If your goal is to advance in ethical hacking or offensive security, you’ve reached the right place. The CompTIA PenTest+ is one of the few industry-recognized credentials that blends technical skill, methodology, and reporting, but preparing for it can be challenging given its wide scope.
This CompTIA PenTest+ Cheat Sheet (PT0-003) gives you a focused overview of the key domains and tools covered in the exam, from engagement management and reconnaissance to exploitation and post-exploitation, helping you review faster and study smarter.
CompTIA PenTest+ Study Guide Search
Search our CompTIA PenTest+ cheat sheet to find the right cheat for the term you're looking for. Simply enter the term in the search bar and you'll receive the matching cheats available.
- CompTIA PenTest+ Study Guide Search
- What Is the CompTIA PenTest+ Certification?
- PenTest+ Cheat Sheet Exam Domains (PT0-003)
- Engagement Management
- Reconnaissance and Enumeration
- Vulnerability Discovery and Analysis
- Attacks and Exploits
- Post-exploitation and Lateral Movement
- CompTIA PenTest+ Cheat Sheet Conclusion
What Is the CompTIA PenTest+ Certification?
CompTIA PenTest+ is an intermediate-level certification aimed at professionals performing penetration testing and vulnerability management. It covers planning and scoping engagements, vulnerability discovery, exploitation, post-exploitation, and reporting. It’s DoD 8570/8140 approved and maps to ANSI/IEC/ISO 17024.
Certification attempters must pass one 165-minute exam with a score of at least 750 on a scale of 100-900. The certification exam consists of a maximum of 85 questions, including both multiple-choice and performance-based questions.
The latest CompTIA PenTest+ exam code is PT0-003. It was released in April 2022 and, based on CompTIA’s typical 3-4-year update cycle, it’s expected to remain active until around 2026, when a new version (PT0-004) will likely be introduced.
PenTest+ Cheat Sheet Exam Domains (PT0-003)
As cyber security continues to advance, the PenTest+ exam evolves to match modern attack methods, tools, and professional practices. CompTIA regularly updates the certification to reflect the latest penetration testing methodologies, tools, and real-world attacker techniques.
The most recent version, PT0-003, introduced an updated set of domains designed to validate both technical and operational skills needed in professional penetration testing engagements.
The current PenTest+ (PT0-003) Domains are as follows:
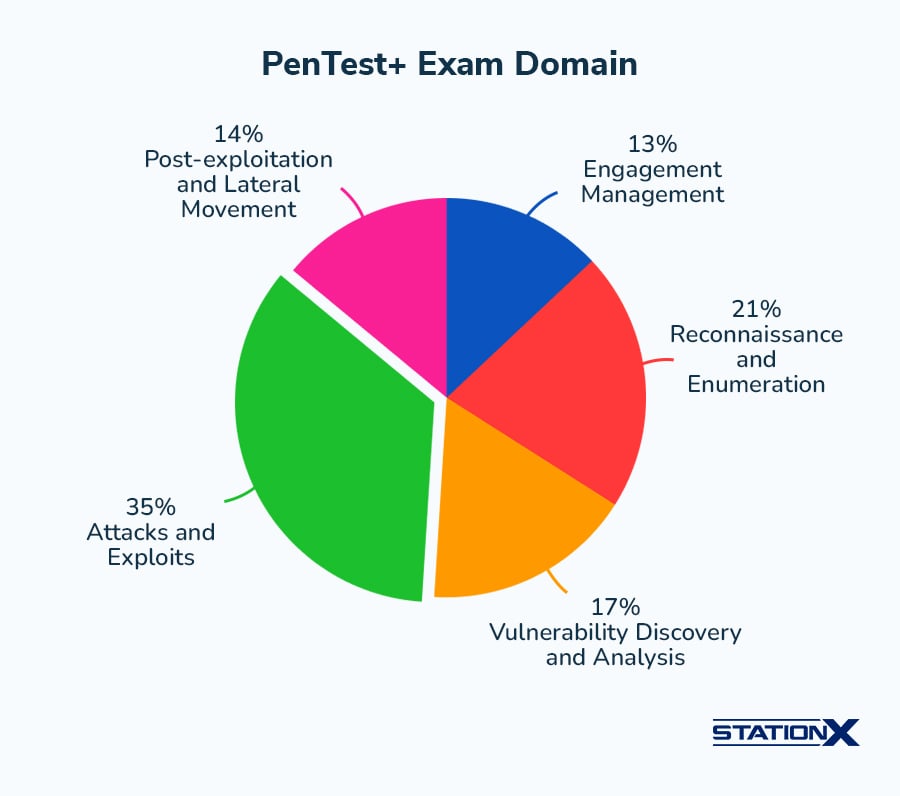
| PenTest+ PT0-003 Domain | Exam Weighting (%) |
| Engagement management | 13% |
| Reconnaissance and enumeration | 21% |
| Vulnerability discovery and analysis | 17% |
| Attacks and exploits | 35% |
| Post-exploitation and lateral movement | 14% |
Without further ado, let’s explore each domain and subdomain and unpack the essential concepts you will encounter in the exam.
Engagement Management
This domain focuses on defining penetration test scope, agreements, and legal boundaries, while ensuring compliance and clear communication with stakeholders. It covers the full engagement lifecycle, from planning and authorization to reporting findings and recommending remediation.
Pre-engagement Activities
| Concept | Description |
| Scope Definition | Defines test scope including privacy, security, rules of engagement, exclusions, test cases, escalation process, and testing window. |
| Agreement Types | Legal agreements that define engagement terms and liabilities: • NDA • MSA • SoW • ToS |
| Target Selection | Specifies the systems and assets to test: • CIDR ranges, • Domains • IP addresses • URLs |
| Assessment Types | Describes the kind of tests conducted: • Web • Network • Mobile • Cloud • API • Application • Wireless |
| Shared Responsibility Model | Clarifies responsibilities among hosting provider, customer, tester, and third parties. |
| Legal and Ethical Considerations | Ensures authorization, compliance with reporting laws, and awareness of tester liability. |
Collaboration and Communication Activities
| Concept | Description |
| Peer Review | Internal review process to validate findings and ensure quality of penetration test results. |
| Stakeholder Alignment | Ensures all relevant parties understand the test goals, risks, and reporting expectations. |
| Root Cause Analysis | Investigates and identifies underlying issues contributing to discovered vulnerabilities. |
| Escalation Path | Process for communicating critical findings to appropriate personnel. |
| Secure Distribution | Ensures sensitive test results and data are transmitted securely to authorized recipients only. |
| Articulation of Risk, Severity, and Impact | Clearly explains how vulnerabilities affect confidentiality, integrity, and availability. |
| Goal Reprioritization | Adjusts test objectives based on emerging risks or client input during engagement. |
| Business Impact Analysis | Evaluates the potential consequences of security weaknesses on business operations. |
| Client Acceptance | Formal confirmation from the client that the engagement results meet agreed-upon objectives. |
Testing frameworks and methodologies
| Framework / Methodology | Description |
| OSSTMM | Open Source Security Testing Methodology Manual |
| CREST | Council of Registered Ethical Security Testers |
| PTES | Penetration Testing Execution Standard |
| MITRE ATT&CK | A knowledge base of adversary tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs) used in real-world attacks. |
| OWASP Top 10 | The ten most critical web application security risks and common vulnerabilities. |
| OWASP MASVS (Mobile Application Security Verification Standard) | Assessing the security of mobile applications across multiple layers. |
| Purdue Model | Securing industrial control systems (ICS) by segmenting layers of control. |
| Threat Modeling Frameworks | • DREAD • STRIDE • OCTAVE |

Penetration Test Report Components
| Component | Description |
| Format Alignment | Ensures the report adheres to client or industry-specific formatting and presentation standards. |
| Documentation Specifications | Defines structure, organization, and level of technical detail included in the report. |
| Risk Scoring | Quantifies the severity of findings using standardized scoring systems like CVSS. |
| Definitions | Clarifies terminology, acronyms, and classification levels used throughout the report. |
| Executive Summary | High-level overview of the assessment, key findings, and business impact for non-technical stakeholders. |
| Methodology | Outlines the testing approach, scope, and frameworks used during the engagement. |
| Detailed Findings | In-depth analysis of vulnerabilities, including affected assets, evidence, and exploit details. |
| Attack Narrative | Chronological account of exploitation steps. |
| Recommendations and Remediation Guidance | Actionable guidance for mitigating vulnerabilities and improving security posture. |
| Test Limitations and Assumptions | Specifies any constraints, exclusions, or assumptions made during testing that may affect results. |
| Reporting Considerations | Addresses legal and ethical requirements, quality control (QC) measures, and AI-assisted reporting considerations. |
Remediation Recommendations
| Control Type | Description and Examples |
| Technical Controls | • System hardening • Sanitizing user input / parameterizing queries • Multifactor authentication • Encryption • Process-level remediation • Patch management • Key rotation • Certificate management • Secrets management solutions • Network segmentation • Infrastructure security controls |
| Administrative Controls | • RBAC • SDLC • Minimum password requirements • Organizational policies and procedures |
| Operational Controls | • Job rotation • Time-of-day restrictions • Mandatory vacations • User security training |
| Physical Controls | • Access control vestibules • Biometric access systems • Video surveillance and monitoring |
Reconnaissance and Enumeration
This PenTest+ domain emphasizes gathering and analyzing intelligence about targets before exploitation.
Information Gathering Techniques
| Technique | Description and Examples |
| Open-source Intelligence (OSINT) | Collecting publicly available information from: • Social media and job boards • Code repositories (GitHub) • DNS • Cached pages, password dumps, or cryptographic flaw databases |
| Network Reconnaissance | Identify live hosts, open ports, and services to map the target network. |
| Protocol Scanning | Scan TCP/UDP ports to discover active services and communication patterns. |
| Certificate Transparency Logs | Review public certificate logs to find related domains and subdomains. |
| Information Disclosure | Locate unintentionally exposed data via errors, metadata, or public files. |
| Search Engine Analysis and Enumeration | Use search engines to find exposed directories and sensitive assets. |
| Network Sniffing | Capture and analyze network traffic, including IoT/OT protocols, for intelligence. |
| Banner Grabbing | Retrieve service banners to identify software versions and configurations. |
| HTML Scraping | Extract metadata, comments, and hidden information from web pages. |
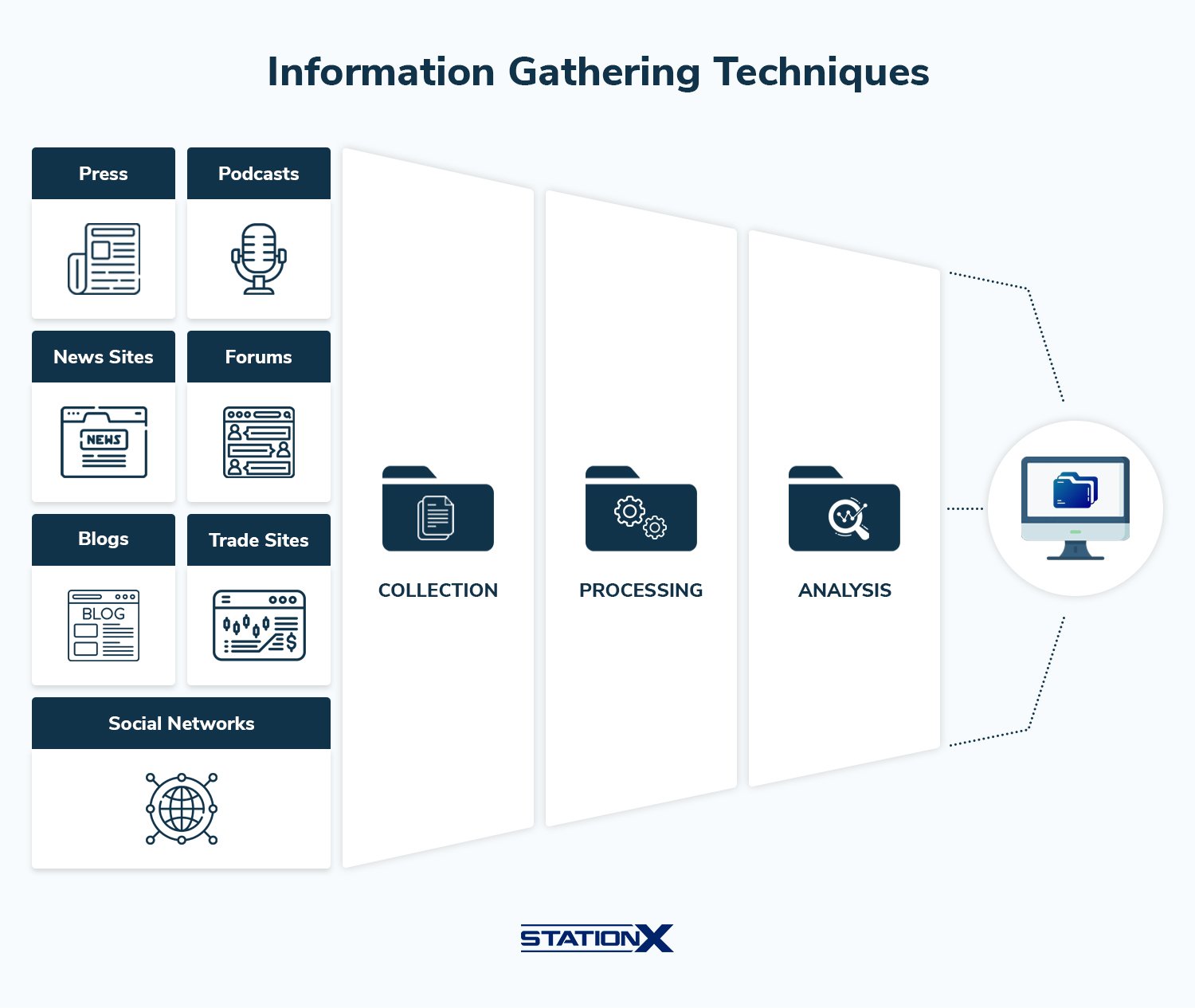
Enumeration Techniques
| Concept | Description |
| OS fingerprinting | Identifying the operating system based on responses. |
| Service discovery | Finding running services on a host. |
| Protocol enumeration | Gathering details about supported protocols. |
| DNS enumeration | Extracting DNS records and domain info. |
| Directory enumeration | Identifying hidden folders/paths. |
| Host discovery | Detecting active systems on a network. |
| Share enumeration | Listing shared folders/resources. |
| Local user enumeration | Identifying local system users. |
| Email account enumeration | Discovering valid email addresses. |
| Wireless enumeration | Scanning wireless networks and details. |
| Permission enumeration | Identifying access rights and privileges. |
| Secrets enumeration | Finding sensitive items like keys/tokens. |
| Cloud access keys | Locating exposed cloud authentication keys. |
| Passwords | Identifying leaked or stored passwords. |
| API keys | Finding accessible API credentials. |
| Session tokens | Locating session identifiers. |
| Attack path mapping | Visualizing possible paths to compromise. |
| WAF enumeration | Detecting and profiling web application firewalls. |
| Origin address | Revealing backend server locations. |
| Web crawling | Automated discovery of site content. |
| Manual enumeration | Hand-checking files and components. |
| Robots.txt | Identifying disallowed indexed paths. |
| Sitemap | Mapping site structure and URLs. |
| Platform plugins | Detecting CMS/plugins in use. |
Reconnaissance and Enumeration Script Modification
| Concept | Description |
| Information gathering | Using scripts to collect data from targets or sources. |
| Data manipulation | Parsing, filtering, and transforming collected information. |
| Bash/Python/PowerShell | Common scripting languages used for automation in recon. |
| Loops & Conditionals | Control flow logic for repeated tasks and decision-making. |
| Boolean/String/Arithmetic operators | Operators used to compare, modify, or calculate values. |
| Libraries, functions, classes | Reusable components to enhance script functionality. |
Reconnaissance and Enumeration Tools
| Tool | Description |
| Wayback Machine | Retrieve archived web pages to identify outdated or exposed content. |
| Maltego | Perform link analysis to map relationships between entities. |
| Recon-ng | Framework for automated OSINT collection. |
| Shodan | Search engine for identifying Internet-connected devices and exposed services. |
| SpiderFoot | Automated OSINT collection across multiple public sources. |
| WHOIS / nslookup / dig | Retrieve domain and DNS information for target profiling. |
| Censys.io / DNSdumpster | Discover network infrastructure and related assets. |
| Amass | Perform DNS enumeration and subdomain discovery. |
| Nmap / NSE | Scan networks, discover hosts, and execute custom vulnerability scripts. |
| theHarvester | Gather emails, subdomains, and hosts from open sources. |
| WiGLE.net / InSSIDer | Map wireless networks and identify nearby SSIDs and BSSIDs. |
| Wireshark / tcpdump | Capture and analyze network packets to detect vulnerabilities. |
| Aircrack-ng | Wireless packet capture and WPA/WEP password cracking toolset. |
| OSINTframework.com | Directory of OSINT tools categorized by data source and purpose. |
Vulnerability Discovery and Analysis
This domain focuses on uncovering and validating system weaknesses through scanning, analysis, and reporting.
Vulnerability Discovery Techniques
| Technique | Description |
| Container Scans | Scan container images/configs for vulnerabilities. |
| Sidecar Scans | Check sidecar containers for security gaps. |
| Application Scans | Test applications for flaws and misconfigurations. |
| DAST | Dynamic Application Security Testing. |
| IAST | Interactive Application Security Testing. |
| SCA | Software Composition Analysis. |
| SAST | Static Application Security Testing. |
| Infrastructure as Code (IaC) Analysis | Review IaC files for configuration risks. |
| Source Code Analysis | Inspect code manually or with scanners for bugs. |
| Mobile Scans | Test mobile apps for insecure storage and behavior. |
| Network Scans | Identify hosts, services, and open ports. |
| Host-Based Scans | Assess local system configs and software. |
| Secrets Scanning | Find exposed keys, passwords, and tokens. |
| Wireless Scanning | Analyze Wi-Fi signals, channels, and SSIDs. |
| ICS Vulnerability Assessment | Evaluate industrial systems for weaknesses. |
| Manual Assessment | Verify findings by hands-on testing. |
| Port Mirroring | Copy network traffic for passive review. |
Want To Get Hands-On Hacking?
Take a look at the following course bundles:
Reconnaissance, Scanning, and Enumeration Phases
| Phase | Description |
| Analysis of Reconnaissance and Scanning Results | Validate and interpret data gathered from prior phases to confirm vulnerabilities. |
| Validate Results | Distinguish between false positives, false negatives, and true positives while ensuring scan completeness. |
| Troubleshooting Scan Configurations | Review scanning parameters and network accessibility issues to improve accuracy. |
| Public Exploit Selection | Match identified vulnerabilities with known public exploits for validation and testing. |
| Scripting for Validation | Automate result verification and exploit proofing using Bash, Python, or PowerShell. |
Physical Security Concepts
| Concept | Description |
| Tailgating | Gaining unauthorized access by following an authorized person into a restricted area. |
| Site Surveys | Inspect premises to identify potential physical vulnerabilities or entry points. |
| USB Drops | Planting infected USB devices to trick users into compromising the network. |
| Badge Cloning | Duplicating access cards or RFID credentials for unauthorized access. |
| Lock Picking | Physically bypassing locks to gain entry to restricted areas or systems. |
Attacks and Exploits
The Attacks and Exploits domain focuses on executing and analyzing real-world cyberattacks across multiple environments.
Network Attacks
| Attack | Description |
| VLAN hopping | An attacker can move from one VLAN to another. |
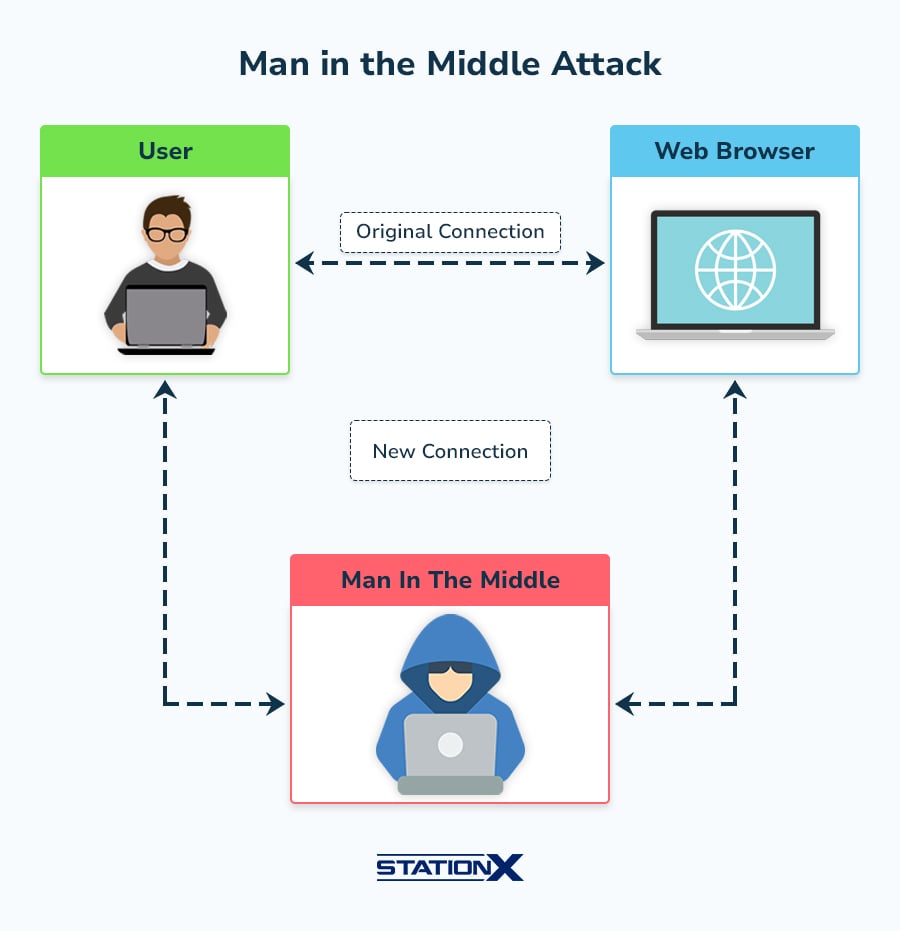
| On-path (MITM) | Intercept a two-party conversation for one’s advantage. |
| Service exploitation | Buffer overflow, RCE, service-specific vulnerabilities. |
| Network Sniffing | Packet capture, protocol analysis, credential interception. |
| Denial-of-Service | SYN flood, UDP flood, application layer DoS. |
Authentication Attacks
| Attack | Description |
| Brute-Force Attacks | Trying all possible passwords until one succeeds. |
| Pass-the-Hash | Using stolen password hashes to authenticate without cracking them. |
| Credential Stuffing | Using leaked username/password pairs across multiple services. |
| Keberoasting | Extracting and cracking Kerberos service tickets to gain elevated access. |
| Password Spraying | Attempting a few common passwords across many accounts to avoid lockouts. |
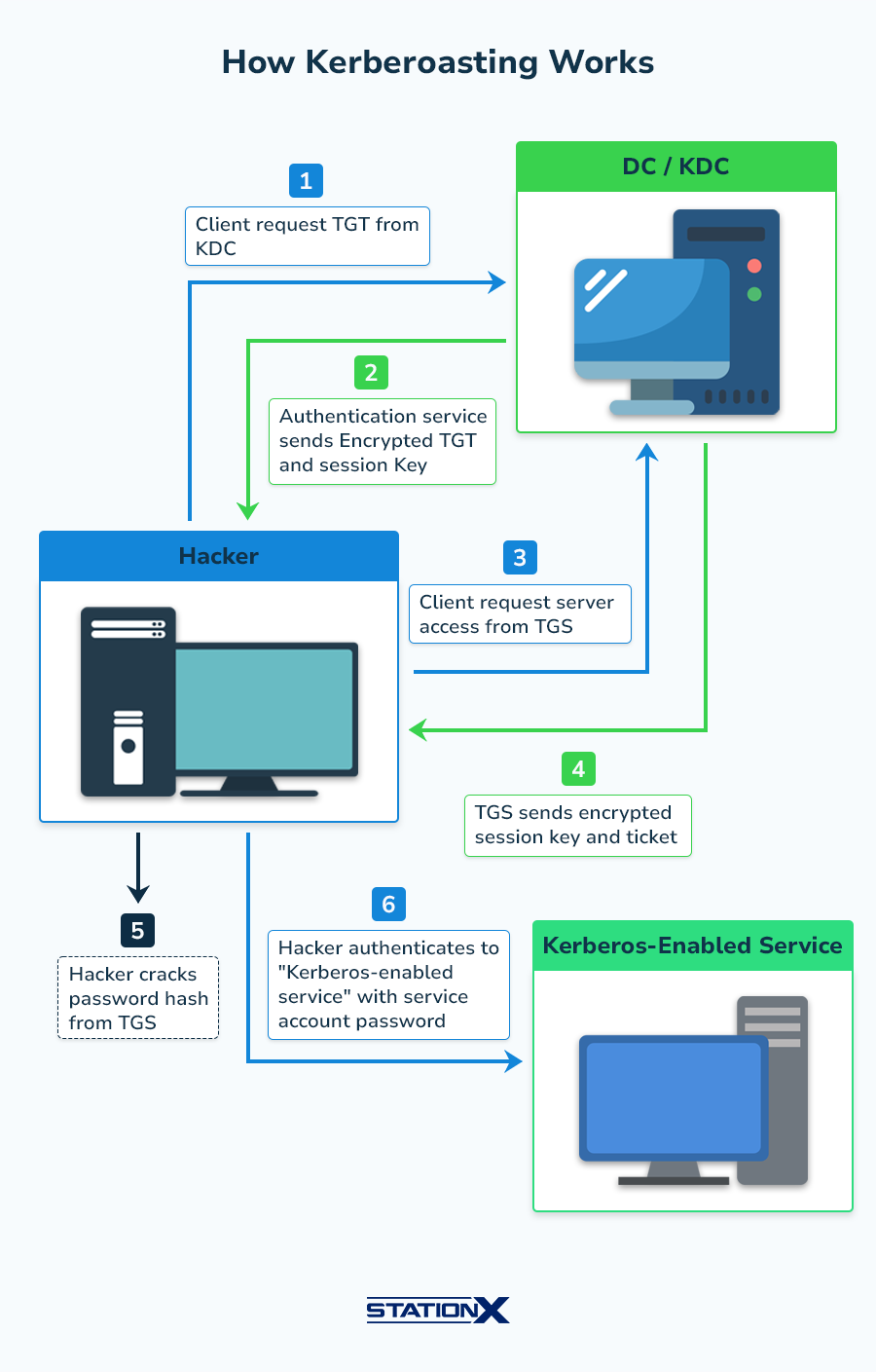
Host-Based Attacks
| Attack | Description |
| Privilege Escalation | Exploiting weaknesses to gain higher privileges, like admin or root access. |
| Process Injection | Running malicious code inside a legitimate process. |
| Credential Dumping | Extracting stored usernames and passwords from memory or files. |
| Living off the Land | Abusing built-in system tools to evade detection. |
| Persistence Mechanisms | Techniques that maintain long-term access to compromised systems. |
Web Application Attacks
| Attack | Description |
| SQL Injection | Injecting malicious input to run unauthorized SQL queries. |
| XSS | Cross-Site Scripting. |
| Directory Traversal | Accessing files or directories outside the intended folder using path manipulation. |
| CSRF | Cross-Site Request Forgery. |
| Authentication Bypass | Skipping or defeating login mechanisms through flaws or misconfigurations. |
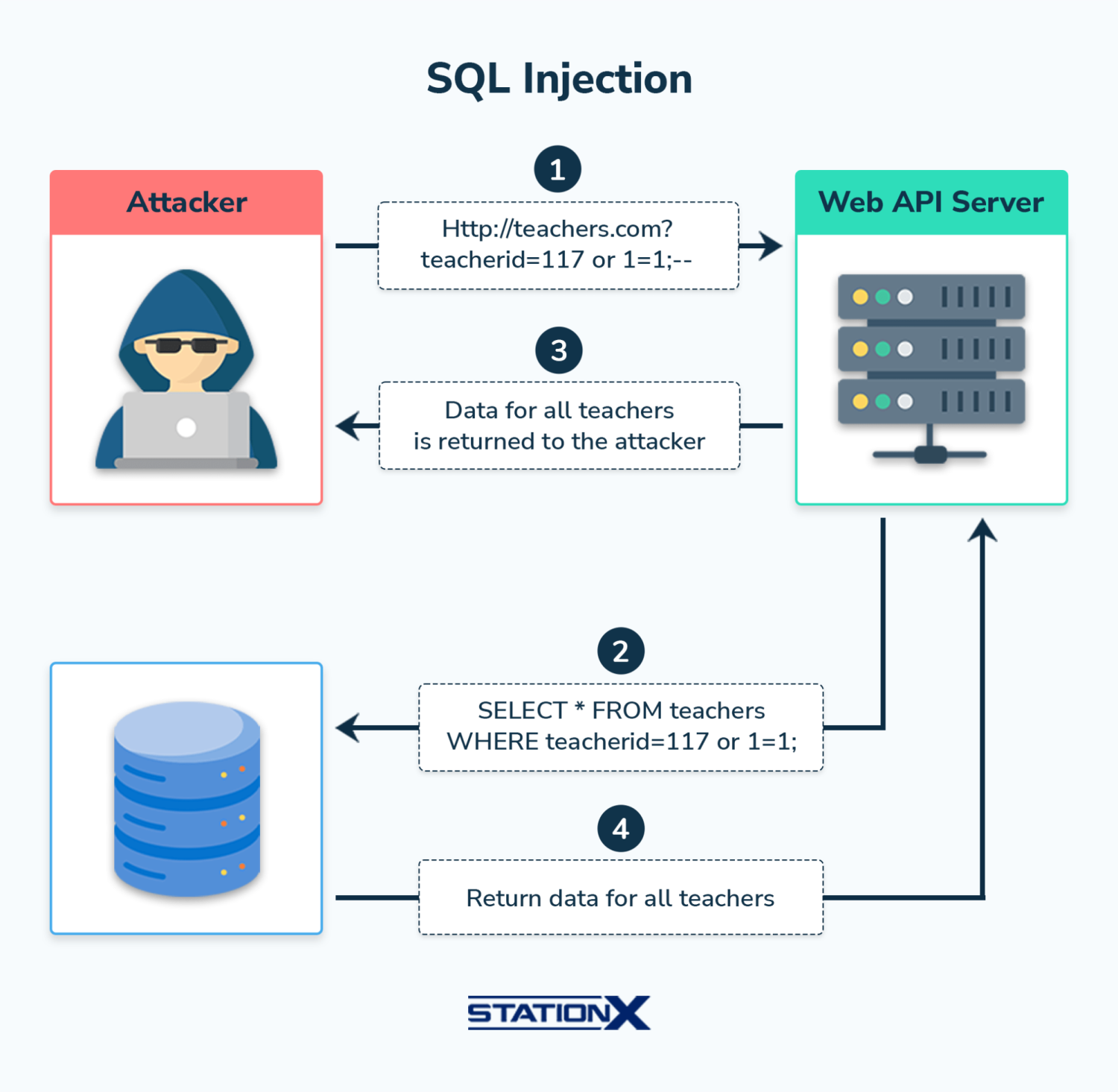
Cloud-Based Attacks
| Attack | Description |
| Container Escapes | Breaking out of a container (like Docker) to access the host system. |
| Metadata Service Attacks | Exploiting cloud metadata endpoints to steal credentials or tokens. |
| IAM Misconfiguration | Weak or overly permissive identity and access settings enabling unauthorized access. |
| S3 Bucket Enumeration | Discovering misconfigured or public cloud storage buckets. |
| Serverless Function Abuse | Triggering or manipulating serverless functions for unauthorized execution. |
AI Attacks
| Attack | Description |
| Prompt Injection | Tricking AI models with malicious input to alter outputs or reveal data. |
| Model Manipulation | Tampering with AI models to change or corrupt their behavior. |
| Data Extraction | Stealing sensitive files, records, or secrets from a target system. |
Wireless Attacks
| Attack | Description |
| WEP Cracking | Breaking outdated WEP encryption through packet capture and key recovery. |
| WPA/WPA2 Attacks | Capturing handshakes and cracking Wi-Fi passwords or exploiting protocol flaws. |
| Evil Twin | Fake Wi-Fi access point to trick people into choosing it over the genuine one |
| WPS PIN brute force | Brute-forcing the 8-digit WPS PIN to gain unauthorized access to a wireless network. |
Tools & Techniques
| Tool | Description |
| Metasploit | Modular exploitation and post-exploitation framework. |
| Netcat | Networking utility for reading/writing data across connections. |
| Nmap | Port scanning and network discovery tool. |
| NSE | Nmap Scripting Engine for automation and vulnerability scripts. |
| Impacket | Python toolkit for network protocols and exploit scripts. |
| CrackMapExec (CME) | Recon and lateral movement automation tool. |
| Wireshark/tcpdump | Open-source packet capture analysis |
| msfvenom | Payload generator for custom shellcode. |
| Responder | LLMNR/NBT-NS poisoning tool. |
| Hydra | Fast password brute-force tool. |
| hashcat | GPU-powered password cracker. |
| John the Ripper | Password cracking utility. |
| BloodHound | AD attack path mapping tool. |
| Medusa | Parallel login brute-force tool. |
| Burp Suite | Web application security testing platform. |
| Rubeus | Kerberos abuse toolset. |
| Certify | AD CS abuse and certificate enumeration. |
| Seatbelt | Windows security assessment tool. |
| PowerShell/ISE | Automation, enumeration, and offensive scripting. |
| PsExec | Remote command execution utility. |
| Evil-WinRM | WinRM exploitation and lateral movement. |
| LOLbins | Native OS binaries used for stealthy attacks. |
| TruffleHog | Search for secrets in code repos. |
| ZAP | OWASP Zed Attack Proxy for web app testing. |
| Postman | API testing and enumeration. |
| sqlmap | Automated SQL injection exploitation tool. |
| Gobuster/DirBuster | Directory and file brute-forcing. |
| Wfuzz | Web fuzzer for parameters and injection tests. |
| WPScan | WordPress vulnerability scanner. |
| Pacu | AWS exploitation framework. |
| Docker Bench | Docker security configuration scanner. |
| Kube-hunter | Kubernetes cluster security tester. |
| Prowler | Cloud security auditing for AWS. |
| ScoutSuite | Multi-cloud security auditing tool. |
| WPAD | Proxy auto-discovery attack tool. |
| WiFi-Pumpkin | Wireless rogue AP and phishing tool. |
| Aircrack-ng | Wi-Fi cracking and monitoring suite. |
| WiGLE.net | Wireless network discovery database. |
| InSSIDer | Wi-Fi scanning and analysis tool. |
| Kismet | Wireless IDS and packet sniffer. |
| SET | Social Engineering Toolkit for phishing attacks. |
| Gophish | Phishing campaign framework. |
| Evilginx | Phishing proxy for token theft. |
| theHarvester | Email, domain, and OSINT harvesting. |
| Maltego | Graph-based OSINT investigation tool. |
| Recon-ng | OSINT reconnaissance automation. |
| BeEF | Browser exploitation framework. |
| Scapy | Packet crafting and manipulation toolkit. |
| tcprelay | iOS debugging and relay utility. |
| MobSF | Mobile application security testing. |
| Frida | Dynamic instrumentation toolkit. |
| Drozer | Android security testing framework. |
| ADB | Android Debug Bridge for device control. |
| Bluestrike | Bluetooth attack and scanning tool. |
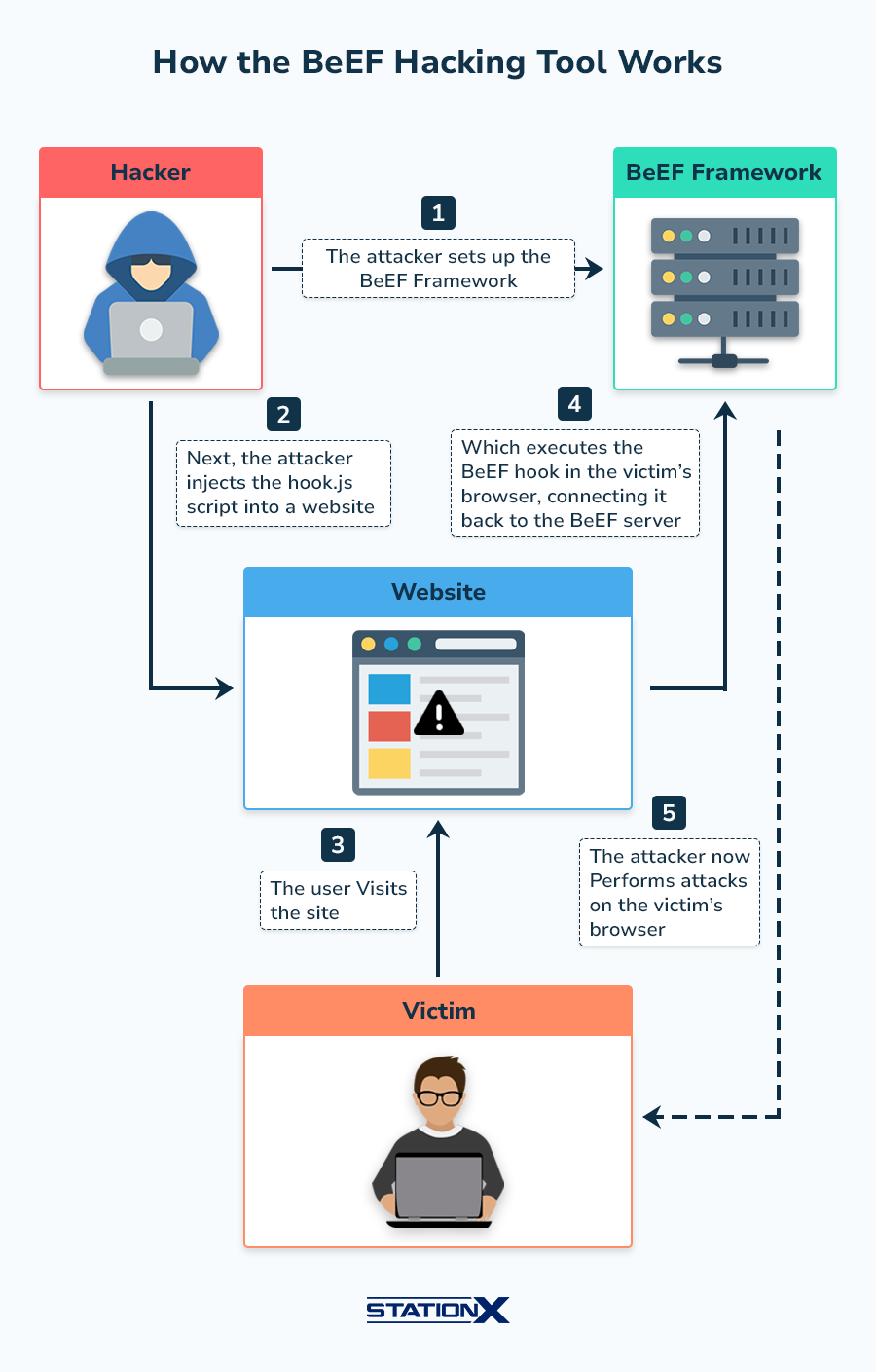
Post-exploitation and Lateral Movement
This PenTest+ domain emphasizes post-exploitation activities like maintaining access, performing lateral movement, and delivering comprehensive documentation with remediation recommendations.
Persistence Techniques
| Technique | Description |
| Scheduled tasks / cron jobs | Create recurring tasks to maintain unauthorized access. |
| Service creation | Install malicious services that restart automatically. |
| Reverse / bind shells | Maintain remote access through shell connections. |
| Account creation | Add hidden or unauthorized user accounts. |
| Credential harvesting | Steal valid credentials for re-entry. |
| Registry key manipulation | Modify autostart registry keys for persistence. |
| C2 frameworks | Use tools like Cobalt Strike, Empire, Covenant for long‑term access. |
| Backdoors | Install web shells, Trojans, and rootkits to regain entry. |
| Browser extensions | Inject malicious extensions for session hijacking or persistence. |
| Tampering with security controls | Disable logs, EDR, antivirus, or monitoring tools. |
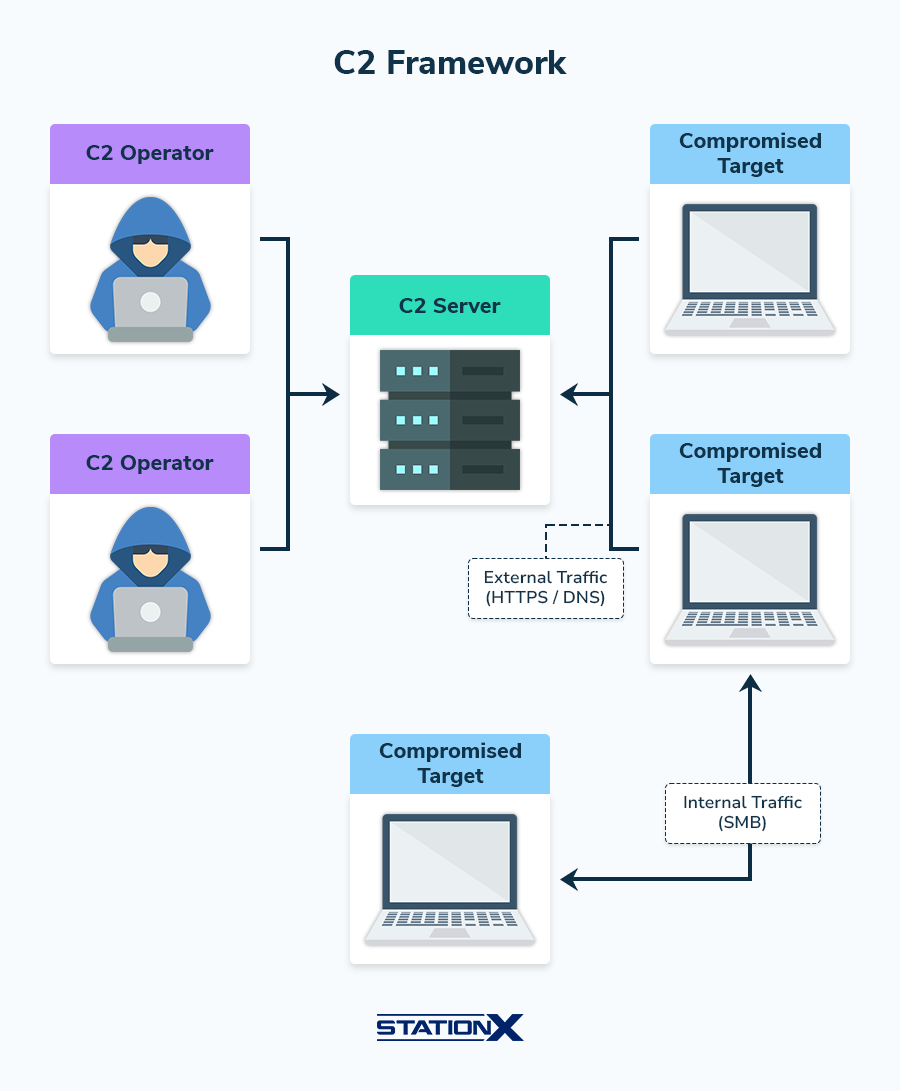
Lateral Movement Techniques
| Technique | Description |
| Pivoting & Relays | Rerouting traffic through compromised hosts to access internal systems. |
| Credential Dumping & Reuse | Extracting and reusing credentials for lateral authentication. |
| Host & Service Enumeration | Identifying services, traffic, shares, and accessible systems. |
| Protocol Discovery | Enumerating SMB, RDP/VNC, SSH, LDAP, RPC, FTP, HTTP/HTTPS, and more. |
| Remote Execution Methods | Using WMI, WinRM, and RPC/DCOM to run commands remotely. |
| LOLBins | Built‑in OS binaries used for stealthy movement: • Netstat • Ftp.exe • rundll32 |
| Offensive Tools | • Metasploit • PsExec • Mimikatz • CME • Impacket • Covenant • Sshuttle • Proxychains |
| Automation Tools | PowerShell ISE, batch scripts, and tunneling utilities for movement. |
Staging and Exfiltration Techniques
| Technique | Description |
| File encryption & compression | Packing data with zip/7z/AES to evade detection during exfiltration. |
| Covert channels | Hiding exfiltration via steganography, DNS tunneling, ICMP, or HTTPS. |
| Email or cloud uploads | Sending stolen data via email, shared drives, or cloud buckets. |
| Cross‑account resource abuse | Using misconfigured shared cloud resources to extract data. |
| Virtual drive mounting / ADS | Staging data in mounted drives or NTFS alternate data streams. |
| Public paste/text sites | Uploading stolen data to anonymous pastebin-type services. |
Cleanup and Restoration Techniques
| Technique | Description |
| Remove persistence mechanisms | Delete scheduled tasks, services, registry keys, shells, and other footholds. |
| Revert configuration changes | Restore system settings to pre-engagement state. |
| Delete tester-created credentials | Remove accounts, tokens, and passwords generated for testing. |
| Remove tools and temp files | Delete payloads, scripts, logs, and utilities used during the assessment. |
| Spin down test infrastructure | Shut down cloud resources, VMs, and C2 servers used in testing. |
| Preserve legal artifacts | Retain screenshots, logs, and necessary evidence for the final report. |
| Secure data destruction | Wipe sensitive data following DoD 5220.22-M or NIST SP 800-88 guidelines. |
CompTIA PenTest+ Cheat Sheet Conclusion
Ideal for quick review and last-minute prep, this CompTIA PenTest+ Cheat Sheet provides a focused overview of the exam domains.
To boost your chances of success, make sure you check out our CompTIA PenTest+ Courses Bundle, available as a one-time purchase. This grants lifetime access to two full video courses, 884 practice questions, over 500 flashcards, and more.
Plus, you can save up to 30% on your official PenTest+ exam voucher when you purchase through us, making certification prep both effective and affordable.
For a complete career roadmap, mentorship, and access to 30,000+ cybersecurity courses and labs, explore the StationX Master’s Program.
Whichever path you take, we wish you good luck on your way to becoming a certified penetration tester!
The CompTIA PenTest+ Courses Bundle PT0-003 includes:
- Total CompTIA PenTest+ Course
- PenTest+ Practice Questions PT0-003
- CompTIA PenTest+ Certification Flash Cards
- Penetration Testing Training for Beginners






































