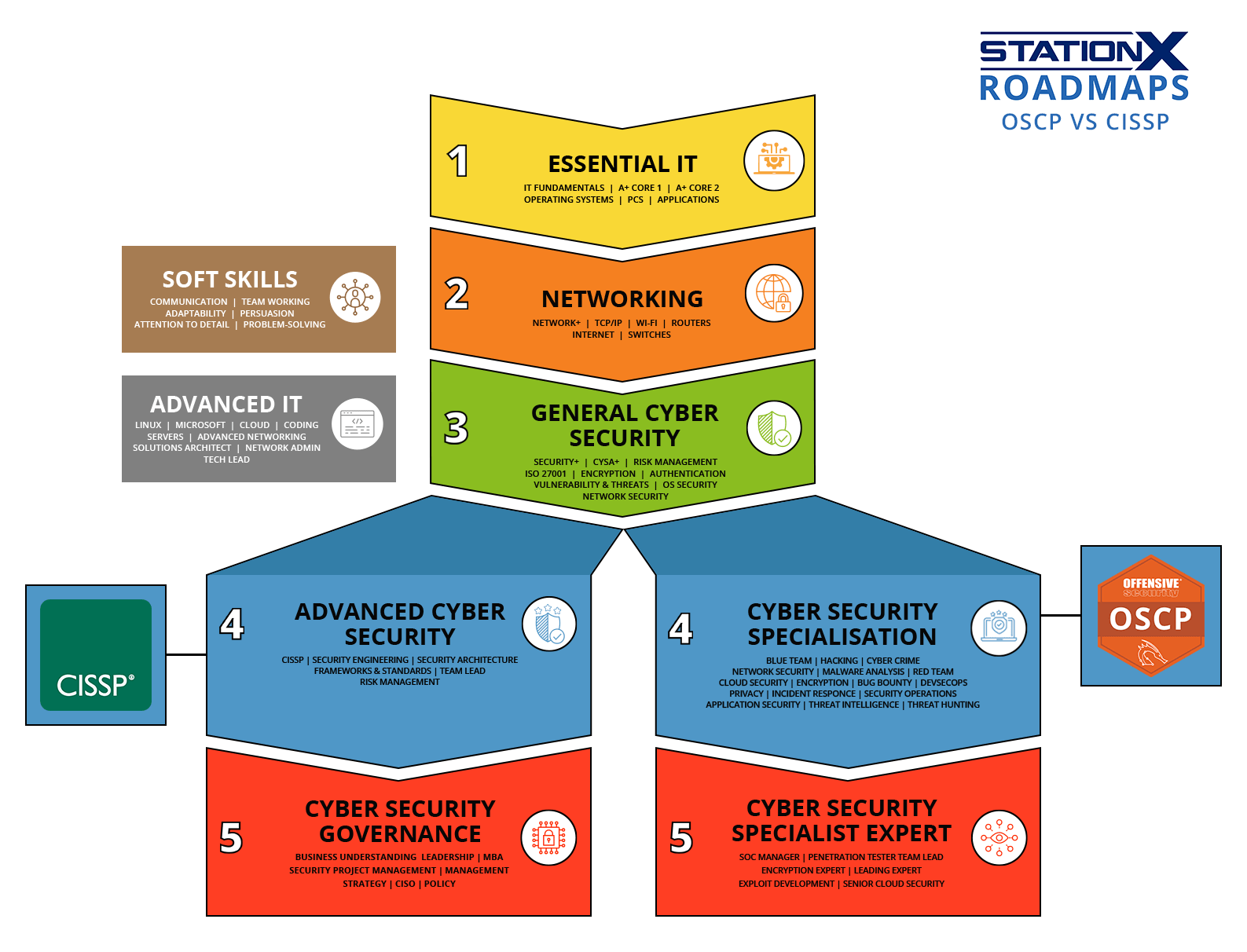
When comparing OffSec Certified Professional (OSCP) and the Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), it's easy to assume they compete for the same audience. In reality, they represent two entirely different cyber security paths.
Both are globally respected, mid-level certifications. But while OSCP measures your ability to attack systems hands-on, CISSP validates your capacity to design, manage, and secure them at scale.
If you already have a foundational certification like Security+ and are deciding which direction to take next — technical or managerial — this OSCP vs CISSP guide will help you make the right choice.
What Are OSCP and CISSP Certifications?
While both certifications are highly respected to the point of being synonymous with information security, they differ greatly in their audience, goals, and structure. Let’s take a look.
About OSCP
OffSec Certified Professional (OSCP - formerly called Offensive Security Certified Professional), issued by OffSec (formerly Offensive Security), is one of the most recognized hands-on penetration testing certifications in the world.

It focuses on real-world penetration testing and Active Directory exploitation. Candidates must complete a grueling 24-hour practical exam where they compromise multiple targets, perform privilege escalation, and submit a professional report documenting their findings.
This is not an entry-level certification, but it is considered the entry point for serious offensive security and ethical hacker work when compared to advanced OffSec credentials like OSEP or OSWE. OSCP is ideal for professionals ready to demonstrate serious technical capability and practical skills in offensive security.
Typical job titles OSCP holders include:
- Penetration Tester
- Red Team Operator
- Security Consultant
- Offensive Security Engineer
- Vulnerability Researcher
About CISSP
Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP) is managed by ISC2, one of the most recognized names in cyber security certification.

CISSP validates a professional's ability to design, manage, and oversee enterprise-level security programs. It covers eight domains of the ISC2 Common Body of Knowledge (CBK), including Security and Risk Management, Asset Security, Security Architecture and Engineering, Communication and Network Security, Identity and Access Management, Security Assessment and Testing, Security Operations, and Software Development Security.
Rather than testing how well you can hack into systems, CISSP measures your understanding of how to protect and govern them, making it a top credential for management roles, architects, and CISOs.
Typical job titles for CISSP holders include:
- Chief Information Security Officer (CISO)
- Security Manager
- Security Architect
- Compliance Officer
- Security Program Manager
- IT Director
Career Progression and Certification Pathways
Both OSCP and CISSP sit at the mid-career level and assume solid foundational knowledge, but they serve distinctly different career trajectories.
If you're passionate about hands-on offensive security and ethical hacking, OSCP builds on technical expertise and leads naturally toward red teaming, exploit analysis, or adversary simulation. It's for professionals who want to break into systems ethically and understand how attackers think.
If you're more interested in security strategy, architecture, and compliance, CISSP prepares you for leadership and governance roles across enterprise environments. It's for professionals who want to manage teams, design security programs, and make strategic decisions.
Stackability and Strategic Positioning
Some professionals eventually pursue both certifications, combining tactical skill with strategic oversight. Starting with OSCP builds deep technical credibility, while adding CISSP later opens doors to management and leadership positions. Conversely, those who earn CISSP first and later pursue OSCP gain the technical training and depth that makes them more effective as security leaders.
Exam Details
These two exams have wildly different exam formats. It’s critical to understand what you’re preparing for.
OSCP Exam
Format: 24-hour hands-on penetration testing exam in a VPN-based lab environment
Objective: Compromise three independent targets (worth 20 points each, split into 10 for initial access and 10 for privilege escalation) and exploit a three-machine Active Directory environment (worth 40 points total, with partial credit available)
Environment: Kali Linux; all tasks must be completed manually with no automated exploitation tools (like SQLmap); limited use of Metasploit
Reporting: Candidates have 24 hours after the exam ends to submit a professional penetration testing report documenting all findings and steps to reproduce
Passing Score: 70 points minimum
The OSCP exam is designed to replicate real-world testing under pressure, assessing not only technical skill but also persistence, enumeration ability, and problem-solving under time constraints.
CISSP Exam
Format: Computerized adaptive testing (CAT) with 100–150 multiple-choice and advanced innovative questions (drag-and-drop, hotspot-style questions)
Duration: Up to three hours
Scoring: 700 out of 1,000 points to pass
Focus: Broad coverage of eight domains, from risk management and cryptography to security operations and software development security
Assessment: Theoretical and managerial; tests breadth of knowledge across the security field rather than hands-on technical execution
What is CAT (Computerized Adaptive Testing)?
CAT is an exam format that adjusts question difficulty in real-time based on your performance. Here's how it works:
When you answer a question correctly, the system selects a harder question from the same knowledge domain. When you answer incorrectly, it selects an easier one. This continues throughout the exam, with the algorithm constantly reassessing your competency level.
The exam ends when the system reaches 95% confidence that you've either passed or failed, or when you hit the maximum question count (150 for CISSP). This means you could finish in as few as 100 questions if you're consistently performing at a passing level.
Why CAT feels harder:
Most candidates report feeling like they're failing during a CAT exam. That's actually normal — the system is designed to keep you at the edge of your knowledge, constantly challenging you with questions just beyond your comfort zone. If questions start feeling easier, it might mean the system has determined you're not performing at the passing level.
Key difference from traditional exams:
Unlike linear exams where you can review and change answers, CAT is final. Each answer you submit influences the next question, so you can't go back. This makes question strategy and time management crucial.
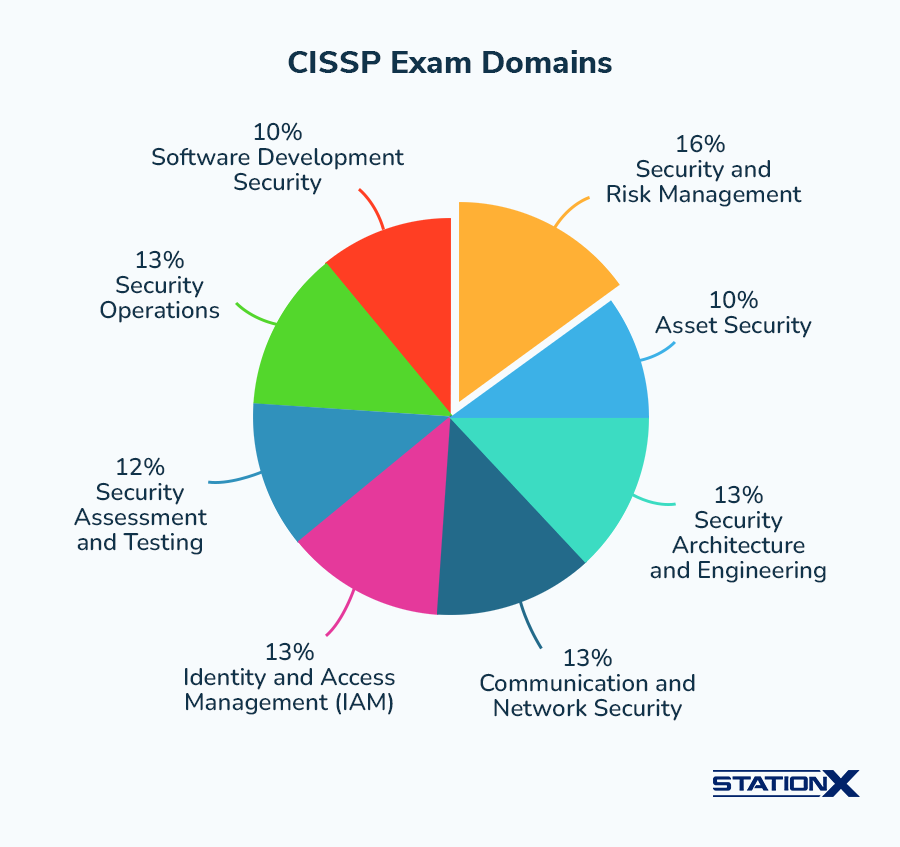
CISSP exam domains and their weightings are:
| Domain | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Security and Risk Management | 16% |
| Asset Security | 10% |
| Security Architecture and Engineering | 13% |
| Communication and Network Security | 13% |
| Identity and Access Management | 13% |
| Security Assessment and Testing | 12% |
| Security Operations | 13% |
| Software Development Security | 10% |
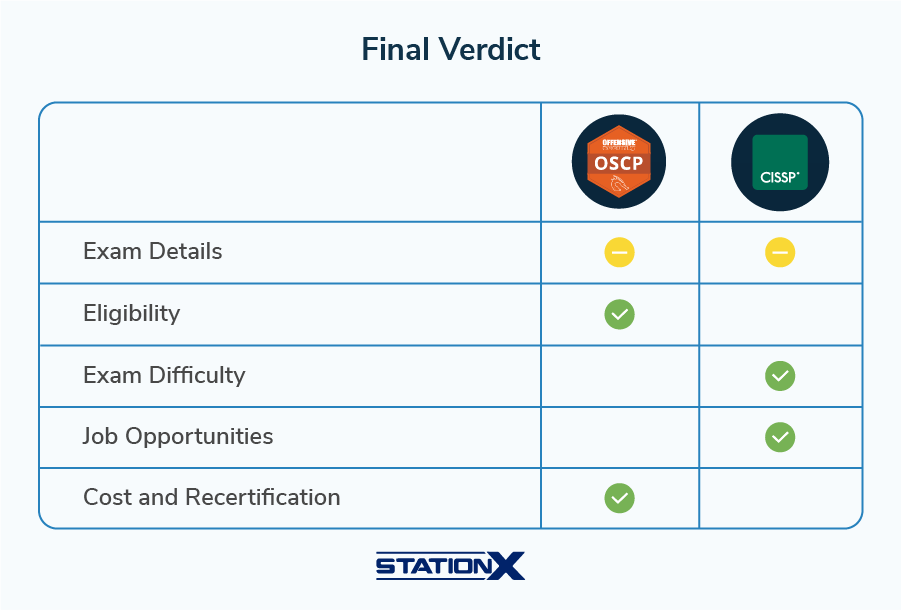
Winner: Draw
This is genuinely difficult to call because these exams test completely different skill sets. CISSP provides a more complete knowledge base across the entire cyber security domain, covering everything from governance and risk management to technical operations and software security. Its eight domains represent the comprehensive body of knowledge needed to manage enterprise security programs.
OSCP, by contrast, goes incredibly deep on offensive security, Active Directory exploitation, and penetration testing methodology. It's hyper-focused on one crucial area of cyber security rather than attempting to cover everything.
For someone building a well-rounded security career, CISSP's broader knowledge base wins. But for someone specializing in offensive security, OSCP's depth is more valuable than CISSP's breadth.
Eligibility Requirements
Both of these certifications are considered advanced and require prior knowledge, but only one requires documented paid experience.
OSCP Requirements
OffSec does not impose strict prerequisites to sit for the exam, but candidates should have:
- Strong Linux and networking fundamentals
- Familiarity with basic scripting (Python, Bash, or PowerShell)
- Understanding of common penetration testing tools like Nmap, Burp Suite, and Metasploit
OffSec recommends 2–4 years of professional IT or cyber security experience, but this is not enforced. You can purchase the PEN-200 course and exam at any time without proving your background.
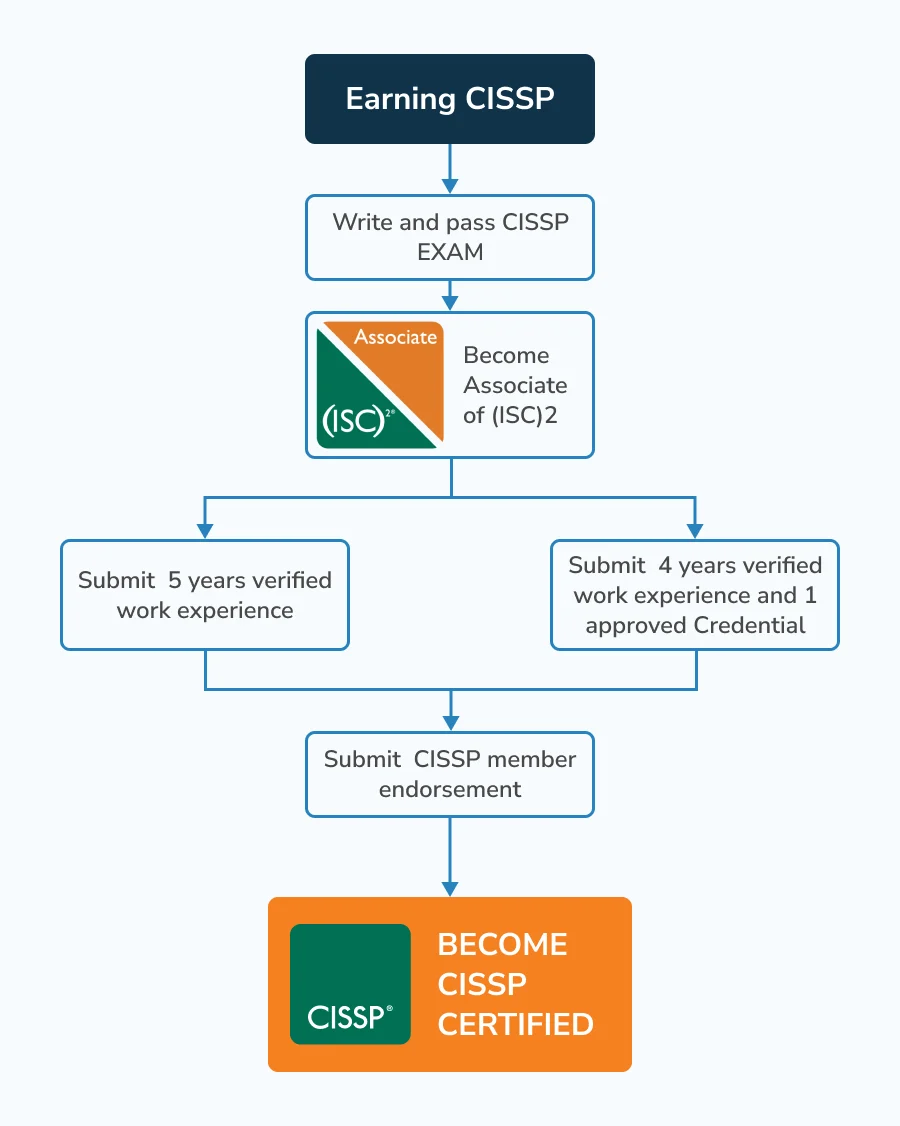
CISSP Requirements
To become a CISSP, you must:
- Have five years of cumulative paid work experience in two or more of the eight CISSP domains
- Obtain endorsement from a current CISSP in good standing
- Complete 120 Continuing Professional Education (CPE) credits every three years to maintain certification
- Pay an annual maintenance fee of $125
You can waive up to one year of experience with a relevant four-year degree or an approved certification (such as Security+ or OSCP itself).
If you pass the exam without meeting the experience requirements, you become an Associate of ISC2. You'll have six years to accumulate the necessary experience before earning the full CISSP credential.
Winner: OSCP
OSCP has no formal prerequisites, no endorsement requirements, and no mandatory required experience. While OffSec recommends prior experience, you can sit for the exam and earn the certification immediately upon passing. CISSP requires verifiable work experience and an endorsement, making it significantly harder to obtain for early-career professionals.
Exam Difficulty
The OSCP is widely considered one of the hardest mid-level certifications in cyber security. Its challenge lies not in theory but in real-world problem-solving: exploiting networks, evading defenses, escalating privileges, and maintaining focus during a 24-hour exam. Many candidates fail on their first attempt, and the pass rate reflects the exam's notorious difficulty.
CISSP, while not technically hands-on, is also challenging due to its breadth. The CAT format continuously adjusts difficulty based on your performance, meaning you're always being pushed to the edge of your knowledge. It demands a working understanding of governance frameworks, laws, risk management, and hundreds of interconnected security concepts. The CAT system makes many candidates feel like they're failing even when they're passing.
In short: OSCP tests what you can do under pressure. CISSP tests what you know across the entire security landscape.
Winner: CISSP
While both exams are difficult, CISSP is the more passable of the two. It's a multiple-choice exam testing breadth of knowledge, and with proper study and preparation, candidates can pass by demonstrating competency across eight domains.
OSCP requires you to actually compromise live systems under extreme time pressure. Even well-prepared candidates often fail due to rabbit holes, enumeration gaps, or simply running out of time. The hands-on nature and 24-hour duration make OSCP objectively harder to pass.
Job Opportunities
OffSec and ISC2 both claim there is high demand and high reward for their respective certification holders. Does this claim hold water?
OSCP Job Market
At the time of writing, job searches reveal:
- Indeed: Approximately 578–688 jobs explicitly mentioning OSCP in the United States
- Glassdoor: Approximately 565 jobs for OSCP, with 210 specifically for penetration testing roles requiring OSCP
- ZipRecruiter: OSCP jobs with salary ranges from $96,000 to $195,000
OSCP is often listed alongside or as an alternative to other offensive security certifications like CEH, GPEN, and PenTest+. Jobs requiring OSCP typically include:
- Penetration Tester: $75,000 – $134,000
- Red Team Operator: $95,000 – $158,000+
- Security Consultant: $90,000 – $140,000
- Offensive Security Engineer: $100,000 – $150,000
- Vulnerability Researcher: $110,000 – $160,000+
Tech & Cyber Security Resume Writing Services
Ready to land your dream cybersecurity job? Our Resume Writing Services apply ATS-optimized, industry-specific expertise to boost your interview rate by an average of 60% — trusted by thousands of tech professionals worldwide.
CISSP Job Market
At the time of writing, job searches reveal:
- Indeed: Approximately 9,460–11,796 jobs mentioning CISSP in the United States
- Glassdoor: Approximately 8,866–10,005 jobs mentioning CISSP
- CyberSeek: Over 70,000 cybersecurity job postings specifically requesting CISSP certification
- LinkedIn: Over 34,000 jobs mentioning CISSP globally
CISSP is one of the most requested certifications across cyber security positions, often appearing as either required or strongly preferred. Jobs requiring CISSP typically include:
- CISO: $148,000 – $232,500
- Security Manager: $110,000 – $160,000
- Security Architect: $120,000 – $180,000
- IT Director: $109,000 – $149,500
- Compliance Officer: $95,000 – $140,000
- Security Consultant: $131,000 – $195,000
Salary Comparison
According to multiple salary sources:
OSCP:
- ZipRecruiter: $119,895 average (range: $96,000 – $141,000)
- PayScale: $103,000 average
CISSP:
- ZipRecruiter: $112,302 average (range: $95,000 – $150,000)
- PayScale: $131,000 average
- Glassdoor: $161,315 average (range: $120,986 – $225,841)
- InfoSec Institute: $143,708 average base salary, $175,583 with bonuses
Winner: CISSP
CISSP dominates in both job market demand and salary potential. With nearly 50 times more job postings and higher average salaries (especially when including bonuses and total compensation), CISSP offers significantly better career opportunities.
While OSCP salaries are competitive for offensive security roles, CISSP prepares you for leadership positions that command higher pay. The certification's recognition across industries (finance, healthcare, government, tech, and more) makes it the more marketable credential overall.
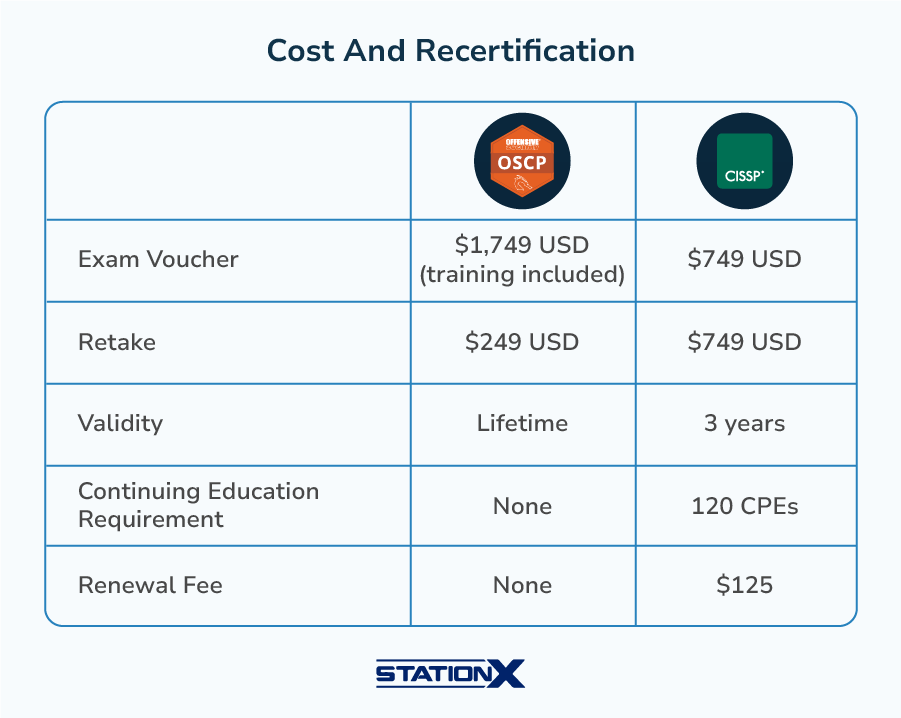
Cost and Recertification
It’s important to consider both the upfront and long-term costs of both certifications.
OSCP Cost
Course and Exam Options:
- Learn One subscription: $2,749 annually (includes one year of lab access, PEN-200 OSCP training, and two exam attempts)
- Course & Exam Bundle: $1,749 (includes 90 days of lab access, PEN-200 course, and one exam attempt)
- Retake fee: $249 (if purchased separately outside subscription plans)
Recertification: The OSCP does not expire. It's a lifetime certification with no maintenance fees or continuing education requirements.
CISSP Cost
Initial Exam: $749
Annual Maintenance Fee: $125 per year
Recertification: Every three years, requiring 120 Continuing Professional Education (CPE) credits. CPE credits can be earned through:
- Taking security courses
- Earning additional certifications
- Attending conferences
- Publishing security content
- Professional work experience
Total three-year cost: $749 (exam) + $375 (three annual fees) + continuing education costs = $1,124+ minimum
Winner: OSCP
While OSCP has a higher upfront cost ($1,749–$2,749), it's a lifetime certification with no recurring fees. CISSP costs less initially ($749) but requires $125 annually plus the time and money needed to earn 120 CPE credits every three years.
Over a 10-year career span:
- OSCP: $1,749–$2,749 (one-time)
- CISSP: $749 + $1,250 (annual fees) + continuing education costs = $2,000–$3,000+
OSCP's lifetime validity makes it significantly cheaper in the long run.
OSCP vs CISSP: The Final Verdict
The OSCP and CISSP are both career-defining advanced certifications, but they serve entirely different purposes. To know the best certification for you, ask yourself, “What are my professional goals?”
Choose OSCP if you want to:
- Work hands-on in penetration testing or red teaming
- Build deep technical expertise in offensive security
- Demonstrate persistence and problem-solving under real-world constraints
- Specialize in finding and exploiting vulnerabilities
Choose CISSP if you want to:
- Move into management, policy, or architecture roles
- Lead security programs or enterprise teams
- Build credibility for executive and compliance positions
- Develop a comprehensive understanding of the entire security landscape
Which one is better overall?
Winner: CISSP
CISSP wins on career breadth, job market demand, and long-term earning potential. It's the more universally recognized credential and opens significantly more doors across industries and job levels. If you're unsure about your exact career path or want maximum flexibility, CISSP is the safer choice.
However, OSCP has undeniable value for those committed to offensive security. It's the gold standard for penetration testing roles and provides hands-on credibility that CISSP cannot match. For specialized technical roles in red teaming and security testing, OSCP is often the preferred or required certification.
If you're still undecided, ask yourself: "Do I want to break systems — or protect them at scale?"
Both paths are highly respected, and some professionals eventually pursue both, combining tactical skill with strategic oversight — the ultimate blend of red-team and blue-team mastery.
Ready to start your certification journey? The StationX Master's Program provides access to over 30,000 courses and labs, including comprehensive CISSP training and penetration testing courses that prepare you for OSCP. With mentorship, study groups, and hands-on labs, you'll have everything you need to earn either certification and accelerate your cyber security career.
You can also see our Information Security Training Bundles, granting lifetime access to top courses for a one-time purchase. Learn ethical hacking, cyber security, and prepare for top certifications.
We have bundles on:
- Pentesting, red teaming, and web app hacking
- Certification prep, including CompTIA, ISC2, AWS, Cisco, and Azure
- DevSecOps and Coding
- Linux
- AI
- And much more!