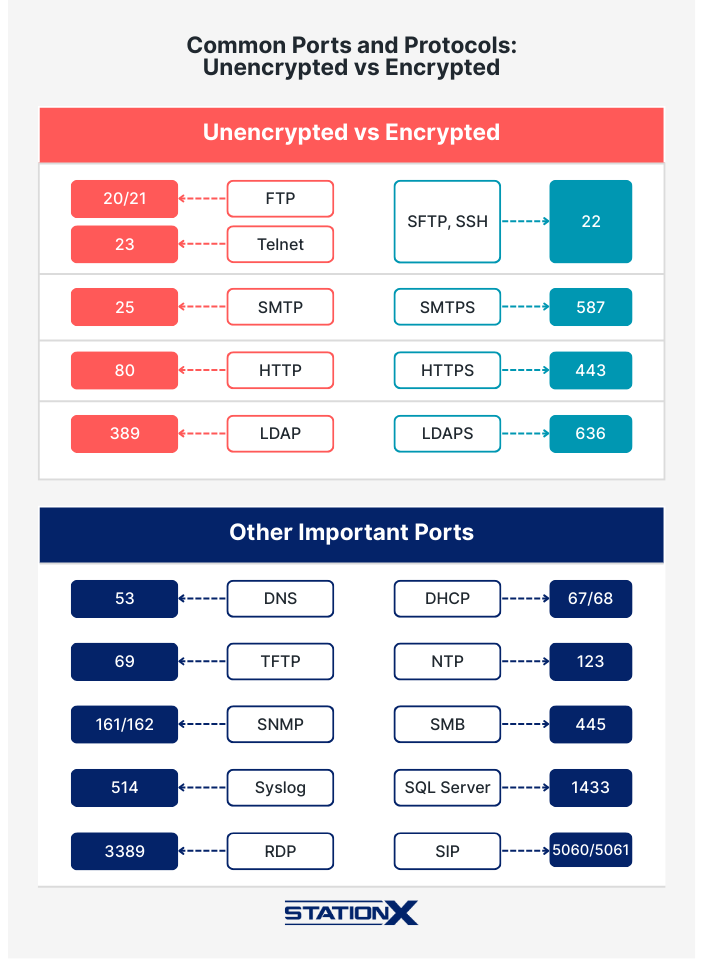
Ports and Protocols:
| Port | Network protocol |
|---|---|
| 21 | File Transfer Protocol (FTP) |
| 22 | Secure Shell (SSH) |
| 23 | Telnet |
| 25, 587 | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) |
| 53 | Domain Naming System (DNS) |
| 67/68 | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) |
| 80 | Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) |
| 110 | Post Office Protocol (POP3) |
| 137–139 | NetBIOS |
| 143 | Internet Message Access Protocol (IMAP) |
| 389 | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) |
| 443 | HTTP Secure (HTTPS) |
| 445 | Server Message Block (SMB)/Common Internet File System (CIFS) |
| 3389 | Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) |
Remember to check out our Common Ports Cheat Sheet.
Common ports and protocols
Hardware
Acquaint yourself with different hardware specifications and their purposes.
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Motherboard | For connecting all components.Form factors: ATX, microATX, and ITX.Types of expansion buses: PCI Express (PCIe) and PCI.Intel chipsets link to CPU via DMI or QPI.AMD CPU-to-chipset connection is HyperTransport. |
| Central processing unit (CPU) | Handles most calculations. Each core contains L1/L2 cache. The entire CPU shares L3 cache. Intel CPUs use these sockets:LGA77511501155115613662011 AMD CPUs use these sockets:AM3AM3+FM1FM2FM2 |
| Serial Advanced Technology Attachment (SATA) | Consists of a 15-pin power connection and a 7-pin data connector. Revisions:Rev 1 (1.5 Gb/s),Rev 2 (3 Gb/s),Rev 3 (6 Gb/s),Rev 3.2 (SATA Express) (16 Gb/s),Rev 3.2 (SATA Express) (16 Gb/s). mSATA = mini-SATA.eSATA = External SATA. |
| Redundant Array of Independent/Inexpensive Disks (RAID) | RAID 0 = striping; not fault-tolerant.RAID 1 = mirroring. RAID 1 + two disk controllers = disk duplexing.RAID 5 = striping with parity.RAID 6 = double-parity RAID for fault tolerance and data redundancy.RAID 10 = mirrored sets in a striped set. |
| Small Computer Systems Interface (SCSI) | Modern SCSI standards:Serial Attached SCSI (SAS)Internet SCSI |
| IPS | In-plane switching. Possesses wider viewing angle. |
| TN | Twisted nematic |
| OLED | Organic light-emitting diode |
| Mini-LED | Mini light-emitting diode |
| Optical media | Optical disc drives use changeable media to store and retrieve data. Versions:read-only memory (ROM)write-once ®rewritable/write-many (RW) |
| Laptop | Portable miniaturized versions of desktop computers. Uses M.2, Mini PCIe, and Mini PCI (internal) and ExpressCard /34 and /54 (external). Replaceable components:KeyboardsTouchpadsSODIMM RAMScreensInvertersBatteriesOptical disc drivesSmart card readersHard drives (SSD, HDD, or hybrid). |
| Heat sink | When installing a heat sink, use thermal paste or pads for filling in gaps and increasing thermal conductivity between CPU and heat sink. Liquid-based cooling systems have higher thermal transfer capabilities than air cooling. To minimize overheating, a “dual-rail” power supply unit (PSU) separates and controls the current in each wire. |
| Sound card | Links as x1 PCIe (or PCI cards) and will typically have PC 99 color-coded 1/8” mini-jacks for I/O and speakers and optical I/Os known as S/PDIF. |
| Video card | You link them to motherboards through x16 PCIe or PCI expansion slots. Video connector types and cables:DVIVGAHDMIMini-HDMIDisplayPortMini DisplayPortS-VideoComponent Video/RGBComposite Typical color depths:16-bit24-bit32-bit Typical resolutions (aspect ratio)1280×720 (720p, 16:9)1920×1080 (1080p, 16:9)1366×786 (16:9)1680×1050 (WSXGA+, 8:5)1920×1200 (WUXGA, 8:5)640×480 (VGA, 4:3) |
| BIOS/Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI) | Locates, tests, and initializes components and boots to the hard drive, optical disc, USB flash drive, or network by PXE.CMOS stores time/date and passwords.A CR2032 lithium battery powers the CMOS. |
| Thunderbolt | Version 1 is 10 Gb/s and uses DisplayPort;Version 2 is 20 Gb/s and also uses DisplayPort;Version 3 is 40 Gb/s and uses USB-C. |
| Universal Serial Bus (USB) | USB 2.0USB 3.0USB-CmicroUSBminiUSB |
| T568A | White/greenGreenWhite/orangeBlueWhite/blueOrangeWhite/brownBrown |
| T568B | Swap “green” and “orange” in T568A |
| Single-mode vs. multimode | (Optic fiber) Allowing one or multiple light modes to propagate |
| Coaxial | F-type, Bayonet Neill–Concelman |
| Twinaxial/twinax | Has two inner conductors instead of one as in coaxial |
| STP/UTP | Shielded/Unshielded twisted pair; RJ45, RJ11 (Registered jack) |
| Optical | SC, ST, LC, FC, MT-RJ |
| SC | Subscriber connector |
| ST | Straight tip |
| LC | Lucent connector |
| FC | Fibre Channel |
| Plenum-rated | Fire-resistant cable; compare with riser-rated, non-plenum rated, and PVC |
| UTP category | Define speed and length of cables:Cat 3Cat 5Cat 5eCat 6/6aCat 7Cat 8 |
| Molex | Power connector in older computers and fans |
| Lightning | Proprietary Apple connection interface for charging and data transfer |
| DisplayPort | For connecting a video source to a display device such as a monitor. Be prepared to compare DisplayPort vs HDMI in exam questions. |
Virtualization and Cloud Computing
Both virtualization technologies and cloud computing were minor topics in earlier versions of A+, but they’re only getting more popular. Therefore, they’re here to stay.
| Abbreviation | Explanation |
|---|---|
| IaaS | Infrastructure as a service |
| PaaS | Platform as a service |
| SaaS | Software as a service |
| VDI | Virtual desktop infrastructure |
Virtual machines (VMs) come in these two types:
| Hypervisor | Elaboration |
|---|---|
| Type 1 | Bare or native metal |
| Type 2 | App-like VM on the operating system |
Here are additional virtualization concepts to grasp:
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Ingress/Egress | Management of network traffic entering/leaving a specific environment |
| Elasticity | Dynamic adjustability of resource allocation in response to changing workload demands |
| Availability | Operationability and accessibility despite failures or planned downtime |
| Multitenancy | A single instance of an application serves multiple users while maintaining separate data and configurations. |
Core 2 220-1202 Cheat Sheet
This section covers key ideas for Core 2. We skip the domain on troubleshooting as it builds upon the other domains.
Operating Systems
It’s essential to become familiar with various operating systems, particularly Windows. You can also get our command-line cheat sheets for Linux and Unix (applies to Mac).
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Master boot record (MBR) | A hard drive has up to four partitions but only one extended partition. |
| GPT (GUID Partition Table) | A hard drive has 128 partitions and may exceed MBR’s 2 TB limit. Stored in multiple locations. Requires UEFI-compliant motherboard. |
| EOL | End-of-life |
| CDFS | Compact disc file system |
| NFS | Network file system |
| NTFS | New Technology File System |
| ReFS | Resilient File System |
| FAT32 | File Allocation Table 32 |
| ext4 | Fourth extended file systems |
| exFAT | Extensible File Allocation Table |
| XFS | Extended filesystem |
| APFS | Apple File System |
Security
Here are some essential cyber security concepts you must know to pass A+.
Wireless encryption protocols:
| Acronyms | Explanation |
|---|---|
| WPA2, WPA3 | Wi-Fi Protected Access (version 2 and 3) |
| TKIP | Temporal Key Integrity Protocol |
| AES | Advanced Encryption Standard |
| RADIUS | Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service |
| TACACS+ | Terminal Access Controller Access-Control System |
Social Engineering:
| Technique | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Phishing/Vishing/Smishing | Attack by email/telephone or voicemail/SMS |
| QR code phishing | Attack by QR code |
| Spear phishing | Attack by emails purportedly from trusted senders |
| Whaling | Phishing that targets high-ranking people, such as C-suite executives |
| Shoulder surfing | Look over someone’s shoulder, often with a recording device |
| Tailgating | Unauthorized entity follows authorized party into secured premises |
| Impersonation | Attacks using stolen credentials or personal information |
| Dumpster diving | Recover information from trash |
| Evil twin | Setting up a fake Wi-Fi access point, hoping people choose it over the genuine one. |
Threats:
| Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Denial of service (DoS) | Overwhelming a target using a single machine |
| Distributed denial of service (DDoS) | DoS using multiple machines |
| Zero-day attack | Vulnerability unbeknownst to developers |
| Spoofing | Faking authorized access |
| On-path attack | Wi-Fi network as a trap |
| Brute-force attack | Trying character combinations |
| Dictionary attack | Using lists of probable passwords |
| Insider threat | An insider potentially uses their authorized access or understanding of an organization to harm that organization |
| Structured Query Language (SQL) injection | Manipulating SQL to modify remote database (such as by using sqlmap) |
| Cross-site scripting (XSS) | Injecting malicious scripts into normal websites |
| Business email compromise (BEC) | Hijacking chain-of-command |
| Supply chain/pipeline attack | Compromising the supply chain |
Mitigations:
The following table is not an exhaustive list of mitigations.
| Acronym | Explanation |
|---|---|
| EDR | Endpoint detection and response |
| MDR | Managed detection and response |
| XDR | Extended detection and response |
| ACL | Access control list |
| Email security gateway | Incoming/outgoing email monitoring/filtering gatekeeper |
| Software firewall | Network traffic monitor and controller |
Malware:
| Name | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Virus | Runs on a computer without the user’s knowledge. Example: Boot sector virus |
| Worm | Replicates itself across a network |
| Trojan Horse | Useful utility covering for malicious programs |
| Spyware | Spies on a computer and records its activities. Examples: keylogger, adware, stalkerware |
| Rootkit | Gains administrator-level access to the system core undetected |
| Ransomware | Holds a computer hostage until the user pays |
| Cryptominer | CPU hijacker to mine crypto |
| Fileless malware | Runs legitimate programs on RAM without creating or downloading files |
| PUP | Potentially unwanted program |
Best Practice Procedures for Malware Removal
Operational Procedures
The following table outlines some best practices related to documentation, change management, and backup/recovery.
| Acronym/concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| CMDB | Configuration Management Database |
| SLA | Service-level agreement |
| SOP | Standard operating procedures |
| GFS | Grandfather-father-son Other backup rotation schemes:Onsite vs. offsite3-2-1 backup rule |
| ESD | Electrostatic discharge |
| Ticketing systems | User informationDevice informationDescription of issuesCategoriesSeverityEscalation levelsIssue descriptionProgress notesIssue resolution |
| Backup | FullIncrementalDifferentialSynthetic full |
CompTIA A+ Cheat Sheet Conclusion
We hope this updated CompTIA A+ cheat sheet helps you in your studies as a brief recap of key points.
Don’t forget to look into our latest CompTIA A+ courses and practice tests for comprehensive exam preparation. You can purchase our Complete CompTIA A+ Training Bundle (Version 15), granting lifetime access to Tech+ and A+ courses, practice tests, and flashcards.
Or join the StationX Master’s Program for access to over 30,000 courses and labs, covering everything you need for a career in IT, Network Administration, or Cyber Security.
You can also purchase your exam voucher through StationX at a discounted price. We offer savings of up to 30% on CompTIA exam voucher. See our voucher page for more details.
Above all, we wish you success in the exam and beyond.