To be a penetration tester, you must master your tools. This curated guide details the top 20 network penetration testing tools you need to learn to elevate your skills and become a legendary hacker.
The tools have been split into eight key categories, essential for a network penetration test:
- Network Scanning
- Post Exploitation Frameworks
- Pivoting and Lateral Movement
- Active Directory Assessment
- Spoofing and Eavesdropping
- Credential Harvesting
- Credential Dumping and Looting
- Password Cracking
This guide will walk you through a range of powerful tools to help you conquer every stage of a network penetration test. You’ll be able to evaluate computer systems, perform security testing, and deliver thorough network security assessments that give your client a clear picture of their overall security posture.
Before jumping in and using the tools in this guide, let’s first look at what network penetration testing is and why you need these tools to perform a complete assessment.

What Is Network Penetration Testing?
Network penetration testing (a.k.a an internal pentest) is a security assessment of an organization’s internal infrastructure and defenses. A network pentest will begin with an assumed breach, where the pentester is provided initial access to the internal network and is tasked with assessing the security of this environment. This allows a penteser to spend more time testing an organization’s internal defenses and security controls rather than trying to gain initial access.
To perform a thorough network penetration test, you must perform network scanning, Active Directory enumeration, and lateral movement to compromise high-value systems and access valuable information. This requires specialized pentesting tools, which have been handpicked for you to learn in this guide.
Most of these tools come with Kali Linux, so you can get started using them immediately. You can learn to install Kali Linux on VMware and VirtualBox in these guides:
- How to Install Kali Linux on VMware: The Ultimate How-to Guide
- How to Install Kali Linux on VirtualBox & Start Hacking Now
Let’s jump in and start mastering our tools!
Network Scanning Tools
One of the first phases of a network penetration test is Scanning and Enumeration. During this phase, you will scan a target for potential vulnerabilities you can exploit. To help you do this, here are several popular scanning tools.
1. Nessus

Nessus is a widely used commercial vulnerability scanner that organizations use to identify and remediate security vulnerabilities and misconfigurations in their environment. It is a comprehensive solution that can be extended through plugins, offers compliance and credentials-based scanning, and integrates with SIEM solutions for enterprise environments.
Why we like Nessus:
- The plugin architecture can be used for system, application, and network scanning.
- Great for compliance monitoring.
- Can audit the configuration of your software and provide best practice advice.
- Automatically generates custom reports.
Needs to be installed from Tenable’s Products page. The Expert version starts at ~$6,900 yearly, and the Professional version at ~$4,683 yearly. However, both come with a free 7-day trial, or you can use Nesssus Essentials for free.
2. Nmap

Nmap (Network Mapper) is a powerful open-source network scanning tool that can be used for network discovery, port mapping, and vulnerability assessments using its extensible scripting engine. It is the defacto tool for enumerating any network, and you can learn more about it in How to Use Nmap to Scan a Network: A Step-by-Step Guide or using this cheatsheet.
Why we like Nmap:
- Great for network host discovery on internal networks.
- Lightweight and versatile.
- Capable of performing quick vulnerability scans and service enumeration.
Included with Kali Linux.
Learn more about how Nessus, OpenVAS, and Nmap compare in The Best Vulnerability Scanners for Kali Linux.
Post Exploitation Frameworks
Post-exploitation frameworks let you easily maintain access and control over compromised targets during a network pentest. Here are some of the ones you will likely encounter during your pentesting career.
3. Cobalt Strike

Cobalt Strike is the gold standard post-exploitation and command-and-control (C2) framework for adversary emulation and red team operations. It is packed with features that allow you to emulate real-world threat actors' tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) and is made extensible through its Resource and Community kits.
Why we like Cobalt Strike:
- Build to emulate real-world threats.
- Integrates with other security tools, such as Metasploit.
- Generates customizable reports to document your findings.
Needs to be installed. Cobalt Strike costs $3,540* per user for a one-year license and can be downloaded with a purchased license key.
4. Metasploit
Metasploit is a popular open-source penetration testing and exploitation framework with an extensible module framework that provides post-exploitation capabilities. Pentesters and red teamers use it to identify vulnerabilities, exploit them, and maintain access to compromised systems.
Metasploit is a tool all pentesters should know how to use, and you can learn more about it in How to Use Metasploit in Kali Linux: A Step-By-Step Tutorial or by using this Metasploit module cheatsheet.
Why we like Metasploit:
- Has a vast collection of pre-built exploits, payloads, and auxiliary modules that make identifying and exploiting vulnerabilities easy.
- Includes the Meterpreter shell, which excels at post-exploitation activities, such as privilege escalation, file manipulation, data exfiltration, and lateral movement.
- Lets you automate exploitation with its modular framework.
- Offers reporting capabilities that let you document your findings.
Included with Kali Linux.
Red Team Hacker Bundle: Learn Hacking Online Red Team Style
Train like a professional adversary with the Red Team Hacker Bundle. Learn offensive security tactics, privilege escalation, and post-exploitation techniques used by real red teams.
5. Sliver
Sliver is an open-source, cross-platform command-and-control (C2) framework used for adversary emulation, red teaming, and advanced penetration testing. Developed by Bishop Fox, Sliver provides operators with secure communications, implant generation, session management, and post-exploitation tooling. It supports Windows, Linux, macOS, and containerized environments, making it a flexible alternative to proprietary C2 tools.
Why we like Sliver:
- Modern, actively maintained C2 framework suitable for professional red-team operations.
- Cross-platform implants with support for Windows, Linux, macOS, and ARM.
- Encrypted communication with multiple transport options (mTLS, WireGuard, HTTP(S), DNS, etc).
- Powerful post-exploitation modules, including process injection, port forwarding, file operations, and lateral movement.
- Team-based operations with multi-user support and robust operator controls.
Can be installed through the official Kali Linux repository using the command sudo apt install sliver or from its GitHub page.
Pivoting and Lateral Movement
To conduct a thorough network penetration test, you must perform pivoting and lateral movement to compromise high-value targets scattered throughout the internal network. Here are some tools for doing just that.
6. Evil-WinRM

Evil-WinRM is an open-source tool used to perform lateral movement. It takes in credentials you have gathered and uses the WinRM (Windows Remote Management) protocol to let you jump between hosts on an internal network or execute commands/scripts remotely.
You can learn how to use Evil-WinRM to perform lateral movement in Pass the Hash Attacks: How to Make Network Compromise Easy.
Why we like Evil-WinRM:
- Provides remote shell access on compromised Windows machines through the WinRM protocol.
- Blends in with legitimate internal network communication with encrypted WinRM traffic.
- Lets you remotely execute commands/scripts and upload/download files.
Needs to be installed. You can install Evil-WinRM through its Kali package or via its GitHub page.
7. Ligolo-ng
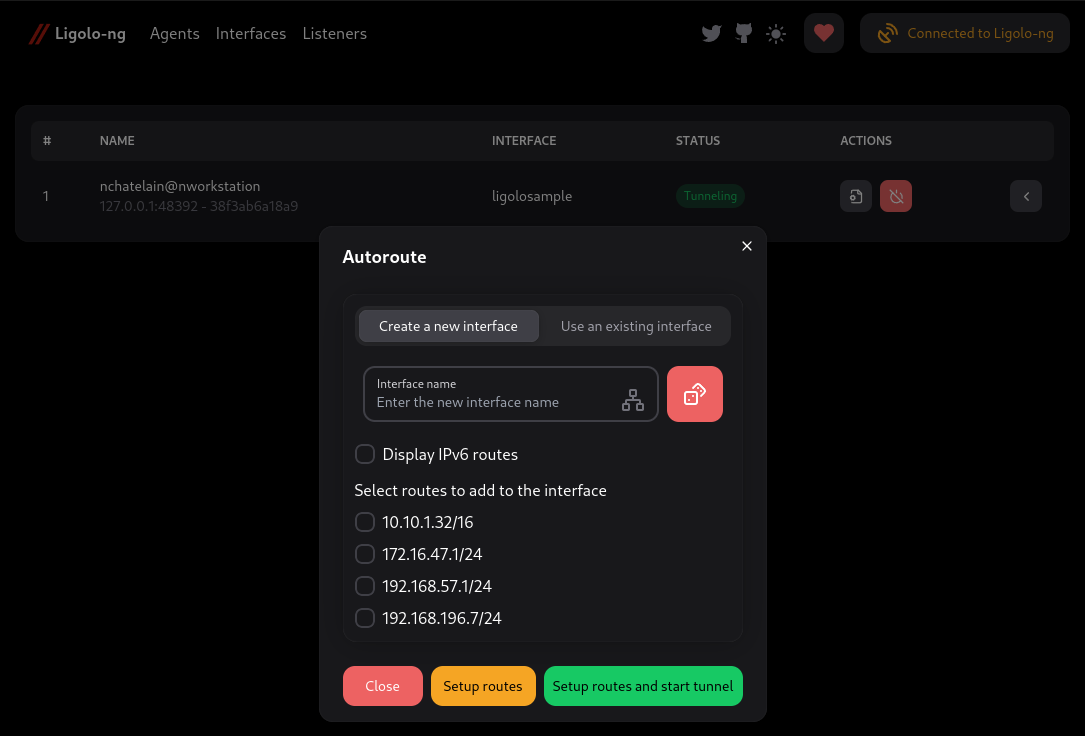
Ligolo-ng is a lightweight, high-performance tunneling/pivoting tool that lets penetration testers create secure network tunnels via a reverse TCP/TLS connection over a TUN interface, without relying on traditional SOCKS proxies. You can learn how to transfer files and catch reverse shells in our How to Use Ligolo-ng (Easy to Follow Pivoting Tutorial) guide.
Why we like Ligolo-ng:
- Fast, reliable tunneling with support for multiplexing and multiple simultaneous tunnels.
- Cross‑platform agents (Windows, Linux, macOS, BSD) with no special privileges required on the agent side.
- Enables reverse/bind tunnels, port forwarding, and full network pivoting, ideal for segmented or restricted internal environments.
Ligolo‑ng is not included in Kali Linux by default. You can install it by downloading the prebuilt binaries from its GitHub releases page or by building it from source using Go.
Active Directory Assessment
Around 90% of Fortune 1000 companies use Windows Active Directory to manage their IT infrastructure. To be an effective network penetration tester, you must know how to attack Active Directory and assess potential vulnerabilities. Here are some of the tools you can use.
8. PowerView

PowerView is an open-source PowerShell tool that you can use to gain situational awareness in a Windows environment. It can enumerate Active Directory domains, users, networks, forests, shares, and system information, as well as provide lateral movement and privilege escalation capabilities. PowerView is often used to help perform Kerberoasting. You can learn more in How to Perform Kerberoasting Attacks: The Ultimate Guide.
Why we like PowerView:
- Great for Active Directory enumeration
- Useful for identifying vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and potential attack paths in Active Directory environments.
- Lightweight and versatile.
Needs to be installed. You can download the PowerView PowerShell script from its GitHub page.
9. Bloodhound
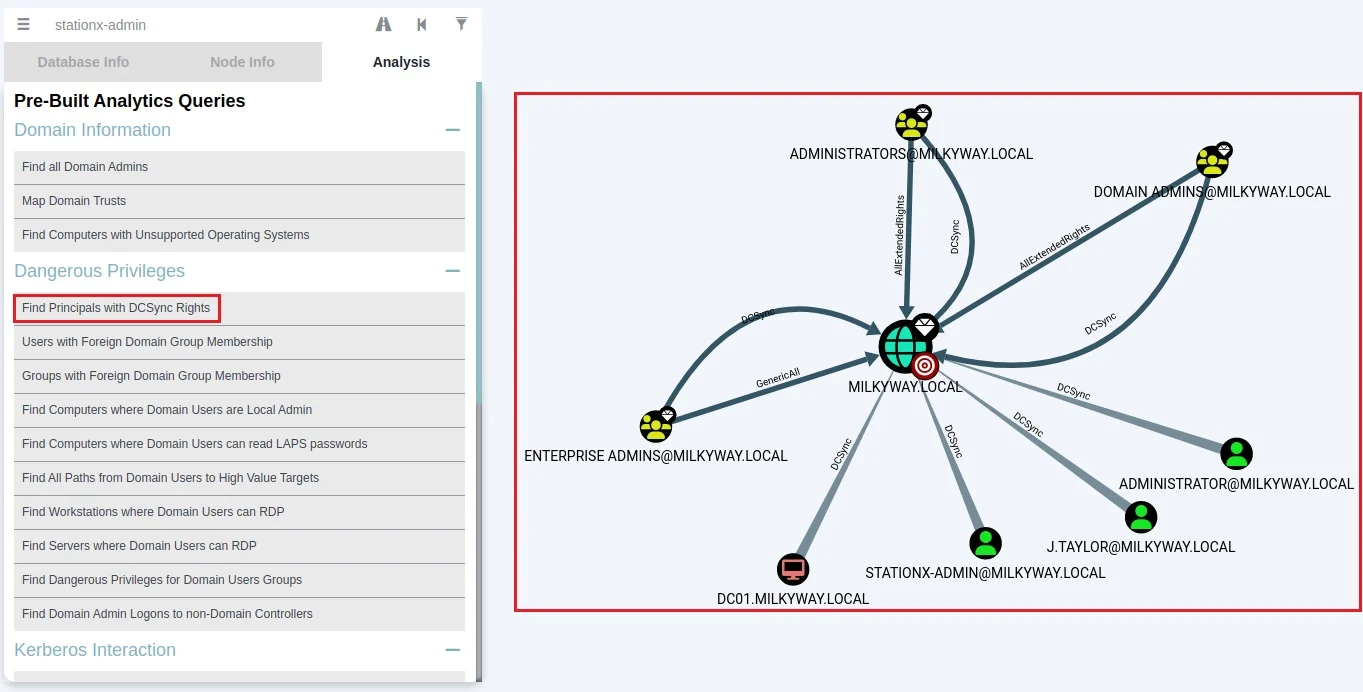
Bloodhound is a powerful post-exploitation tool that uses graph theory to map hidden or unintentional relationships within an Active Directory environment. You can exploit these relationships to gain access to sensitive information and systems.
Learn more about Bloodhound in How to Use BloodHound to Hack Active Directory: A Full Guide.
Why we like Bloodhound:
- Provides a visualization of an environment’s Active Directory attack surface.
- Supports a custom query language for identifying security issues and opportunities for exploitation.
- Helps identify opportunities for lateral movement and credential abuse.
Needs to be installed. You can install Bloodhound through its Kali package or via its GitHub page.
10. NetExec
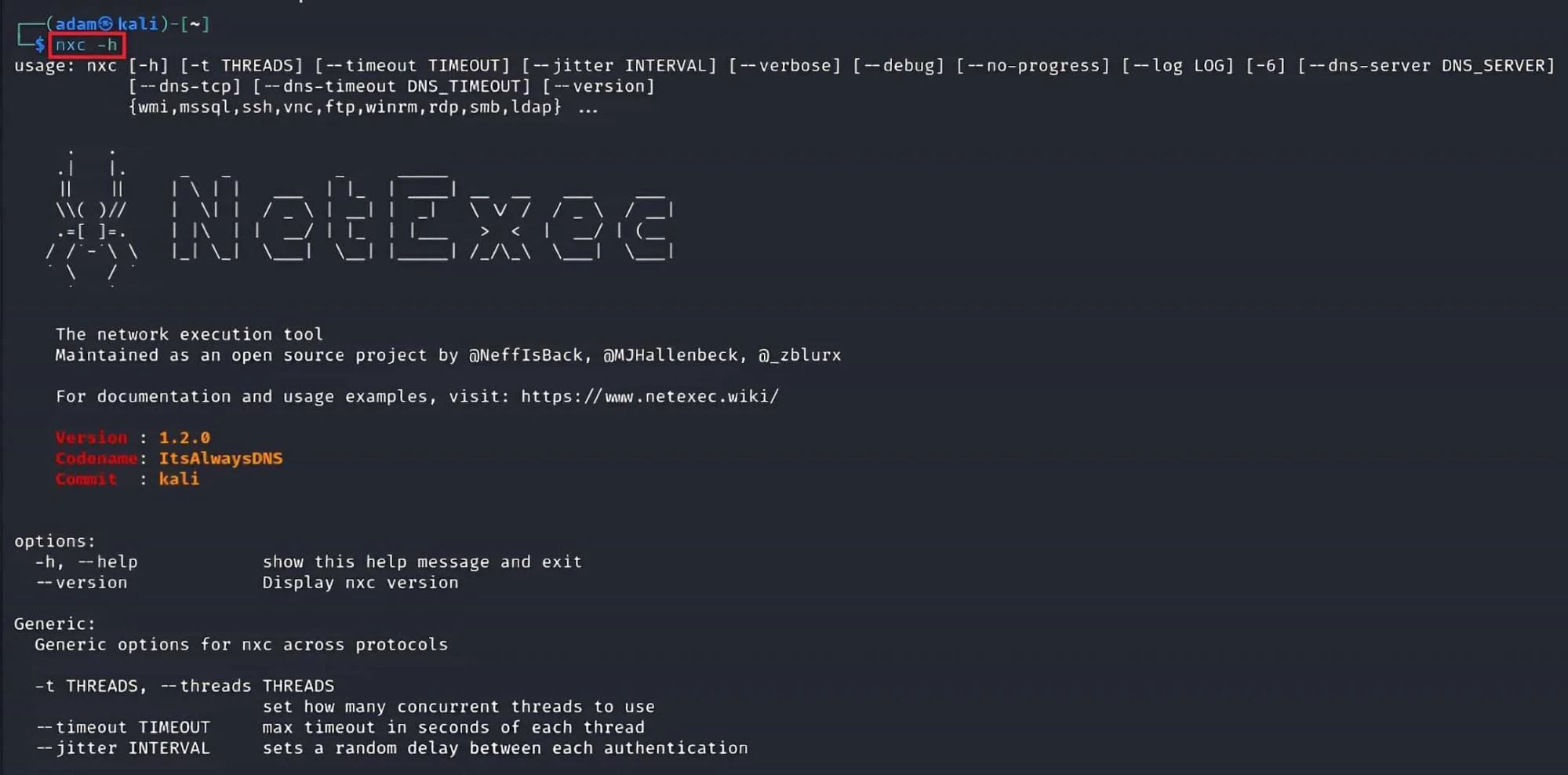
NetExec is a powerful, open‑source post‑exploitation and network enumeration tool designed for security professionals working in Windows, Linux, and Active Directory environments. It streamlines credential validation, command execution, file transfers, and lateral movement across large enterprise networks.
As the successor to CrackMapExec, NetExec offers improved stability, modularity, and compatibility with modern security architectures, making it a go‑to tool for internal penetration tests and red‑team engagements. You can learn more about it in this cheat sheet.
Why we like NetExec:
- Excellent for large‑scale Active Directory enumeration.
- Supports SMB, WinRM, SSH, MSSQL, and other protocols for broad network coverage.
- Ideal for testing credentials, automating common attack paths, and validating lateral movement.
- Modular and extensible, with a plugin‑based architecture.
NetExec is included in Kali Linux by default.
Spoofing and Eavesdropping
After gaining access to a target’s internal network, you must look for opportunities to extend your access to higher-value targets by performing lateral movement. A good way to do this is through intercepting, spoofing, and poisoning traffic traveling over the local network. Here are some tools that will help you.
11. Responder

Responder is a popular open-source spoofing and credential harvesting tool for man-in-the-middle attacks. It impersonates legitimate Windows services and poisons the LLMNR, NBT-NS, and MDNS protocols. When a Windows machine communicates with Responder, the tool spoofs the network traffic and hijacks login credentials. It uses these credentials to perform credential relaying and pass the hash attacks.
Why we like Responder:
- It is difficult to defend against if a Windows network uses the LLMNR and NBT-NS network protocols.
- Can automate pass the hash and credential relaying attacks when used with other tools, such as MitM6.
- It can capture traffic that uses common network protocols, such as DNS, HTTP, and SMB.
Included with Kali Linux.
12. bettercap

bettercap is a powerful open-source networking security framework used to perform reconnaissance and attacks on internal networks. It is written in Go and used for various network-based attacks, including sniffing traffic, spoofing network protocols, harvesting credentials, hijacking cookies, etc.
Why we like bettercap:
- Has an easy-to-use GUI version and a CLI version.
- Can scan IP network hosts passively to evade detections.
- Can perform SSL/TLS stripping to intercept unencrypted data transmitted over encrypted connections, such as HTTPS.
Included with Kali Linux.
Credential Harvesting
Once you gain initial access to a system, you need to extract password hashes, Kerberos tickets, and other sensitive information to move laterally around the internal network. Here are some of the most popular credential harvesting tools you can use.
13. Mimikatz
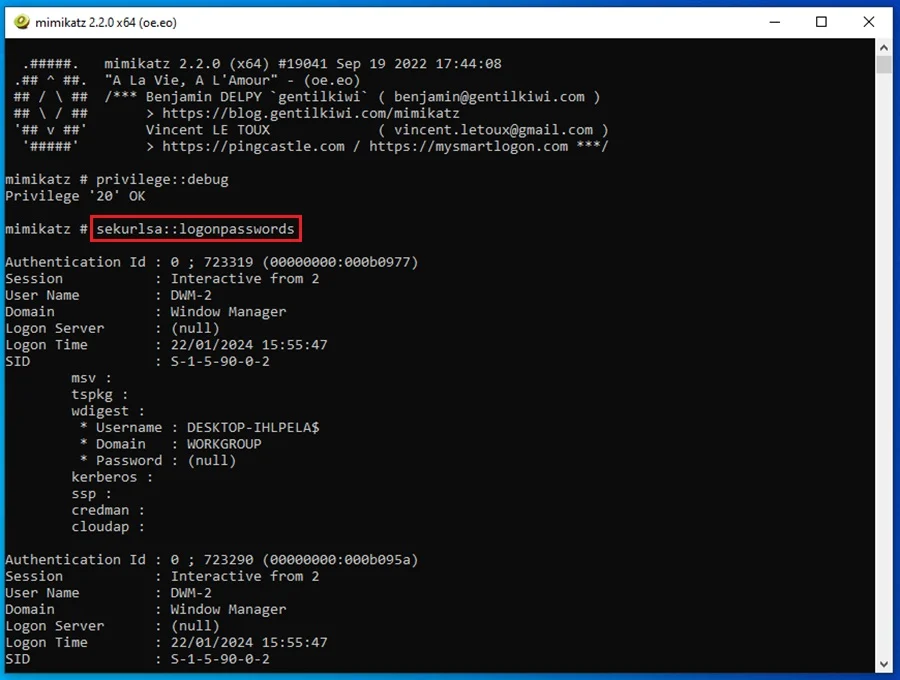
Mimikatz is a tool for exploiting weaknesses and vulnerabilities in the Windows authentication and security protocols. It can dump credentials stored in the Windows Security Account Manager (SAM) database and the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) process memory. The tool can also extract plaintext passwords and Kerberos tickets for pass the hash attacks and pass-the-ticket, respectively.
Why we like Mimikatz:
- It is the defacto tool for dumping credentials on Windows systems.
- It can be used for performing lateral movement using the credentials it extracts.
- Widely supported by various post-exploitation and C2 frameworks.
Included with Kali Linux.
14. Rubeus

Rubeus is an open-source tool in C# that abuses the raw Kerberos protocol for privilege escalation and lateral movement in Windows Active Directory environments. The tool can extract Kerberos tickets, perform pass-the-ticket attacks, create silver and golden tickets, perform Kerberoasting and AS-REP roasting, and more.
Why we like Rubeus:
- A versatile tool for abusing Kerberos and performing lateral movement.
- It can be easily modified to evade detection.
- Blends in with legitimate network traffic by interacting with the raw Kerberos protocol.
Needs to be installed. You can compile the C# files from the Rubeus GitHub or download the standalone binaries.
15. Kerbrute
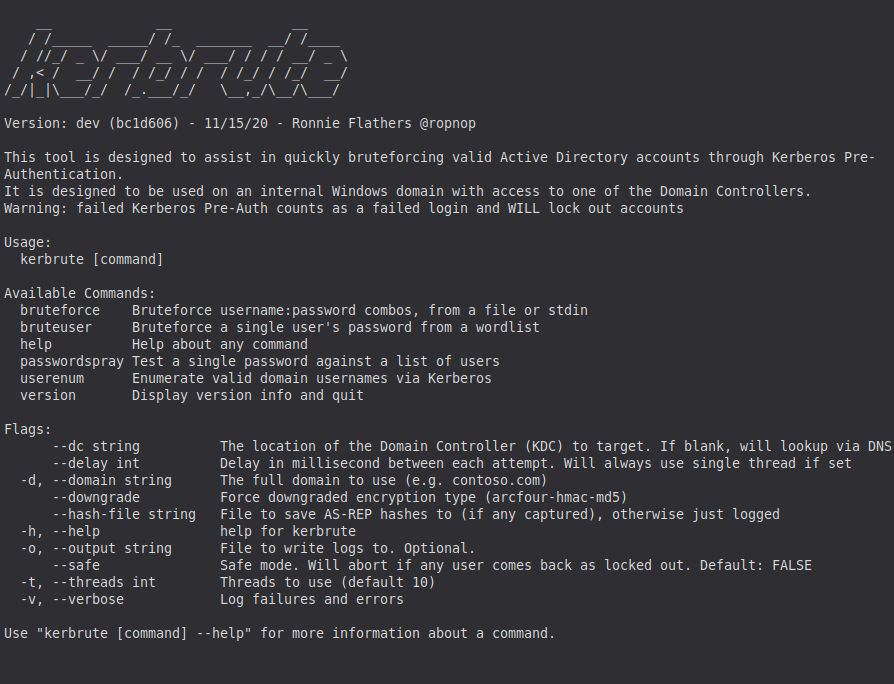
Kerbrute is a fast, flexible tool used for enumerating and brute-forcing accounts in Active Directory environments by abusing the Kerberos protocol. Instead of relying on traditional network authentication methods, Kerbrute sends Kerberos requests directly, making it extremely efficient for username discovery, password spraying, and validating credentials without noisy SMB or LDAP traffic. It’s a staple tool for red teams and internal penetration testers working with Windows domains.
Why we like Kerbrute:
- Extremely fast for enumerating valid AD usernames.
- Supports password spraying and credential validation via Kerberos.
- Less noisy than traditional brute-forcing methods, it helps avoid excessive lockouts or detection.
- Lightweight, portable, and easy to run from most OS environments.
Needs to be installed. You can download pre-built binaries from its GitHub releases page or build it from source. The tool is free and open source.
16. Certipy
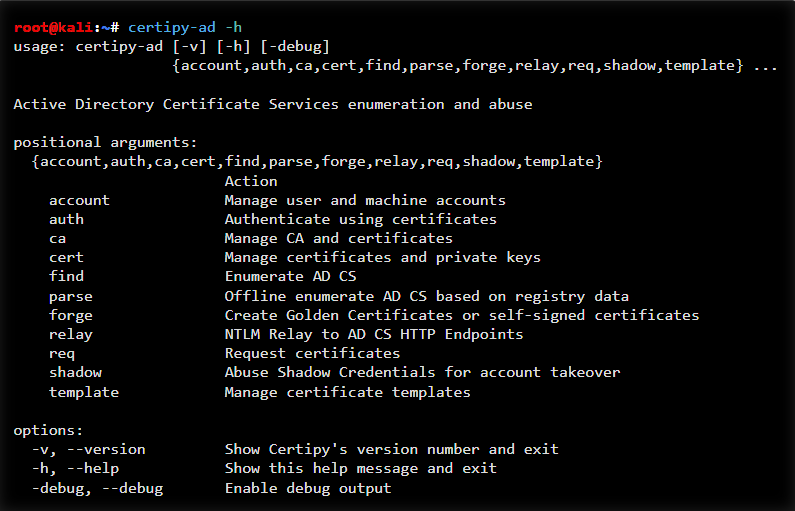
Certipy is a powerful Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS) exploitation tool used for discovering, enumerating, and abusing certificate-based privilege escalation paths. It helps penetration testers identify misconfigurations such as ESC1–ESC8, request vulnerable certificates, perform NTLM relaying to AD CS, and even obtain domain admin privileges through certificate abuse.
In modern Windows environments where AD CS is increasingly deployed, Certipy has become an essential tool in any red-team or internal assessment toolkit.
Why we like Certipy:
- Excellent at detecting AD CS misconfigurations (ESC chains).
- Automates enumeration, exploitation, and abuse of certificate templates.
- Supports certificate requests, relay attacks, and privilege-escalation workflows.
- Integrates well with other tooling, such as Impacket and Rubeus-style attacks.
- One of the most complete AD CS exploitation frameworks available.
You can install it via pip (pip install certipy-ad), build it from source, or download it directly from its GitHub repository.
Credential Dumping and Looting
Once you’re inside a network, one of the fastest ways to expand your access is by harvesting credentials from compromised systems. Credential dumping and looting tools automate this process, allowing you to extract authentication material from LSASS, the registry, domain controllers, file shares, and more. With these credentials in hand, you can escalate privileges, impersonate users, or move laterally across the environment with far greater efficiency.
17. Impacket
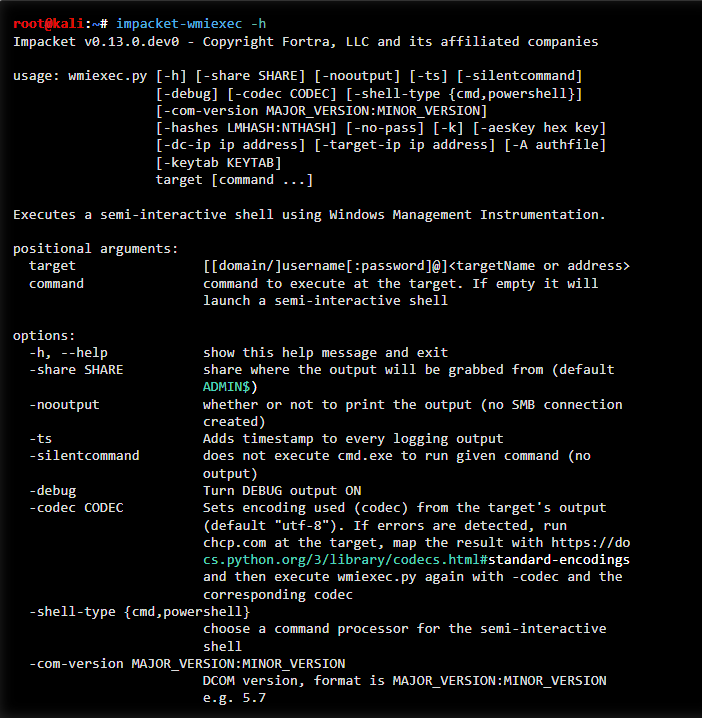
Impacket is one of the most widely used libraries and tool collections for interacting with Windows networks, Active Directory, and a variety of network protocols. It provides a suite of powerful scripts for credential extraction, authentication abuse, Kerberos manipulation, and remote command execution.
Because of its versatility and depth, Impacket is considered an essential toolkit for penetration testers, red teams, and incident responders working in Windows environments.
Why we like Impacket:
- Cred harvesting & Kerberos attacks:
- GetUserSPNs - perform Kerberoasting to extract service tickets for offline cracking.
- secretsdump - dump NTLM hashes, LSA secrets, Kerberos keys, and more from remote systems.
- ticketer - forge Kerberos tickets (Golden, Silver, and more) for privilege escalation.
- Lateral movement (Impacket provides multiple methods for executing commands on remote Windows systems):
- wmiexec - semi-interactive shell using WMI.
- smbexec - executes commands through SMB, writing output to disk.
- psexec - full interactive shell leveraging SMB and Windows services.
- atexec - schedules tasks for execution via the Windows Task Scheduler.
- Supports a wide range of network protocols (SMB, MSRPC, LDAP, Kerberos, etc).
- Frequently updated and widely supported in the penetration testing community.
Impacket is included in Kali Linux
18. Lsassy
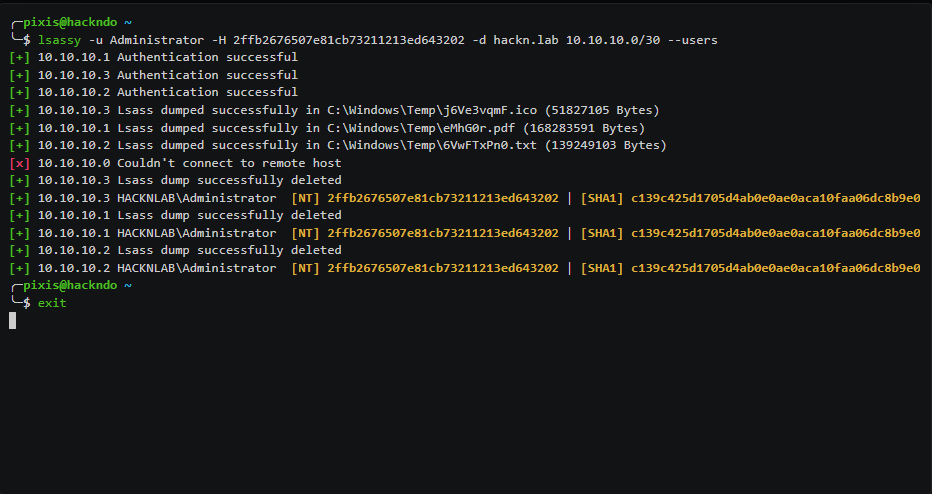
Lsassy is a credential extraction tool designed to dump Windows credentials from the Local Security Authority Subsystem Service (LSASS) process on remote machines. It automates the process of remotely retrieving LSASS memory using various execution methods (such as SMB, WinRM, or Impacket exec techniques) and then parses the dump using tools like pypykatz.
Lsassy is frequently used in post-compromise scenarios to gather NTLM hashes, clear-text passwords (when available), and Kerberos credentials.
Why we like Lsassy:
- Automates LSASS dumping: No need to manually grab LSASS memory, Lsassy handles the retrieval and parsing for you.
- Works seamlessly with Impacket exec methods like wmiexec, psexec, and others.
- Integrates with CrackMapExec/NetExec, enabling extremely efficient credential collection across multiple hosts.
- Useful for rapid lateral movement and privilege escalation once an initial foothold is established.
You can Lsassy it via pip (pip install lsassy) or clone it from the official GitHub repository. The tool is free and open source.
CompTIA PenTest+ Voucher
Launch your pentesting career with a discounted CompTIA PenTest+ Voucher. Save up to 30% and earn your certification with an authorized CompTIA partner.
19. Snaffler
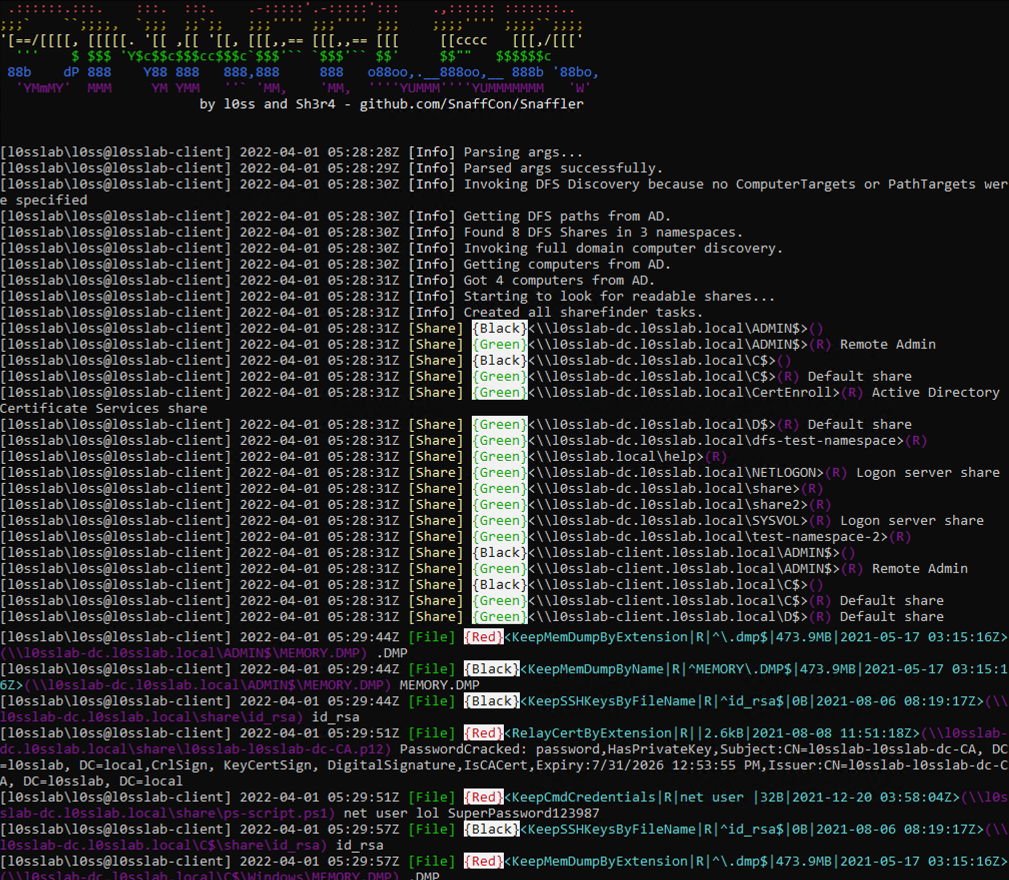
Snaffler is a Windows domain data discovery tool that automatically searches for and identifies sensitive files, credentials, configuration data, and other high-value information across network shares. It crawls SMB shares at scale, prioritizes potentially valuable items, and flags misconfigurations or exposed data that attackers can leverage for privilege escalation or lateral movement.
Why we like Snaffler:
- Excellent for finding “loot” fast - credentials, config files, scripts, password stashes, and misconfigured shares.
- Highly efficient at crawling large AD environments without manual enumeration.
- Uses smart filtering and scoring to surface the most valuable data first.
- Great for both penetration testers and defenders, validating what’s exposed in their environment.
You can download and run Snaffler from its GitHub repository.
Password Cracking
Once you’ve captured password hashes, whether through network interception, credential dumping, Kerberos attacks, or misconfigurations, the next step is attempting to crack them. Password‑cracking tools help you recover plaintext passwords, audit password strength, and identify weak or reused credentials that can enable further privilege escalation or lateral movement.
20. Hashcat
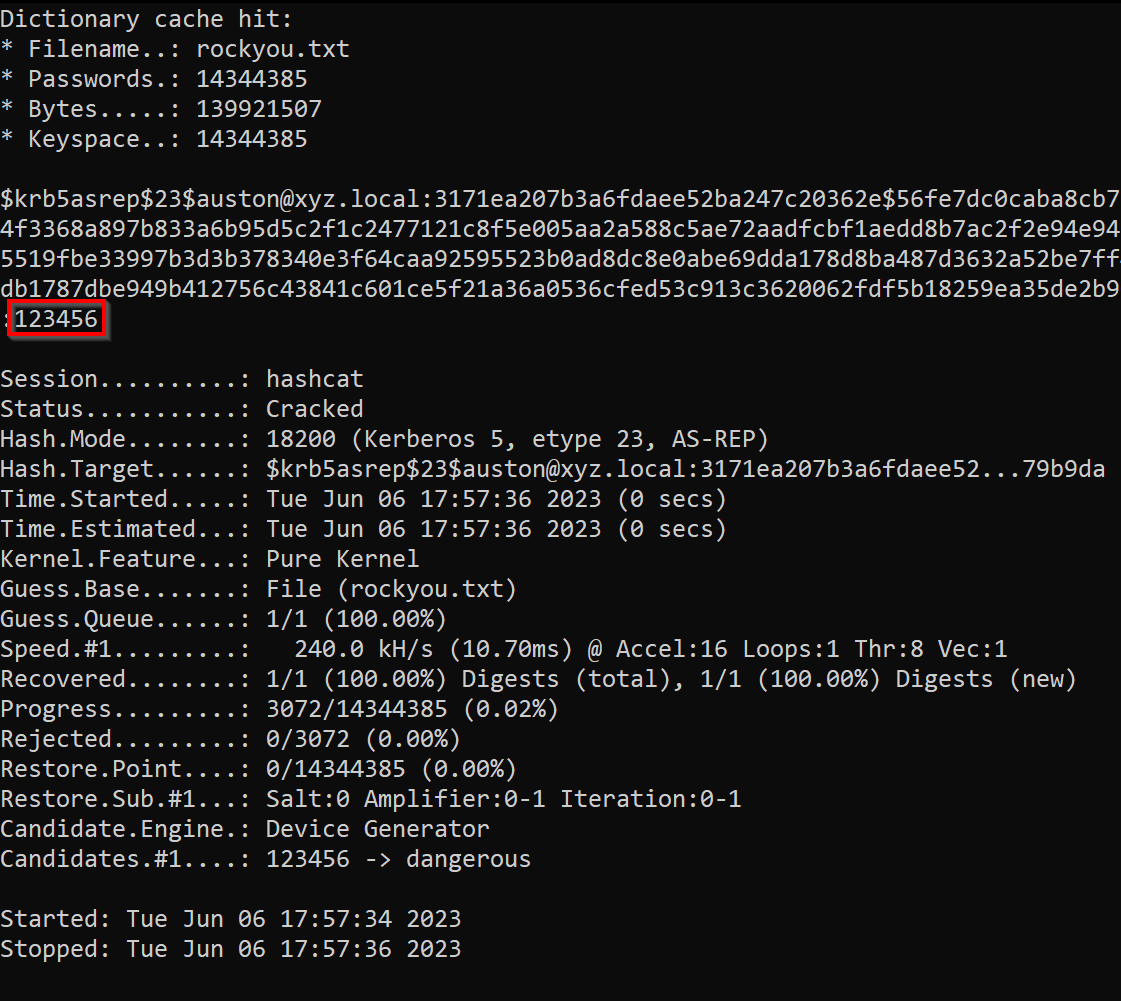
Hashcat is one of the fastest and most widely used password‑cracking tools in cyber security. Known for its high performance and extensive algorithm support, Hashcat can crack a wide range of hash types, including Windows, Linux, web application, wireless, and encrypted file formats, using CPU or GPU acceleration. It is a staple for penetration testers performing credential attacks.
For a detailed walkthrough, check out our How to Use Hashcat for Password Cracking guide.
Why we like Hashcat:
- Extremely fast, especially with GPU acceleration.
- Supports 300+ hash types, including NTLM, Kerberos, bcrypt, SHA‑1/256/512, WPA/WPA2, and many more.
- Ideal for offline password cracking of credentials captured with tools like Responder, Impacket, Kerbrute, or Mimikatz‑style dumping tools.
- Highly customizable with rule‑based attacks, masks, hybrid modes, dictionary attacks, and brute force.
Hashcat is included in Kali Linux by default.
Conclusion
The success of your network pentest will often rely on the tools you use. This guide detailed 20 of the best network penetration testing tools - from vulnerability scanners and network sniffing utilities to exploit modules, custom scripts, and automated pentesting frameworks. You explored tools for network scanning, post‑exploitation, lateral movement, assessing Active Directory environments, spoofing traffic, harvesting credentials, and analyzing packet data.
Whether you prefer a full-featured Linux distribution for offensive security or rely on lightweight utilities with strong community support, these tools help you perform efficient, accurate, and sometimes automated attacks that strengthen your overall assessment.
Try playing around with these tools in your own virtual hacking lab, learn how to use them effectively, and add them to your arsenal for the next time you need to perform a network penetration test!
For a complete, career‑focused learning path, including mentorship, a certification roadmap, hands‑on labs, and access to 30,000+ courses, explore the StationX Master’s Program. It gives you everything you need to learn network penetration testing tools and the skills required to use them effectively, providing a complete pathway to launch and grow a successful pentesting career.
If you want to go deeper into ethical hacking tools and techniques, consider our Ethical Hacking Bundle. It includes five online hacking courses, 55+ hours of on‑demand video, and 70+ articles and downloadable resources, a cost‑effective way to level up your skills.
The Ethical Hacking Courses Bundle: Learn Hacking for Beginners includes:
- Learn Hacking From Scratch: Ethical Hacking Course
- Pentesting and Website Hacking Course: Learn From Scratch
- How to Hack WiFi and Wired Networks: Beginner's Course
- Learn Social Engineering Testing From Scratch
- Cloud Hacking: How to Do Penetration Testing Using the Cloud




