You’ve made a brilliant decision aiming for the CompTIA Network+ certification. Given the deluge of information on networking and limited time to prepare for the examination, it can be frustrating to decide what aspects of Network+ are high-priority items to review.
Our CompTIA Network+ cheat sheet is handy as an overview or a refresher for this broad-based certification exam. This N10-009 cheat sheet serves as an excellent companion to our Security+ cheat sheet, which builds upon Network+, delving deeper into major networking topics than those briefly mentioned in our A+ cheat sheet.
Download a copy of this CompTIA Network+ cheat sheet here. When you’re ready, let’s dive in.
What Is CompTIA Network+ Certification
CompTIA Network+ is a vendor-neutral certification covering the fundamental knowledge and skills in essential computer networking functions over five domains. Although CCNA is more popular as an entry-level networking credential in some locations, Network+ lays the foundation for the ubiquitously in-demand Security+ cyber security certification.
Its wide but shallow coverage is best suited for those preparing for a cyber security career who require a broad understanding of networking without the depth of a Network Engineer.
Successful candidates can explain basic data center, cloud, and virtual networking concepts, establish network connectivity by deploying wired and wireless devices, monitor and troubleshoot network performance, implement network security hardening techniques, configure common network services, and manage network documentation and infrastructure.
You’ll need to answer at most 90 questions, including both multiple-choice and performance-based, in this 90-minute examination and complete a survey after it ends. The passing score is 720 on a scale of 100–900. The exam costs $390 USD (see all pricing).
The latest exam code is N10-009. This version of the exam has been available since June 2024, and it will retire in 2027–2028. Compared with past Network+ versions, this updated exam includes a much greater overlap with Security+ topics.
Domains
Advancements in networking technologies and new threats to network security prompt updates to what constitutes a competent network administrator. Therefore, every three years, CompTIA updates the Network+ exam to highlight the most up-to-date industry needs in each focus area (Domain) of networking.
Here’s the latest breakdown of Network+ Domains:

| Domain | Exam Weighting (%) |
| Networking Concepts | 23% |
| Network Implementation | 20% |
| Network Operations | 19% |
| Network Security | 14% |
| Network Troubleshooting | 24% |
Without further ado, let’s explore each Domain and unpack the key concepts and acronyms you’ll encounter in the exam.
Networking Concepts
The following items are essential networking knowledge.
| Concept | Elaboration |
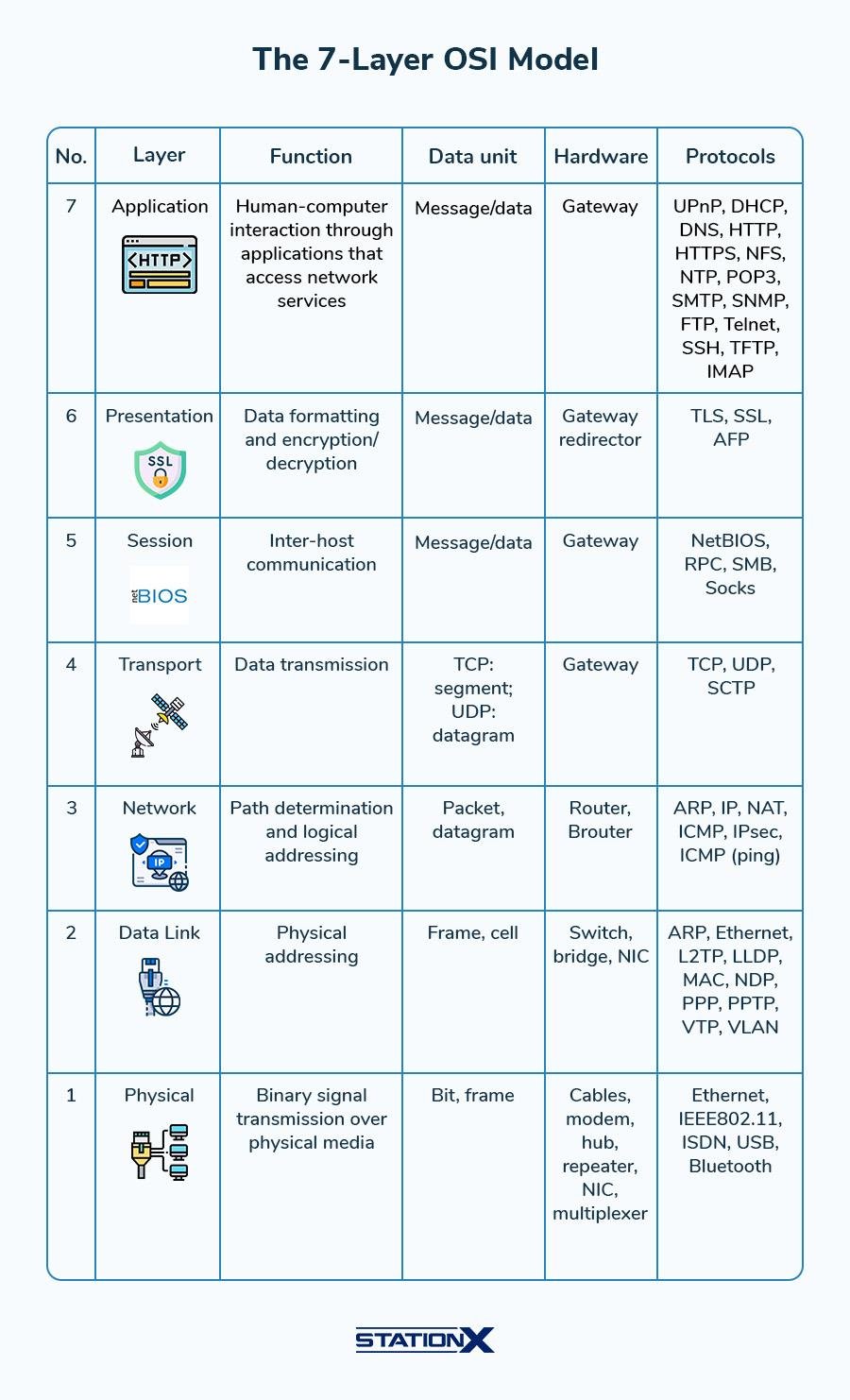
| OSI model | Open Systems Interconnection: 1. Physical 2. Data Link 3. Network 4. Transport 5. Session 6. Presentation 7. Application OSI model layer memory aid: Please Do Not Throw Sausage Pizza Away (alternatives) |
| LAN | Local Area Network |
| Subnet | Short for “subnetwork,” a logical or physical subdivision of a larger network |
| Router | Connects ≥ 2 LANs to the Internet |
| Switch | Connect computers in LAN |
| Firewall | Safeguards computers and networks against unauthorized access |
| Proxy | Gateway between users and Internet |
| NAS | Network-attached storage |
| SAN | Storage area network |
| AP | Access point |
| IDS | Intrusion detection system |
| IPS | Intrusion prevention system |
| Load balancer | Distributes traffic across servers |
| CDN | Content Delivery Network |
| QoS | Quality of service |
| TTL | Time to live |
| Network security list | Set of security rules applied to all devices on a subnet |
| Network security group | Set of security rules applied to a group of network devices |
| Internet gateway | Allows inbound and outbound connections between private subnets and public networks |
| Network address translation (NAT) gateway | Allows outbound connections from a private subnet to public network services while shielding it from inbound connections from outside |
| Cloud | Considerations: • Scalability • Elasticity • Multitenancy Deployment models: • Public • Private • Hybrid |
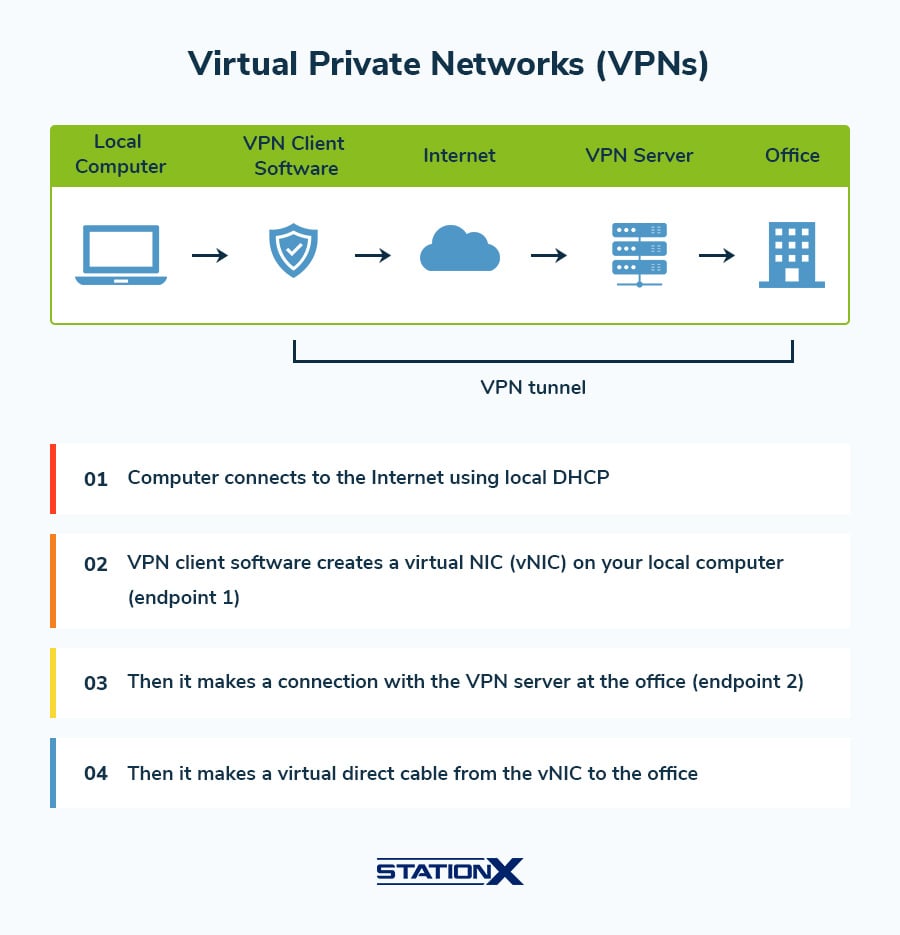
| VPN | Virtual Private Network |
| Concept | Elaboration |
| NFV | Network function virtualization |
| VPC | Virtual private cloud |
| SaaS | Software as a Service |
| IaaS | Infrastructure as a Service |
| PaaS | Platform as a Service |
| Direct Connect | Your on-premises infrastructure connects to a cloud provider’s network, bypassing the public Internet |
| Internet Protocol (IP) | IPv4 and IPv6 |
| Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) | Most commonly used for ping packets |
| Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) | Connection-oriented, SYN-ACK handshake |
| User Datagram Protocol (UDP) | Connectionless, best-effort |
| IPv4 address | 32-bit number, consisting of four decimals from 0 to 255 separated by period (.), e.g., 192.168.1.1 |
| IPv4 loopback/localhost | 127.0.0.1 |
| Automatic Private IP Addressing (APIPA)/link-local | 169.254.x.x |
| Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) | CIDR IPv4 addresses have a prefix; e.g., “/24” in “10.150.23.58/24” denotes a 255.255.255.0 subnet mask. |
| 802.11 standards | For Wi-Fi communication |
| 802.3 standards | For wired Ethernet networks |
| Transceiver | Combined transmitter and receiver of signals |
| Form factor | Hardware specifications |
| TIA/EIA-568A | 1. White/green 2. Green 3. White/orange 4. Blue 5. White/blue 6. Orange 7. White/brown 8. Brown |
| TIA/EIA-568B | Swap “green” and “orange” in TIA/EIA-568A |
| Single-mode vs. multimode | (Optic fiber) Allowing one or multiple light modes to propagate |
| DAC | Direct attach copper |
| Coaxial | F-type, BNC |
| BNC | Bayonet Neill–Concelman |
| Twinaxial/twinax | Has two inner conductors instead of one as in coaxial |
| Twisted pair | RJ45, (RJ)11 |
| (RJ)11 | Registered jack |
| STP/UTP | Shielded/Unshielded twisted pair |
| Fiber optic | SC, ST, LC, FC, MT-RJ |
| SC | Subscriber connector |
| ST | Straight tip |
| LC | Local connector |
| FC | Fibre Channel |
| Plenum-rated | Fire-resistant cable; compare with riser-rated, non-plenum rated, and PVC |
| UTP category | Define speed and length of cables: • Cat 3 • Cat 5 • Cat 5e • Cat 6/6a • Cat 7 • Cat 8 |
| SFP | Small form-factor pluggable |
| QSFP | Quad small form-factor pluggable |
| MPO | Multi-fiber push on |
| Network topology | • Mesh • Hybrid • Star/hub-and-spoke • Spine and leaf • Point to point |

| Concept | Elaboration |
| Three-tier hierarchical model | • Core • Distribution • Access |
| Collapsed core | Combine core and distribution layers |
| North-south | Traffic moving between a private network and the outside world |
| East-west | Traffic moving within an organization’s internal network |
| RFC1918 | IP addresses set aside for private networks |
| VLSM | Variable Length Subnet Mask |
| Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) | CIDR IPv4 addresses have a prefix; e.g., “/24” in “10.150.23.58/24” denotes a 255.255.255.0 subnet mask. |
| IPv4 address classes | • Class A: 0.0.0.0 – 127.255.255.255 • Class B: 128.0.0.0 – 191.255.255.255 • Class C: 192.0.0.0 – 223.255.255.255 • Class D: 224.0.0.0 – 239.255.255.255 • Class E: 240.0.0.0 – 255.255.255.255 |
| SD-WAN | Software-defined wide area network |
| SDN | Software-defined networking |
| SD-WAN | Software-defined wide area network |
| IaC | Infrastructure as Code |
| SASE | Secure Access Secure Edge |
| SSE | Security Service Edge |
| VXLAN | Virtual Extensible Local Area Network |
| ZTA | Zero trust architecture |
| DCI | Data center interconnect |
| GRE | Generic Routing Encapsulation |
| IPSec | Internet Protocol Security |
| AH | Authentication Header |
| ESP | Encapsulating Security Payload |
| IKE | Internet Key Exchange |
| Traffic types | • Unicast • Multicast • Anycast |
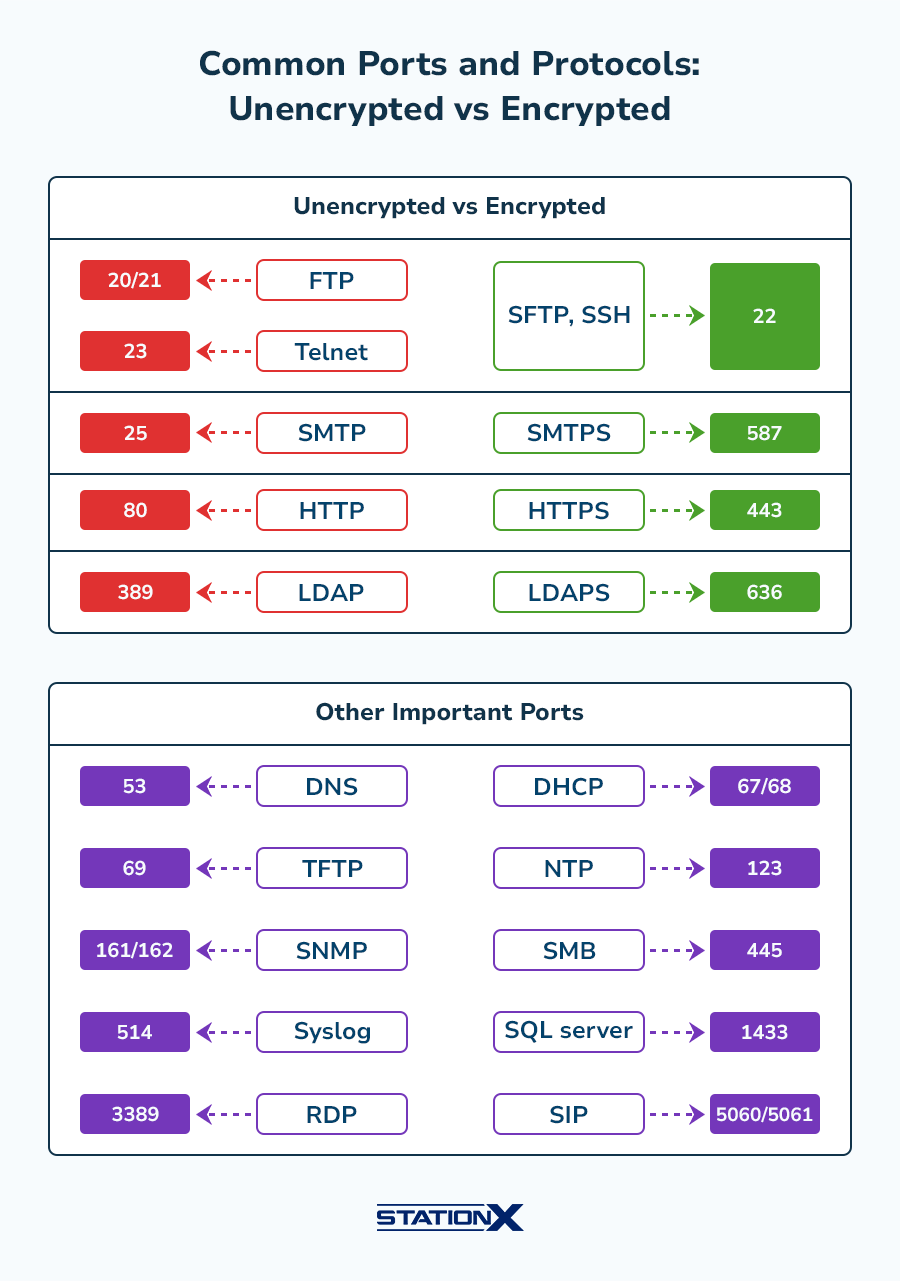
Ports and Protocols
The following table lists the ports and protocols you must know to pass Network+.
| Port number/s | Service name | Description |
| 20/21 | FTP | File Transfer Protocol |
| 22 | SSH, SFTP | Secure Shell, Secure File Transfer Protocol |
| 23 | Telnet | Telnet |
| 25 | SMTP | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol |
| 53 | DNS | Domain Name System |
| 67/68 | DHCP | Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol |
| 69 | TFTP | Trivial File Transfer Protocol |
| 80 | HTTP | Hypertext Transfer Protocol |
| 123 | NTP | Network Time Protocol |
| 161/162 | SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol |
| 389 | LDAP | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol |
| 443 | HTTPS | Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure |
| 445 | SMB | Server Message Block |
| 514 | Syslog | Syslog |
| 587 | SMTPS | Simple Mail Transfer Protocol Secure |
| 636 | LDAPS | Lightweight Directory Access Protocol over SSL |
| 1433 | SQL | Broadcast Structured Query Language (SQL) Server |
| 3389 | RDP | Remote Desktop Protocol |
| 5060/5061 | SIP | Session Initiation Protocol |
The next Domain is about putting these basic concepts into practice.
Network Implementation
This Domain is all about networking hardware: routers, switches, wireless, and installation considerations.
| Concept | Elaboration |
| Static routing | Fix-value routing; no change at runtime unless manually edited |
| Dynamic routing | Routers automatically adjust the paths that data packets take based on network conditions |
| BGP | Border Gateway Protocol |
| EIGRP | Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol |
| OSPF | Open Shortest Path First |
| PAT | Port address translation |
| FHRP | First Hop Redundancy Protocol |
| VIP | Virtual IP |
| VLAN | Virtual Local Area Network |
| SVI | Switch Virtual Interface |
| MTU | Maximum transmission unit |
| SSID | Service set identifier |
| BSSID | Basic service set identifier |
| ESSID | Extended service set identifier |
| WPA2/WPA3 | Wi-Fi Protected Access 2/3 |
| Captive portal | A webpage that appears upon connecting to a public Wi-Fi network, requiring action before granting full Internet access |
| Frequency options | • 2.4GHz • 5GHz • 6GHz |
| Band steering | Making Wi-Fi routers assign the optimal frequency band to a device based on its capabilities and network conditions |
| Network types | • Mesh networks • Ad hoc • Point to point • Infrastructure |
| PSK | Pre-shared key |
| IDF | Intermediate distribution frame |
| MDF | Main distribution frame |
| UPS | Uninterruptible power supply |
| PDU | Power distribution unit |
| Port-side intake | Cool air enters the switch through the side with the ports |
| Port-side exhaust | Hot air leaves the switch from the side with the ports |
| 802.1Q tagging | A standard that enables VLANs on Ethernet networks |
| Link aggregation | Combining multiple physical network connections into a single logical link |
| Duplex switching | Able to transmit and receive data simultaneously or by taking turns doing so |
| STP | Spanning Tree Protocol |
| Jumbo frames | Ethernet frames with a payload larger than the standard 1500 bytes, typically 9000 bytes |
The next big task after building a network is to maintain it—the scope of the next Domain.
Network Operations
Everything related to the smooth running and maintenance of computer networks is the main focus of this Domain.
| Concept | Elaboration |
| Asset inventory | A comprehensive list of all the assets belonging to or used by an organization, tangible and intangible |
| IPAM | IP address management |
| SLA | Service-level agreement |
| Wireless survey/heat map | Visualization for analyzing and mapping Wi-Fi signal coverage and strength in an area |
| OS | Operating system |
| EOL | End-of-life |
| EOS | End-of-support |
| MIB | Management information base |
| SIEM | Security information and event management |
| SNMP | Simple Network Management Protocol |
| High availability | Continued operational performance with minimal downtime |
| Active-active | Multiple active components share the workload and can handle failures by redistributing traffic |
| Active-passive | Relying on a primary, active component backed up by a secondary, standby component |
| Tabletop exercise | Discussion-based activity where participants simulate a disaster or emergency to test and improve plans, policies, and procedures |
| Validation test | “Does this product do what the user needs it to do?” |
| DR | Disaster recovery |
| RPO | Recovery point objective |
| RTO | Recovery time objective |
| MTTR | Mean time to repair |
| MTBF | Mean time between failures |
| BCP | Business Continuity Plan |
| Cold site | Power, networking capability, and cooling; no servers or storage |
| Warm site | Cold site plus storage hardware; still requires data transportation |
| Hot site | Fully functional backup site with important data mirrored to it |
| Dynamic addressing | Automatic assignment of IP addresses to devices on a network typically using DHCP |
| Name resolution | Conversion of human-readable domain names into the corresponding IP addresses using DNS |
| SLAAC | Stateless address autoconfiguration |
| DNSSEC | Domain Name Security Extensions |
| NTS | Network Time Security |
| PTP | Precision Time Protocol |
| DoH | DNS over HTTPS |
| DoT | DNS over TLS |
| Hosts file | Map hostnames to IP addresses using records such as A, AAAA, CNAME, etc. |
| A | IPv4 address |
| AAAA | IPv6 address |
| CNAME | Canonical name |
| MX | Mail exchange |
| TXT | Text |
| NS | Nameserver |
| PTR | Pointer |
| Clientless | Remote users can securely access enterprise resources without traditional client software |
| Split tunnel | Partial encryption of traffic |
| Full tunnel | Encryption of all traffic |
| Jump box/host | Secure intermediary server for accessing and managing devices in a separate network |
| In-band management | Same network infrastructure for data traffic and management |
| Out-of-band management | Using a separate, dedicated network for management |
| GUI | Graphical user interface |
A network administrator doesn’t cut the mustard if they only know how to keep a network running. The next Domain highlights the importance of keeping it secure as well.
Network Security
Maintaining the safety and security of computer networks is a vital component of being a competent professional in computer networking. This Domain doubles as an elementary introduction to cyber security.
| Concept | Elaboration |
| Data at rest | On computer storage |
| Data in transit | Traveling along cables or broadcasting wirelessly |
| Risk | Potential for loss or damage |
| Vulnerability | A defect that creates an exploitable condition, making the system vulnerable to attacks |
| Exploit | Code that takes advantage of a vulnerability in a system or software to gain unauthorized access |
| Threat | Potential danger that can harm your systems, data, or operations |
| Least privilege | Only granting the minimum access necessary to perform actions |
| Honeypot/honeynet | Individual/connected devices inviting attacks to capture information |
| IAM | Identity and access management |
| MFA | Multifactor authentication |
| SSO | Single sign-on |
| PKI | Public Key Infrastructure |
| SAML | Security Assertion Markup Language |
| CIA | Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability |
| RADIUS | For authentication, authorization, and accounting |
| TACACS+ | Terminal Access Controller Access Control System Plus |
| ICS | Industrial Control System |
| BYOD | Bring Your Own Device |
| SCADA | Supervisory control and data acquisition |
| OT | Operational technology |
| GDPR | General Data Protection Regulation |
| PCI DSS | Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| IIoT | Industrial Internet of Things |
| VLAN hopping | Attacker can move from one VLAN to another |
| Media Access Control (MAC) flooding | Displacing legitimate MAC entries, forcing data into broadcast mode |
| Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) poisoning/spoofing | Forged ARP messages to redirect traffic from the victim |
| DoS | Denial-of-service |
| DDoS | Distributed denial-of-service |
| DNS poisoning | Exploit known DNS vulnerabilities |
| DNS spoofing | Forged DNS data to redirect traffic to hacker |
| Evil twin | Fake Wi-Fi access point to trick people into choosing it over the genuine one |
| On-path attack/Man-in-the-middle (MITM) attack | Intercept a two-party conversation for one’s advantage Tools: • Ettercap • Wireshark • tcpdump |
| Phishing | Attack by email; single target |
| Dumpster diving | Recover information from trash |
| Shoulder surfing | Look over someone’s shoulder, often with a recording device |
| Tailgating | Unauthorized entity follows authorized party into secured premises |
| Device hardening | Reducing the attack surface to secure a device |
| 802.1X | For port-based network access control (PNAC) |
| MAC filtering | Control network access by device MAC |
| NAC | Network access control |
| ACL | Access control list |
| Uniform Resource Locator (URL) filtering | Allow/block website access by URL |
| Screened subnet (demilitarized zone, DMZ) | Five components: • External network • External router • Perimeter network • Internal router • Internal network |
Network Troubleshooting
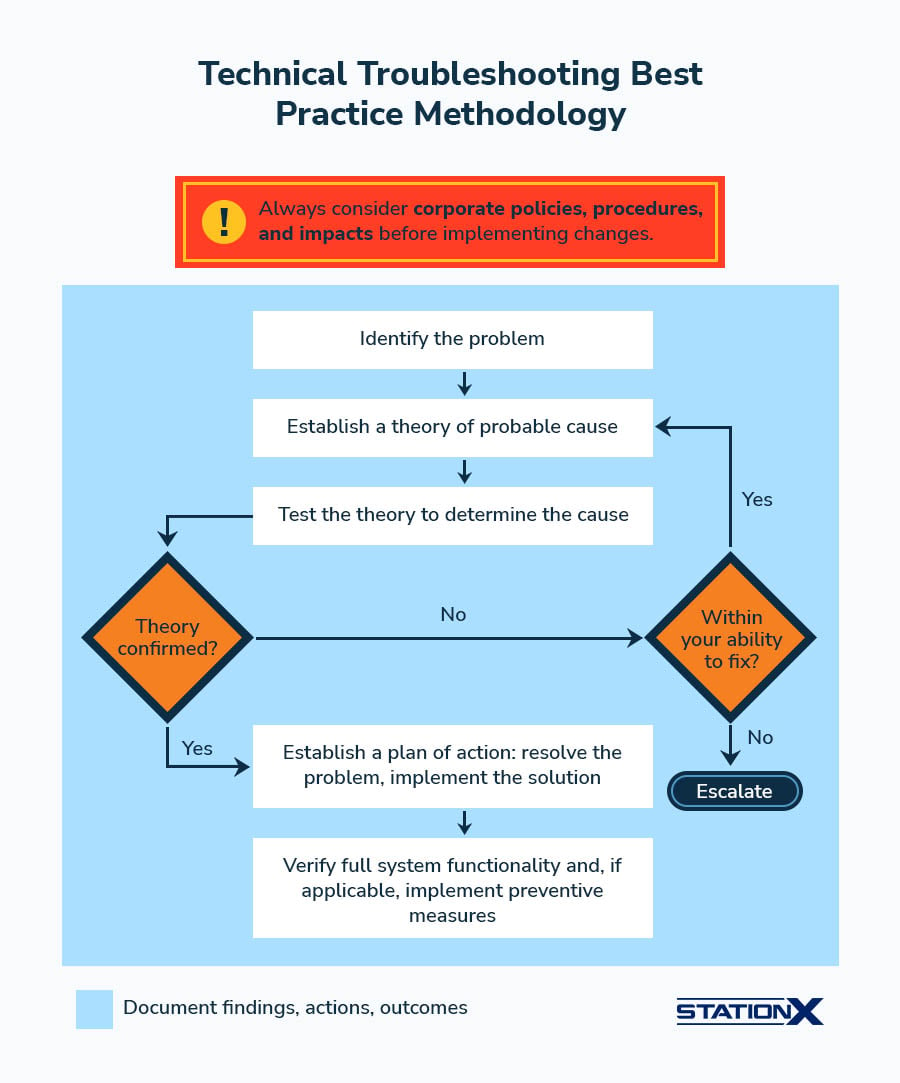
Apply the six technical troubleshooting steps (same as A+) to networking problems. Familiarize yourself with common networking issues.
| Concept | Elaboration |
| On the “establish theory” step in technical troubleshooting | - Top-to-bottom/bottom-to-top - OSI model - Divide and conquer |
| On establishing a plan of action | Identify the potential effects of the resolution |
| On documentation | Document also the lessons learned throughout the troubleshooting process |
| LLDP | Link Layer Discovery Protocol |
| CDP | Cisco Discovery Protocol |
| Troubleshooting tools/protocols | Software tools: • Protocol analyzer • Command line • Speed tester • ping• traceroute/tracert• nslookup• tcpdump• dig• netstat• ip/ifconfig/ipconfig• arp• nmapHardware tools: • Toner • Cable tester • Taps • Wi-Fi analyzer • Visual fault locator Basic networking device commands • show mac-address-table• show route• show interface• show config• show arp• show vlan• show power |
CompTIA Network+ Cheat Sheet Conclusion
We hope this Network+ cheat sheet helps your learning or career journey. Check out our other articles on networking and learn how to pass Network+ on your first attempt.
To maximize your knowledge and exam preparation, take a look at our complete CompTIA Network+ Training Bundle (N10-009). For a one-time purchase, get access to 19 hours of video training, three full practice exams, over 300 flashcards, and more. Click the banner below. Or join the StationX Master’s Program for access to over 30,000 courses and labs, covering everything you need for a career in IT, Network Administration, or Cyber Security.
You can also purchase your exam voucher through StationX at a discounted price. We offer savings of up to 30% on CompTIA exam vouchers. See our voucher page for more details.
We wish you all the best on your exam!
This bundle contains:
- CompTIA Network+ Objectives: Total N10-009 Course
- CompTIA Network+ N10-009 Practice Test
- CompTIA Network+ Course: Practice Exam Flashcards