You’ve made a great choice pursuing the CompTIA Security+ certification if you aspire to work in cyber security. It makes you a catch to employers, but the huge amount of study materials can make this a challenging exam. Good news: we’ve got you covered.
This SY0-701 CompTIA Security+ Cheat Sheet provides a high-level overview of key Security+ concepts and abbreviations to support your exam prep. Since Security+ shares significant overlap with Network+, CCNA, and other networking-focused certifications, networking topics are intentionally excluded and should be reviewed separately.
Fortunately, we also have a Network+ Cheat Sheet available, which you can add to your studies.
Download this CompTIA Security+ Cheat Sheet here. When you’re ready, let’s dive in.
What Is the CompTIA Security+ Certification?
The CompTIA Security+ certification focuses on the day-to-day, real-time application of IT security knowledge in the workplace. More than 700,000 IT professionals hold Security+ certification largely because the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) has approved it as meeting Directive 8140.03-M requirements, and it complies with ISO 17024 standards.
Mastery in the five Security+ domains shows employers that you can perform essential cyber security functions, such as assessing and improving enterprise security posture, monitoring and securing hybrid environments (cloud, mobile, IoT), and handling security incidents while adhering to principles of governance, risk, and compliance.
You’ll need to answer at most 90 questions, either multiple-choice or performance-based, in this 90-minute examination and complete a survey after it ends. The passing score is 750 on a scale of 100–900. The exam costs $425 USD (see all pricing).
The latest CompTIA Security+ exam code is SY0-701. The associated exam has been available since November 2023 and will retire in 2026–2027.
Security+ Domains (SY0-701)
As the landscape of cyber security evolves, so do the primary focus areas (Domains) of the Security+ exam. Every three years, CompTIA updates the Security+ exam to reflect the highest priorities in cyber security.
The latest breakdown of Security+ Domains is as follows:

| Security+ SY0-701 Domain | Exam Weighting (%) |
| General Security Concepts | 12% |
| Threats, Vulnerabilities, and Mitigations | 22% |
| Security Architecture | 18% |
| Security Operations | 28% |
| Security Program Management and Oversight | 20% |
Without further ado, let’s explore each Domain and unpack the essential concepts you will encounter in the exam.
General Security Concepts
This Domain covers essential security concepts, security considerations in change management processes, and cryptography fundamentals.
| Concept | Description |
| Security controls (Learn to classify them based on given scenarios) | Categories: • Technical • Managerial • Operational • Physical Control types: • Preventive • Deterrent • Detective • Corrective • Compensating • Directive |
| CIA | Confidentiality, Integrity, and Availability |
| Non-repudiation | Impossible to deny your involvement |
| AAA | Authentication, Authorization, and Accounting |
| Gap analysis | Identify weaknesses in one’s current security posture and a clear path toward the desired security posture |
| Zero-Trust | Never trust, always verify |
| Physical security | Tangible security measures around buildings and facilities to control access |
| Deception and disruption technology | To catch and understand threat actors. • Honeypot • Honeynet • Honeyfile • Honeytoken |
| Change management | Planning, implementing, and solidifying changes in an organization |
| Ownership | Parties responsible for organizational changes |
| Stakeholders | Parties affected by organizational changes |
| Impact analysis | Analysis of changes within a project and their potential consequences |
| Test results | Outcomes of manual/automated tests used to validate changes |
| Backout plan | Procedures to restore systems to the previous baseline prior to the latest modifications |
| Maintenance window | Predefined, scheduled period for planned changes, updates, or maintenance, minimizing disruption to users |
| Standard operating procedure (SOP) | Clear steps for implementing changes with well-defined roles and responsibilities, and strategies for communication geared toward stakeholders |
| Allow lists/deny lists | List-based access control mechanisms permitting/forbidding access to systems |
| Downtime | Time when a system is unavailable |
| Legacy application | Outdated software still in use, often with known vulnerabilities |
| Dependency | Code packages required by a project to run properly |
| Version control | The practice of tracking and managing changes to files, often collaboratively |
| PKI | Public key infrastructure |
| Encryption levels | • Full-disk • Partition • File • Volume • Database |
| Symmetric cipher | Streaming: • RC4 Block: • DES • Blowfish • 3DES Considerations: • key length • block size • number of rounds |
| Asymmetric cipher | Examples: • Diffie-Hellman key exchange • RSA • Elliptic-curve cryptography |
| TPM | Trusted Platform Module |
| HSM | Hardware security module |
| Key management system | System for managing cryptographic keys and their metadata |
| Secure enclave | Isolated hardware system for protecting sensitive data and operations |
| Steganography | Hide data inside other data |
| Tokenization | Substituting sensitive data elements with non-sensitive equivalents (tokens) with no intrinsic or exploitable meaning or value |
| Data masking | Replacing sensitive data with fake, usable data for added security |
| Hashing | One-way, deterministic process of transforming a string of characters into another |
| Salting | Characters appended to a string (e.g., password) before hashing |
| Digital signature | Public key sender verified to own corresponding private key |
| Key stretching | Method that strengthens weak passwords |
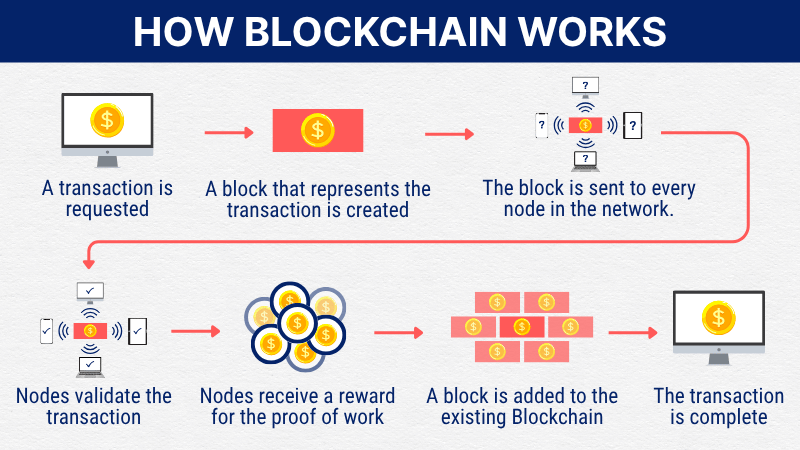
| Blockchain | Decentralized digital ledger of records linked sequentially by cryptographic hashes |
| Open public ledger | Freely accessible and verifiable system of transactional data |
| Certificate authority | Issuer of digital certificates to ensure the legitimacy of web hosts |
| CRL | Certificate revocation list |
| OCSP | Online Certificate Status Protocol |
| Self-signed certificate | Same issuer and subject |
| Third-party certificate | The issuer has no direct affiliation with your hosting or server environment |
| Root of trust | Secure, trusted source within a cryptographic system such as HSM |
| CSR | Certificate signing request |
| Wildcard certificate | Secure a domain and all its first-level subdomains using an asterisk (*) |
| CAPTCHA | Completely Automated Public Turing Test to Tell Computers and Humans Apart |
The next Domain has everything to do with offensive and defensive hacking.
Threats, Vulnerabilities, and Mitigations
All you must know about threat actors, threat vectors, vulnerabilities, indicators of malicious activity, and threat mitigation techniques are in this Domain.
| Concept | Description |
| Threat actor | Vulnerability exploiter.Attributes: • Internal/external • Resources/funding • Level of sophistication/capability Motivations: • Data exfiltration • Espionage • Service disruption • Blackmail • Financial gain • Philosophical/political beliefs • Ethical • Revenge • Disruption/chaos • War |
| Nation-state threat actor/state actor | Foreign government agent |
| Unskilled attacker/script kiddie | Executor of pre-made programs |
| Hacktivist | Politically motivated agent |
| Insider threat | Saboteur inside an organization |
| Organized crime | Profit-driven agent with intent to blackmail |
| Shadow IT | IT systems deployed without the central IT department’s oversight |
| Malware attacks | • Virus • Worm • Trojan • Rootkit • Keylogger • Spyware • Bloatware • Ransomware • Logic bomb |
| MSP | Managed service provider |
| Social engineering | Principles (reasons for effectiveness): • Authority • Intimidation • Consensus • Scarcity • Familiarity • Trust • Urgency |
| Phishing attack | By email; single target |
| Vishing attack | By telephone or voicemail |
| Smishing attack | By SMS text message |
| Misinformation/disinformation | Exploitation of human vulnerabilities |
| Impersonation, identity fraud/theft | Attacks using stolen credentials or personal information |
| Business email compromise | Impersonate trusted leaders to trick employees into sending money or data or granting privileged access |
| Pretexting | Digital gunpoint with the ransom being one’s private information |
| Watering hole | Infect a trusted website |
| Brand impersonation | Pose as a trusted brand to dupe victims and steal their data |
| Typosquatting | Attacks using mistyped web addresses |
| TOC | Time-of-check |
| TOU | Time-of-use |
| SQLi | Structured Query Language injection |
| XSS | Cross-site scripting |
| Memory injection | Injecting malicious code into memory to execute unauthorized commands |
| Buffer overflow | Amount of data in the buffer exceeds its storage capacity |
| Malicious update | Harmful code disguised as a legitimate software update |
| Side loading | Installing mobile apps from sources outside official app stores |
| Jailbreak | Bypassing inbuilt security restrictions in mobile devices to install unauthorized software |
| Agentless | Without requiring the installation of dedicated software agents |
| End-of-life | No longer supported by the vendor |
| Virtual machine (VM) escape | Malicious code running inside a VM gains unauthorized access to the host operating system or other VMs on the same physical server, thus potentially controlling all |
| Race condition | A vulnerability in which multiple process threads “race” against each other to access/change the data simultaneously, leading to unpredictable and potentially harmful outcomes |
| Amplified network attack | Generate such a large volume of traffic that it disrupts normal traffic to a web property; includes DDoS attack |
| Reflected network attack | Flood a victim’s system with traffic by leveraging the responses from a third-party server |
| Radio frequency identification (RFID) cloning | Tamper with access control, authentication, or sensitive data storage by the unauthorized copying or duplication of the information stored on an RFID tag |
| Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack | Cybercrime; flood a server with internet traffic preventing legitimate users from access |
| Domain Name System (DNS) attack | Exploit vulnerabilities in DNS |
| Wireless attack | Compromise the security of a wireless network such as by exploiting vulnerabilities |
| On-path attack | Eavesdrop; secretly intercept or modify communication between two parties who believe they are communicating directly |
| Replay attack | Intercept data and replay later for gaining unauthorized access or triggering unintended actions |
| Credential replay attack | Intercept and reuse stolen authentication credentials (e.g., usernames, passwords, session tokens) to gain unauthorized access |
| Privilege escalation | Gain unauthorized access to higher-level permissions |
| Forgery attack | Deceive the recipient about the identity of the sender |
| Directory traversal | Access files and directories stored outside the web root folder |
| Downgrade attack | Force a system to use a weaker protocol or encryption method |
| Collision attack | Find two different inputs that produce the same hash value when passed through a cryptographic hash function |
| Birthday attack | Exploits birthday paradox (>50% probability of two people sharing the same birthday in a group of 23 people) to find collisions in hash functions |
| Brute-force attack | Trying character combinations |
| Spraying attack | Trying the same password across different accounts |
| Configuration enforcement | Ensuring hardware/software adherence to predefined security settings and policies |
| Application allow list | Block any application not on the list from running |
| ACL | Access control list |
| Patching | Applying updates or fixes to address bugs and vulnerabilities |
| Least privilege | Only grant the minimum necessary rights to perform designated tasks |
| Decommissioning | Retiring assets from operation, including data sanitization |
| Hardening | Tools and techniques to reduce vulnerabilities in systems, applications, etc. |
| Host-based firewall | Network traffic filter on a single computer/server |
| HIPS | Host-based Intrusion Prevention System |
| HIDS | Host-based Intrusion Detection System |

What makes a system vulnerable? The next Domain offers an in-depth look.
Security Architecture
On a macro level, aspiring cyber security professionals must learn about network architecture models, enterprise infrastructure, data protection, and measures for resilience and recovery.
| Concept | Description |
| IPS | Intrusion prevention system |
| IDS | intrusion detection system |
| EAP | Extensible Authentication Protocol |
| WAF | Web application firewall |
| UTM | Unified threat management |
| NGFW | Next-generation firewall |
| IaC | Infrastructure as code |
| Air-gapped | Hardware isolation of computer/network from external connections to protect it from malicious activity |
| Logical segmentation | Division of computer system into isolated segments using software |
| RTBH | Remotely Triggered Black Hole |
| SDN | Software-defined networking |
| ICS | Industrial control systems |
| SCADA | Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition |
| Containerization | Packaging applications and their dependencies together into a single unit (container) |
| Virtualization | Creation of virtual environments from a single physical machine for efficient use of computing resources |
| RTOS | Real-time operating system |
| Fail-open | A system defaults to an operational state, allowing continued functionality in the event of failure |
| Fail-closed | A system defaults to shutdown and prevention of further operations in the event of failure |
| Serverless | Users can write and deploy code without worrying about the underlying infrastructure |
| Microservices | Infrastructure where small, independent, and loosely coupled services make up an application |
| Active device | Actively participate in network traffic flow |
| Passive device | Only observe network traffic |
| Inline device | Sit in the data path, able to block or modify malicious traffic |
| Tap/monitor device | Passively monitor the traffic but won’t take action upon finding anything malicious |
| Jump server | Funnel traffic through firewalls using a supervised secure channel |
| Proxy server | Gateway between end users and the web pages they visit only; able to prevent cyber attackers from entering a private network |
| IEEE 802.1X | Standard for port-based network access control |
| Responsibility matrix | Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, Informed |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| Embedded systems | Small computers integrated into larger systems to execute specific tasks such as graphics, data processing, and sensing |
| Remote access | Connecting to networks and systems from remote locations |
| Tunneling | Data transfer by wrapping a data packet in another |
| VPN | Virtual private network |
| TLS | Transport Layer Security |
| IPSec | Internet protocol security |
| SD-WAN | Software-defined wide area network |
| SASE | Secure access service edge |
| Data at rest | On computer storage |
| Data in use/processing | In RAM being accessed |
| Data in transit/motion | Traveling along cables or broadcasting wirelessly |
| Data sovereignty | A country or jurisdiction has the authority and right to govern and control the data generated within its borders |
| Geolocation | Identify the geographical location of a device or user |
| High availability | A system’s ability to operate continuously for a designated uptime despite individual component failure |
| Load balancing | Distribute workloads or network traffic across multiple servers to prevent overloading and improve application performance and availability |
| Clustering | Combination of servers to function as a single unit for redundancy and increased processing power |
| Snapshots | Point-in-time backups of data or systems to aid recovery |
| Cold site | Power, networking capability, and cooling; no servers or storage |
| Warm site | Cold site plus storage hardware; still requires data transportation |
| Hot site | Fully functional backup site with important data mirrored to it |
| COOP | Continuity of operations |
| UPS | Uninterruptiblepower supply |


We go further into individual components of a system in the next Domain.
Security Operations
On a micro level, aspiring cyber security professionals should also know how to protect and monitor computing resources and data assets, incident response, as well as identity and access management.
| Concept | Description |
| MDM | Mobile device management |
| BYOD | Bring your own device |
| COPE | Corporate-owned, personally enabled |
| CYOD | Choose your own device |
| WPA3 | Wi-Fi Protected Access 3 |
| RADIUS | Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service |
| Application security | Measures to protect software from threats and vulnerabilities during SDLC |
| Input validation | Ensuring data conforms to predefined standards |
| Secure cookies | Transmittable over HTTPS but not HTTP |
| Static code analysis | Examining source code without execution to identify errors, vulnerabilities, and deviations from coding standards |
| Code signing | Digital verification of software authenticity and integrity |
| Sandboxing | Isolation of programs/processes in a virtual environment to limit potential damage |
Finally, we conclude with globally recognized best practices in managing cyber security programs.
Security Program Management and Oversight
This Domain is responsible for cyber security concepts and acronyms related to governance, risk, and compliance.
| Concept | Description |
| SLA | Service-Level Agreement |
| MOA | Memorandum of Agreement |
| MOU | Memorandum of Understanding |
| MSA | Master Service Agreement |
| WO | Work Order |
| SOW | Statement of Work |
| NDA | Non-disclosure Agreement |
| BPA | Business Partners Agreement |
| BCP | Business Continuity Plan |
| COOP | Continuity of operations |
| DRP | Disaster Recovery Plan |
| IRP | Incident Response Plan |
| IoC | Indicators of Compromise |
| AUP | Acceptable Use Policy |
| SDLC | Software Development Lifecycle |
| GDPR | General Data Protection Regulation |
| PCI DSS | Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| CSA | Cloud Security Alliance |
| AV | Asset Value |
| EF | Exposure Factor |
| SLE | Single Loss Expectancy = AV × EF |
| ARO | Annualized Rate of Occurrence |
| ALE | Annualized Loss Expectancy = SLE × ARO |
| BIA | Business impact analysis |
| MTBF | Mean time between failures |
| MTTF | Mean time to failure |
| MTTR | Mean time to repair |
| RTO | Recovery time objective |
| RPO | Recovery point objective |
| Residual risk | Remaining risk after mitigation |
CompTIA Security+ Cheat Sheet Conclusion
This CompTIA Security+ Cheat Sheet is a checklist covering the examination syllabus, excluding networking topics, and we hope it gives you a bird’s-eye view of non-networking key topics in cyber security.
Want to maximize your chances of success? We offer a CompTIA Security+ Course & SY0-701 Practice Test Bundle available as a one-time purchase. This grants lifetime access to over 20 hours of video training, three full-length practice exams, flashcards, and more.
You can also look at our StationX Master’s Program for complete career guidance, mentorship, a personalized certification roadmap, access to over 30,000 courses and labs, and much more.
Don't forget you can purchase an official CompTIA Security+ exam voucher through StationX at a tremendous discount!
However you choose to proceed in your cyber security career, we wish you the best of luck!
This bundle contains:
- CompTIA Security+ Study Guide: SY0-701 Total Course
- CompTIA Security+ Practice Test Series: Ace the SY0-701
- CompTIA Security+ Exam Objectives Flash Cards: SY0-701 Prep



























